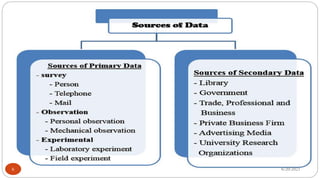
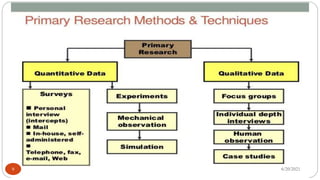
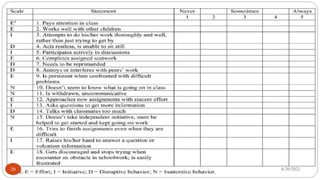
The document outlines the concepts of data and data collection, distinguishing between primary and secondary data, as well as qualitative and quantitative data. It describes various data collection tools and techniques, including surveys, interviews, and focus groups, while emphasizing the importance of systematic data collection methods. Additionally, it highlights the steps involved in data collection, from clarifying goals to validating measurement systems.