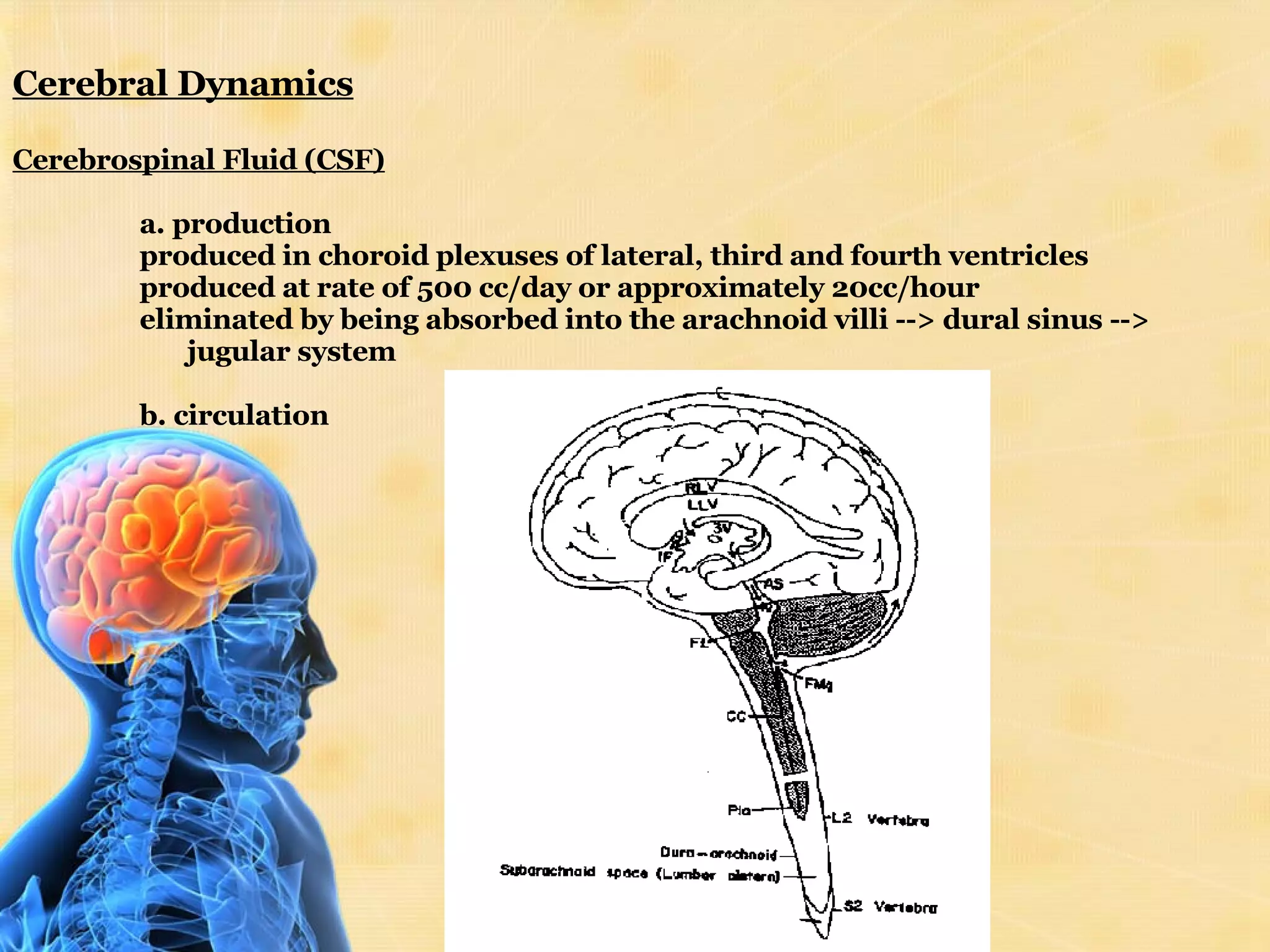
The document discusses increased intracranial pressure (ICP), including its causes, signs and symptoms, and treatment approaches. ICP is normally 7-15 mmHg but can increase due to mass effects from tumors or swelling, increased venous pressure, or obstruction of CSF flow. Goals of treatment are to maintain cerebral perfusion pressure and prevent ischemia. Management includes positioning, monitoring vitals, controlling seizures, administering diuretics like mannitol, and in severe cases, surgical intervention.