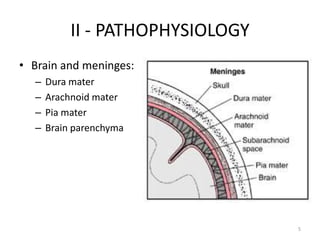
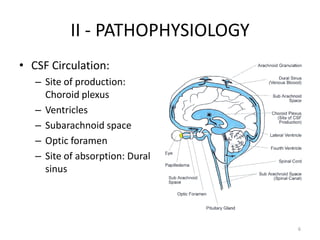
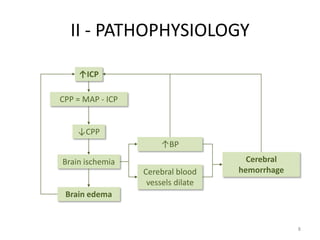
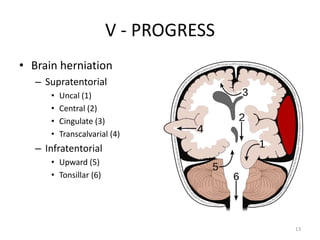
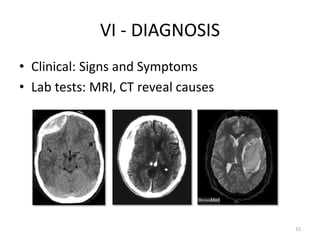
Intracranial Hypertension, also known as IH, is caused by an increase in intracranial volume which raises intracranial pressure (ICP). IH can be caused by trauma such as epidural or subdural hemorrhages, or non-trauma etiologies including tumors, infections, inflammation, increased venous pressure, or brain edema. Symptoms include headache, vomiting, altered mental status, and papilledema visible on exam. Left untreated, IH can progress to brain herniation, with signs of irregular breathing, abnormal posture, and loss of consciousness. Diagnosis involves clinical assessment of symptoms and signs as well as imaging tests. Treatment focuses on reducing ICP through positioning,