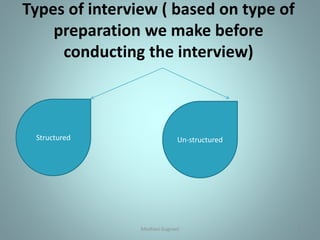
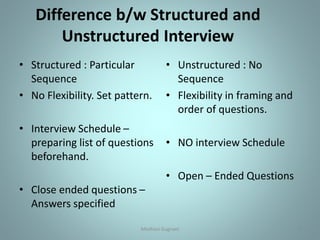
Survey research involves studying a representative sample of a population to make inferences about characteristics of the whole population. It is a technique used in social science research to study opinions, attitudes, and social facts. There are different types of surveys, including personal interviews, questionnaires, telephone surveys, and panel techniques. Personal interviews can be structured or unstructured, and they may involve individual or group interactions. Questionnaires use a predetermined set of questions to collect information through self-reporting. Telephone surveys are convenient but risk superficial answers. Panel techniques interview the same sample successively to understand changes over time but are prone to sample loss.