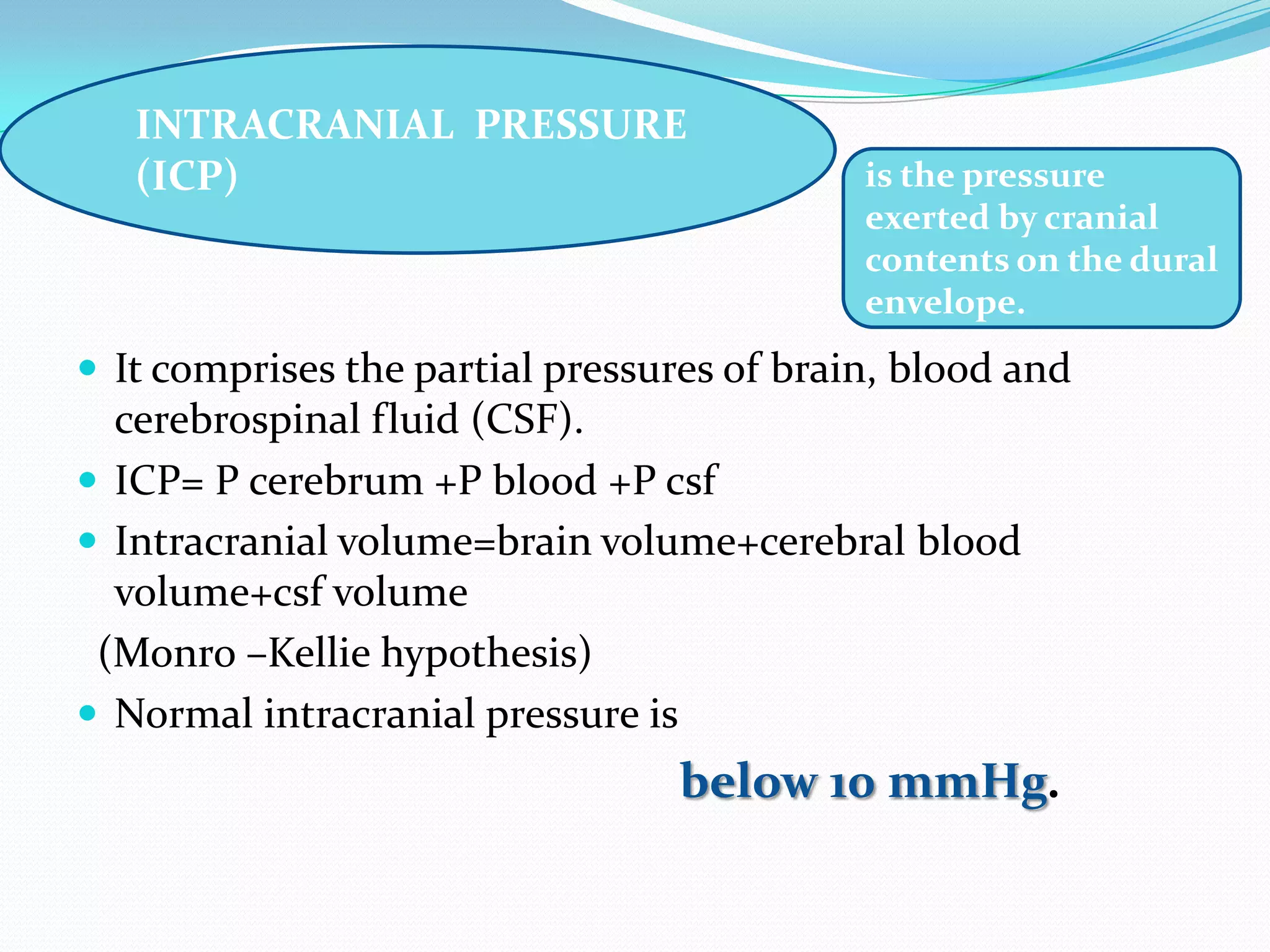
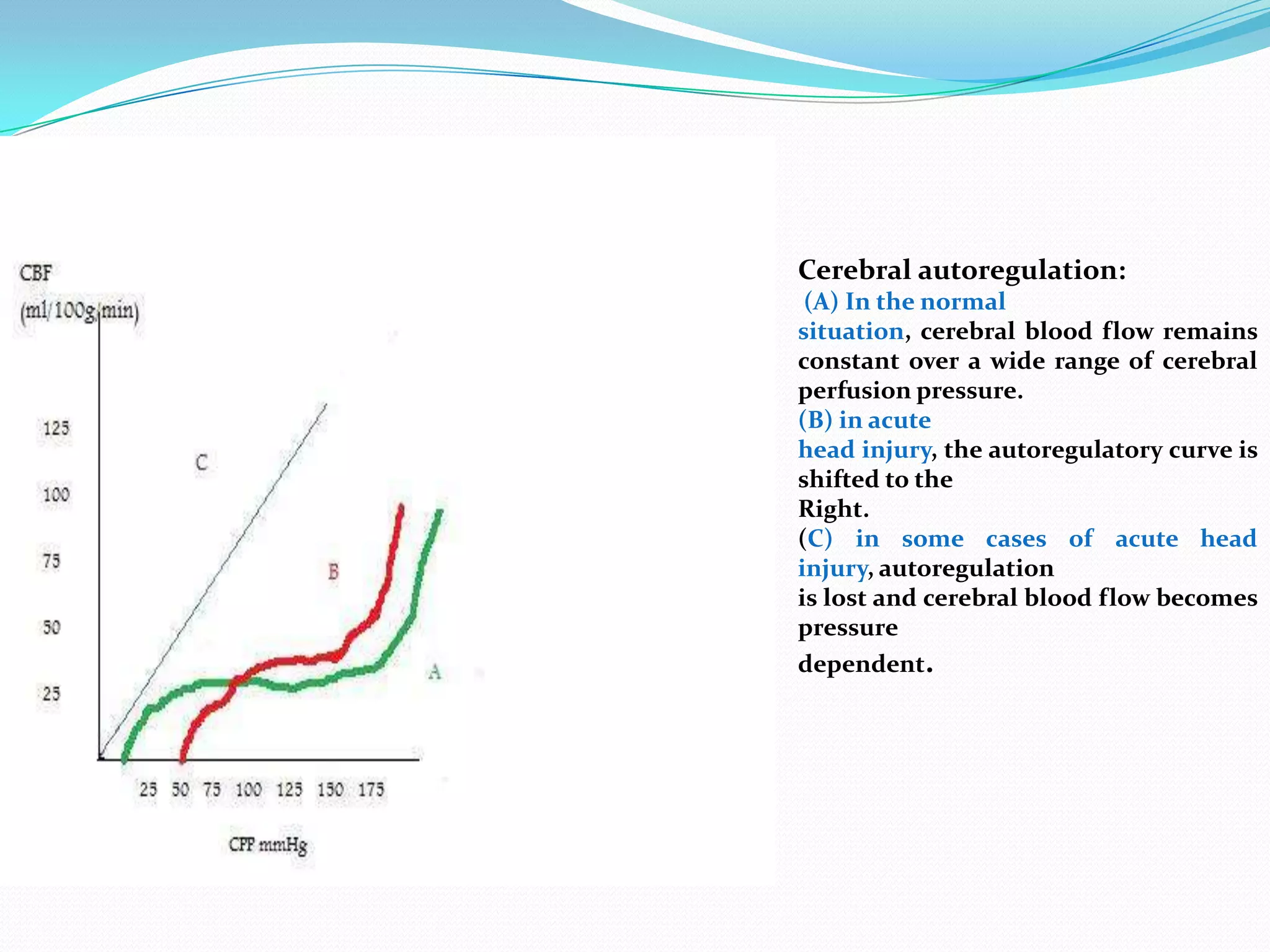
1) The document discusses raised intracranial pressure (ICP), including the definition of ICP, physiology of cerebral circulation, causes of raised ICP, clinical presentation, imaging, and management.
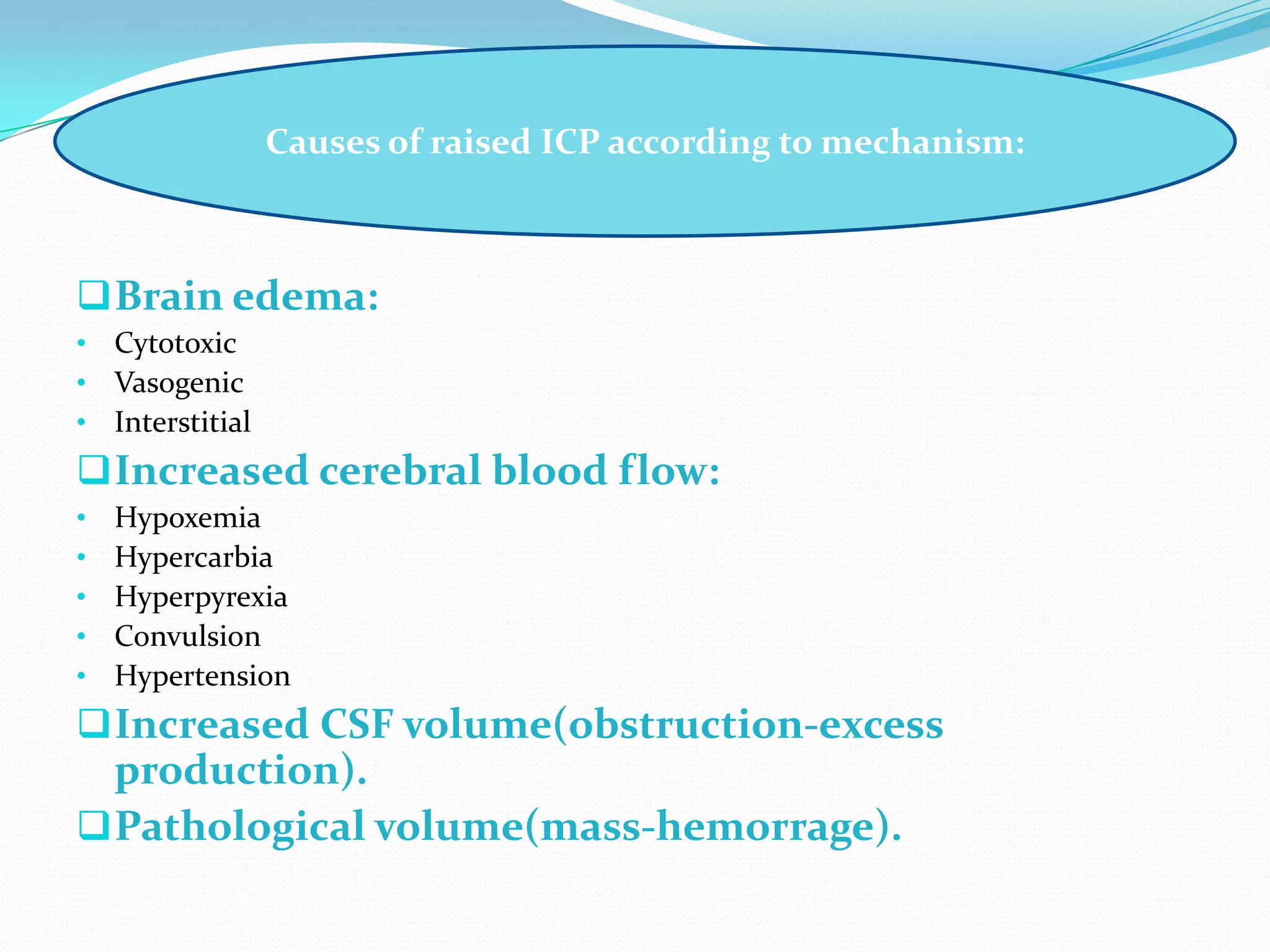
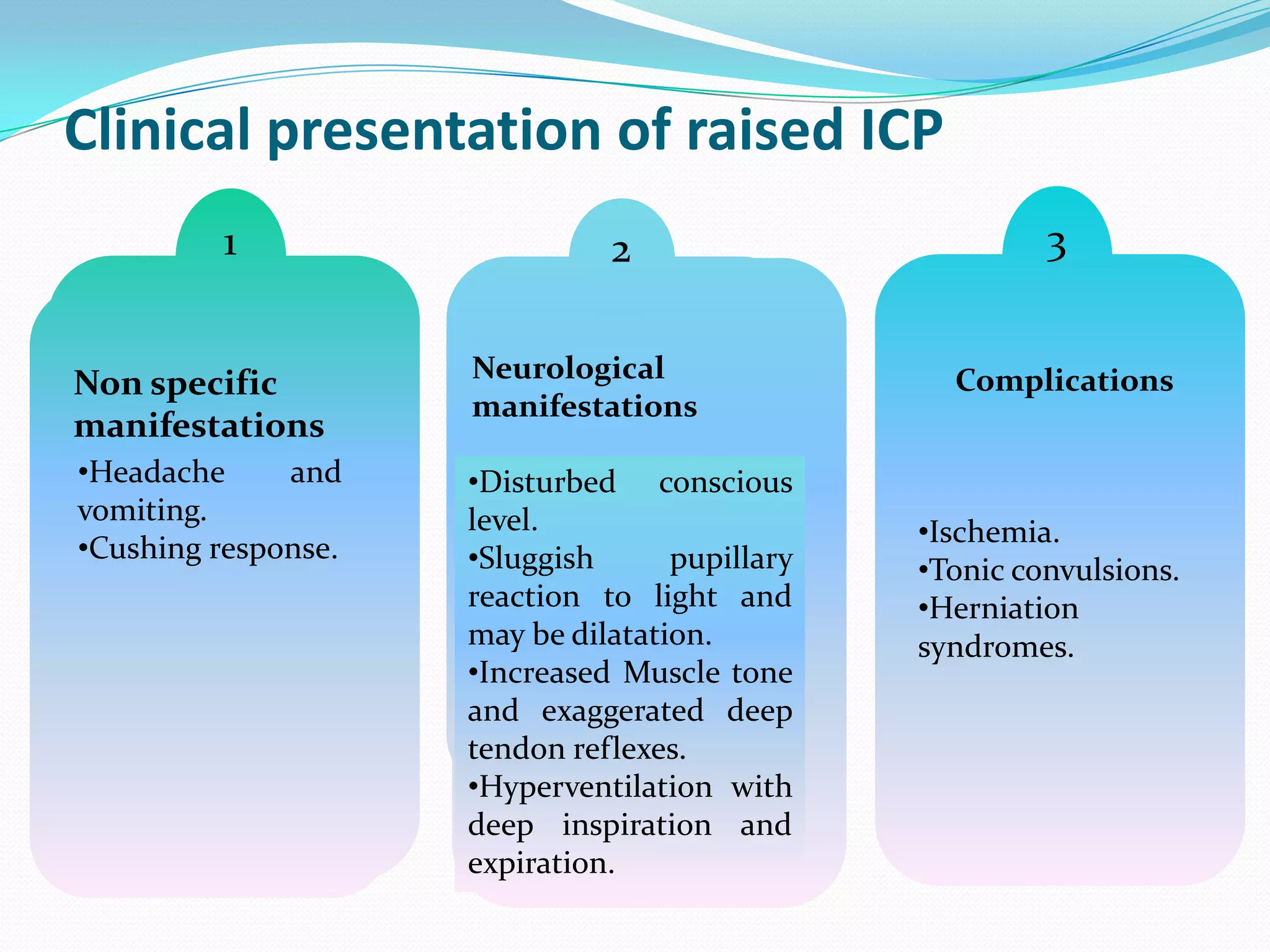
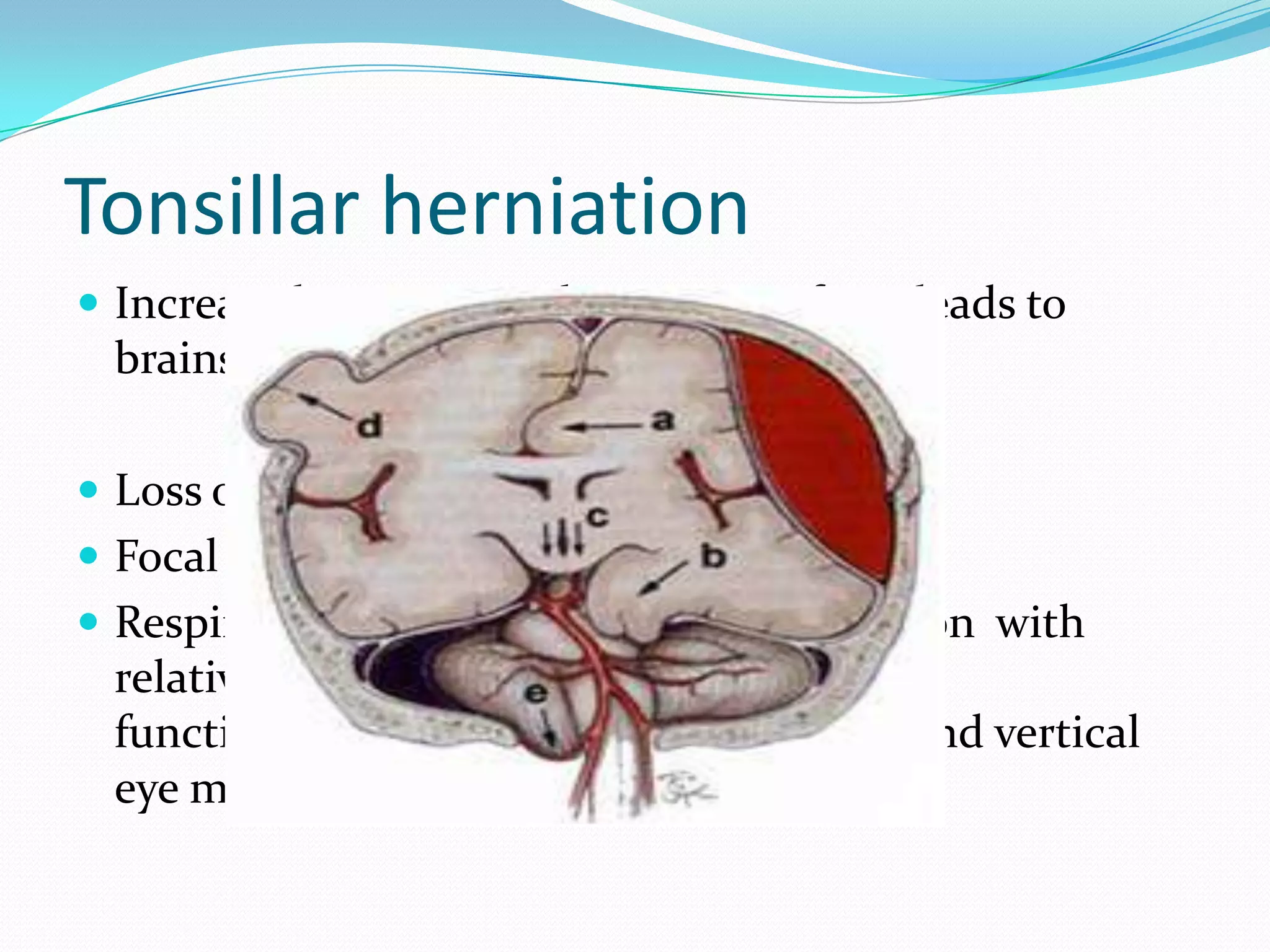
2) Causes of raised ICP include brain edema, increased cerebral blood flow, increased CSF volume, and pathological masses. Clinical manifestations range from non-specific signs to neurological deficits and herniation syndromes.
3) Management involves first-tier approaches like positioning, ventilation, hyperventilation, and hyperosmolar therapy as well as second-tier options of barbiturate coma, hypothermia, and decompressive craniectomy for refractory cases.