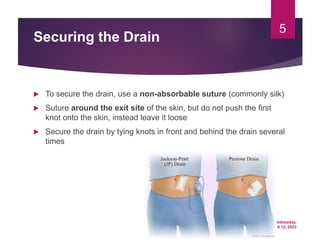
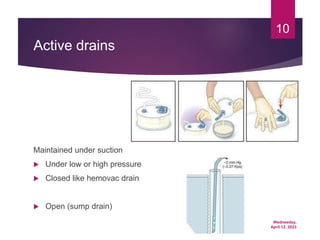
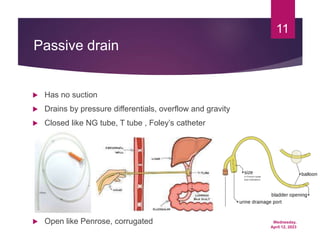
Dr. Hiwa Omer Ahmed gives a presentation on inserting surgical drains. The document discusses the aims of inserting drains such as drainage or monitoring outputs. It describes how to insert a drain by placing it deep in the cavity and securing it with sutures. The document outlines types of drains including open versus closed and active versus passive drains. Finally, it briefly mentions complications and post-removal care.