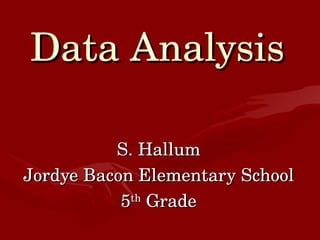
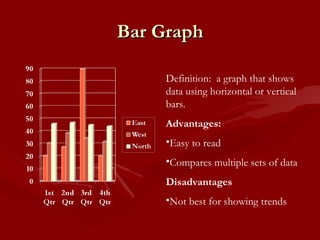
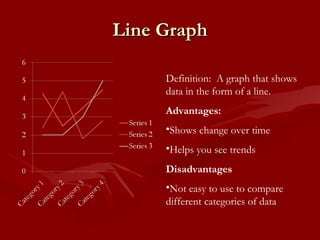
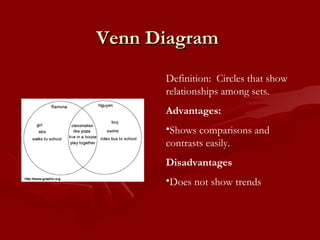
The document provides information about analyzing and interpreting data through various graphs and calculations. It defines terms like mean, median, mode, and range. It explains how to calculate the mean, median, mode, and range of a data set. It also defines and compares different types of graphs like bar graphs, circle graphs, line graphs, line plot graphs, pictographs, and Venn diagrams. Finally, it provides some practice websites for interpreting data.