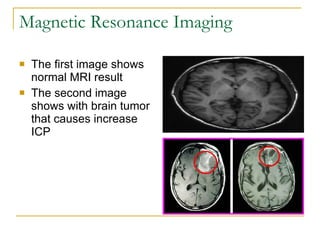
This document discusses increased intracranial pressure (ICP), its causes, diagnostic tools, and nursing care. It describes the Monro-Kellie hypothesis where the skull has a fixed volume, so an increase in one component (blood, CSF, brain tissue) increases pressure. Common causes of elevated ICP are head injuries, brain tumors, and hemorrhages. Diagnostic tools include CT, MRI, angiography and Doppler which can detect abnormalities that may cause increased pressure. Nursing care focuses on maintaining airway, respiration, fluid balance, reducing risk of infection, and preventing complications from immobility.