Embed presentation
Downloaded 43 times

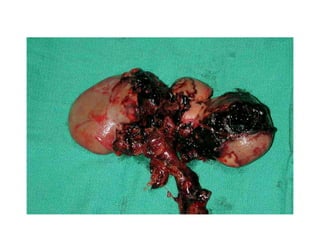
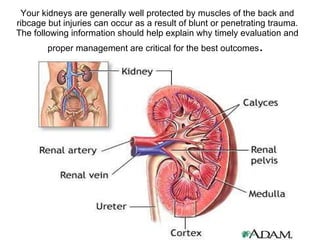


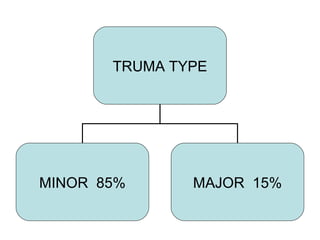
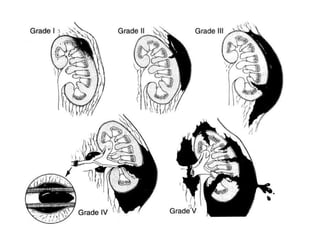


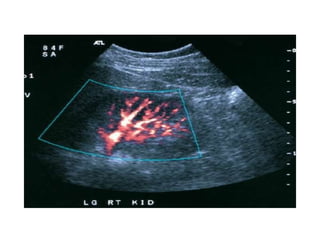
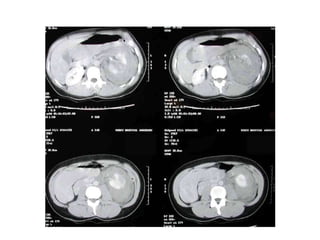
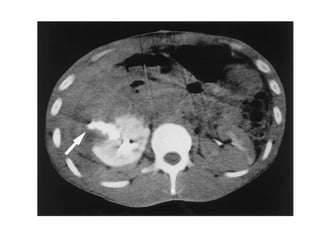
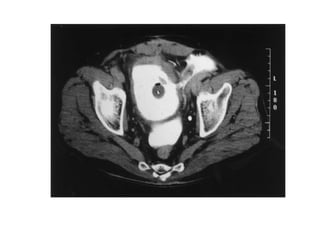
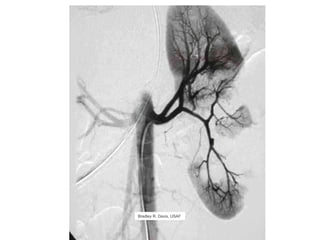
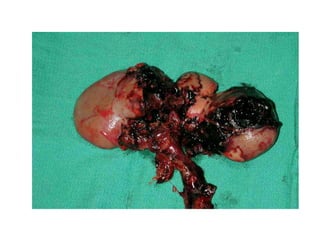
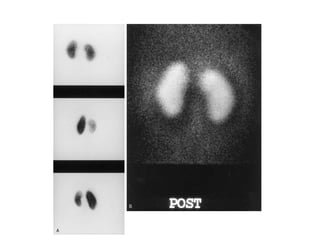

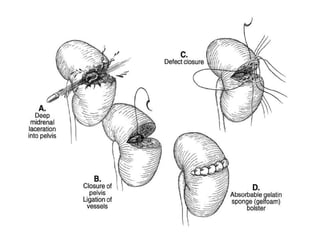
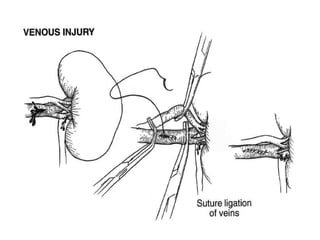



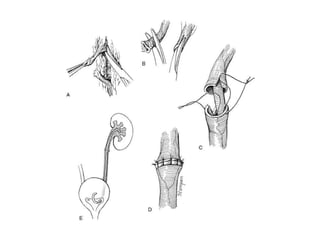
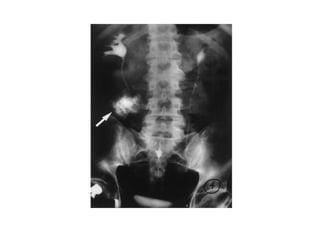
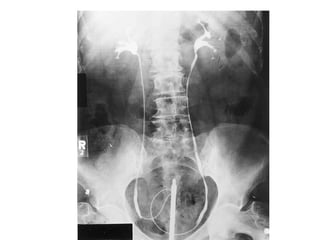

The kidneys can be injured by blunt or penetrating trauma, requiring timely medical evaluation. The kidneys are normally protected by back muscles but can be damaged by severe impacts or objects piercing the skin. Blunt trauma may cause bruising while penetrating injuries like gunshots can enter elsewhere and travel to the kidneys. Most kidney injuries are minor but evaluation with imaging tests like ultrasound or CT scans helps classify the injury and guide management, which may include rest, antibiotics, surgery, or nephrectomy in more severe cases.



























