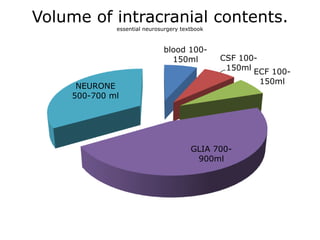
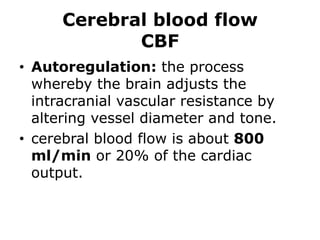
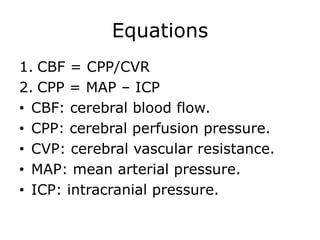
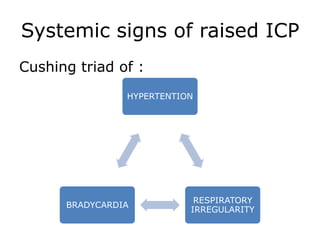
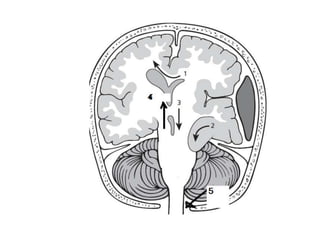
Raised intracranial pressure is caused by an increase in the volume of brain, cerebrospinal fluid, or blood within the rigid skull. Common causes include brain tumors, cerebral edema from trauma or infection, and hydrocephalus. Symptoms include headache, nausea, drowsiness, and papilledema. Management involves reducing the volume of intracranial contents through measures like head elevation, hypertonic solutions, hyperventilation, and diuretics. More severe cases may require surgical interventions such as ventriculostomy or craniectomy to drain cerebrospinal fluid and relieve pressure.