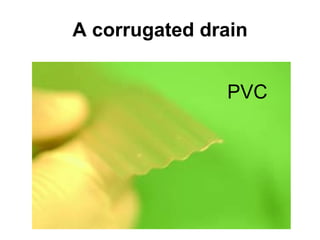
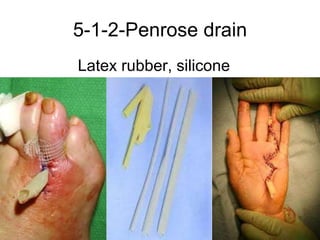
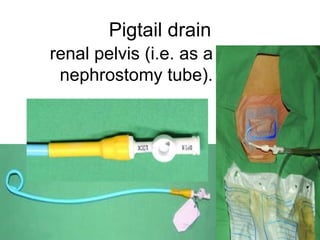
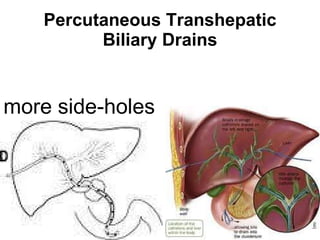
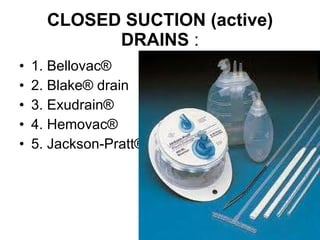
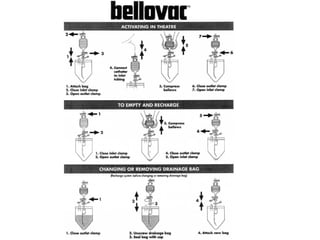
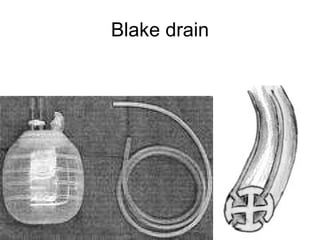
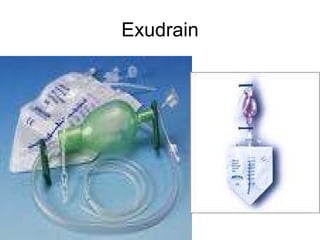
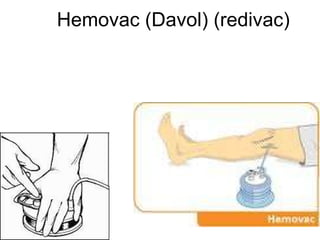
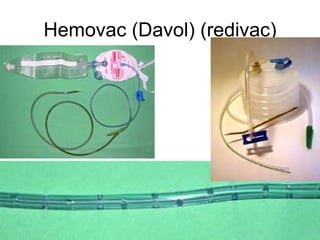
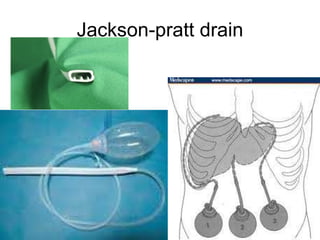
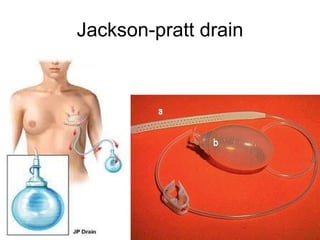
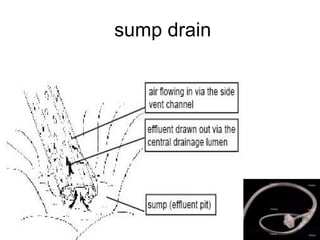
The document discusses different types of drains used in medical procedures including closed and open drains. Closed drains have lower infection rates but limit mobility while open drains are softer and more comfortable. Examples of closed drains include pigtail catheters and urinary catheters while open drains include Penrose and corrugated drains. Potential problems with all drains include tissue trauma, erosion, herniation, leaks, bacterial infection, and fluid/electrolyte loss.