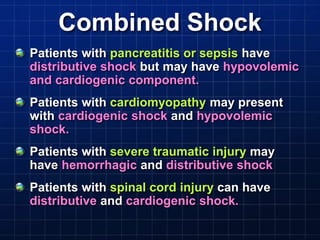
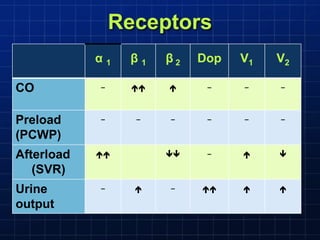
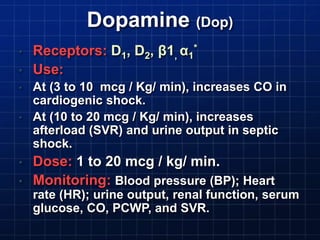
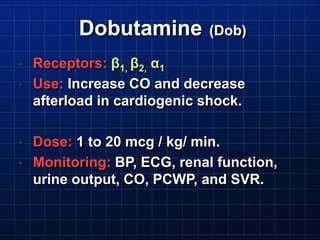
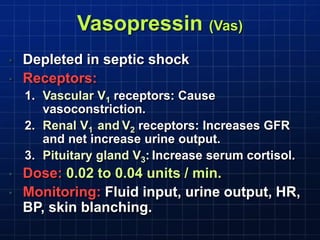
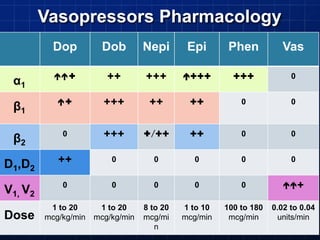
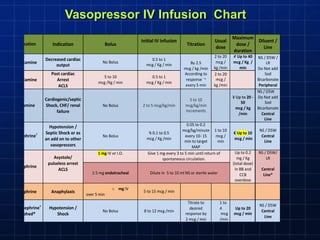
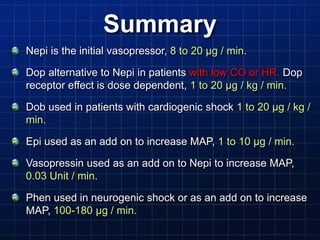
This document discusses types of shock, goals of therapy for different shock states, and vasopressor pharmacology. It defines hypovolemic, cardiogenic, septic, neurogenic, and combined shocks. The goals for hypovolemic shock are to increase preload with fluids, while cardiogenic shock aims to increase cardiac output with drugs like dopamine or dobutamine. Septic and neurogenic shock goals are to first increase preload then increase afterload with vasopressors like norepinephrine, phenylephrine, and vasopressin. Norepinephrine is usually the initial vasopressor, while other drugs like dopamine, epinephrine, vasopressin may be used as adjunct



![Objectives
Define shock.
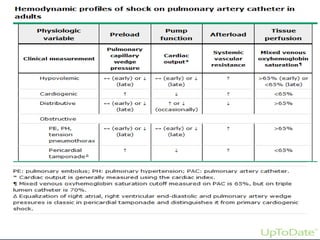
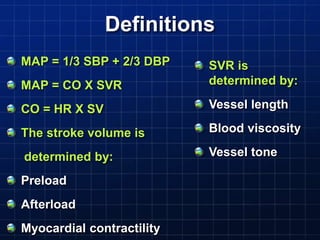
Define and interpret various hemodynamic
parameters [mean arterial pressure (MAP),
preload, afterload, Cardiac output (CO)].
List types, causes, and symptoms of shock.
Describe the pharmacology, doses and use of
vasopressors.
Explain practical issues with using
vasopressors.
Apply knowledge to a patient with a shock
syndrome](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/302d12cb-4d9a-457e-bc40-76f71798800b-160206164717/85/Vasopressors-Presentation_final-4-320.jpg)


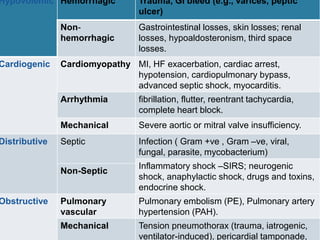
![Shock
Classification & Etiology
• Hypovolemic: (hemorrhagic, Non-hemorrhagic).
• Cardiogenic: (MI, cardiomyopathy, arrhythmia).
• Distributive: (septic, non-septic).
• Obstructive:
• Pulmonary Vascular: [Pulmonary embolus, severe pulmonary
hypertension (PAH)].
• Mechanical: (Tension pneumothorax, pericardial tamponade,
constrictive pericarditis, restrictive cardiomyopathy).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/302d12cb-4d9a-457e-bc40-76f71798800b-160206164717/85/Vasopressors-Presentation_final-10-320.jpg)