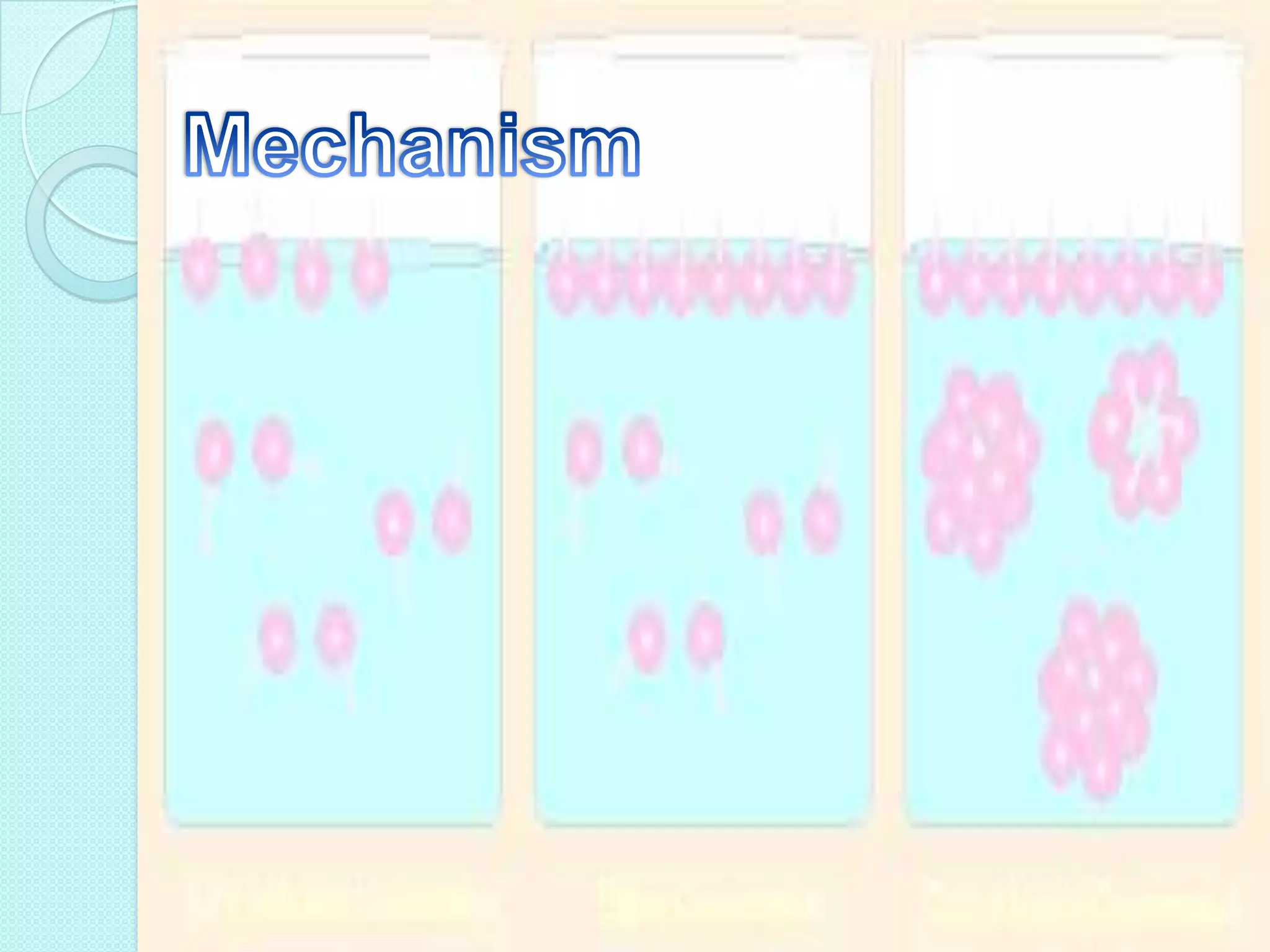
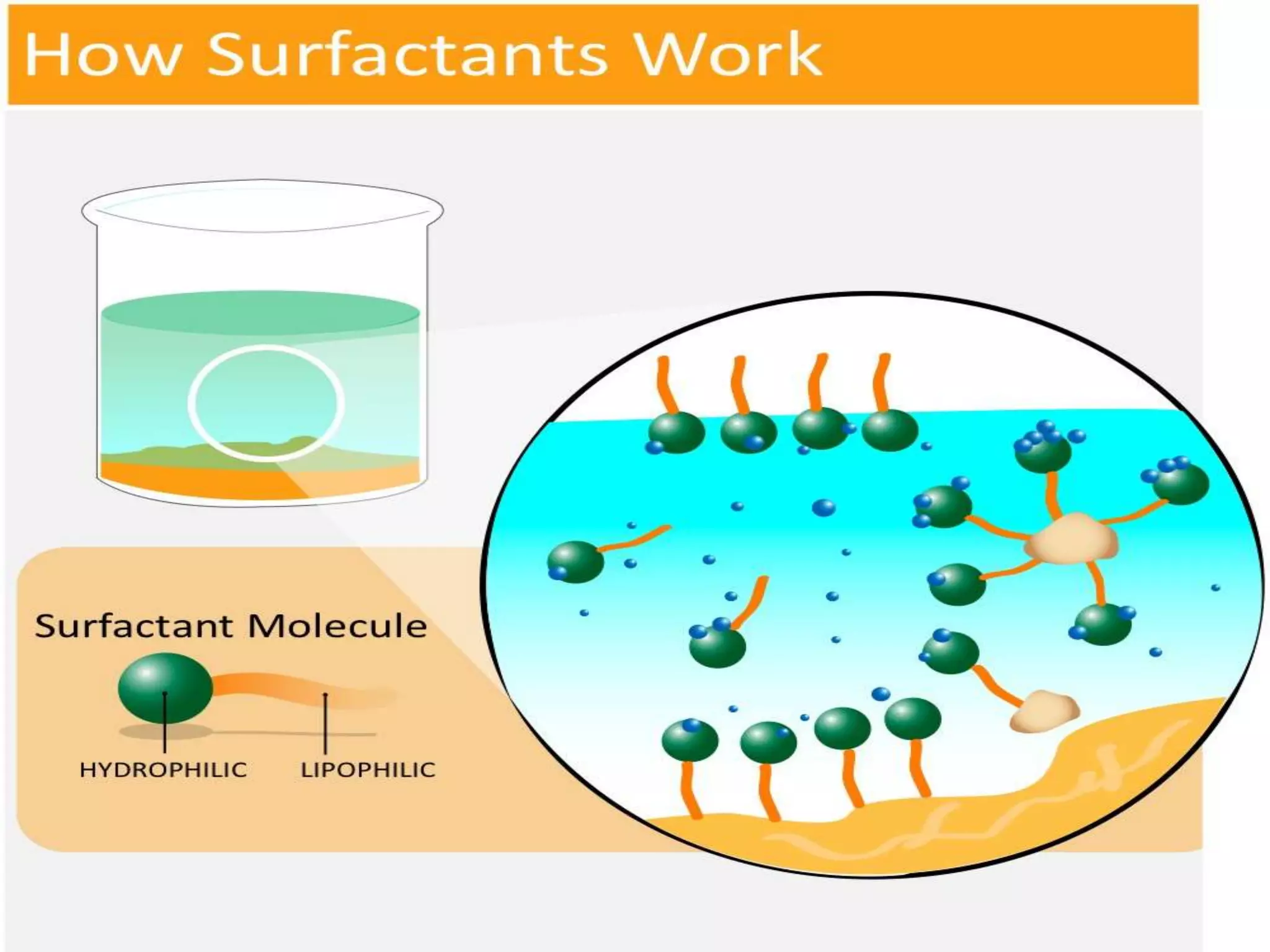
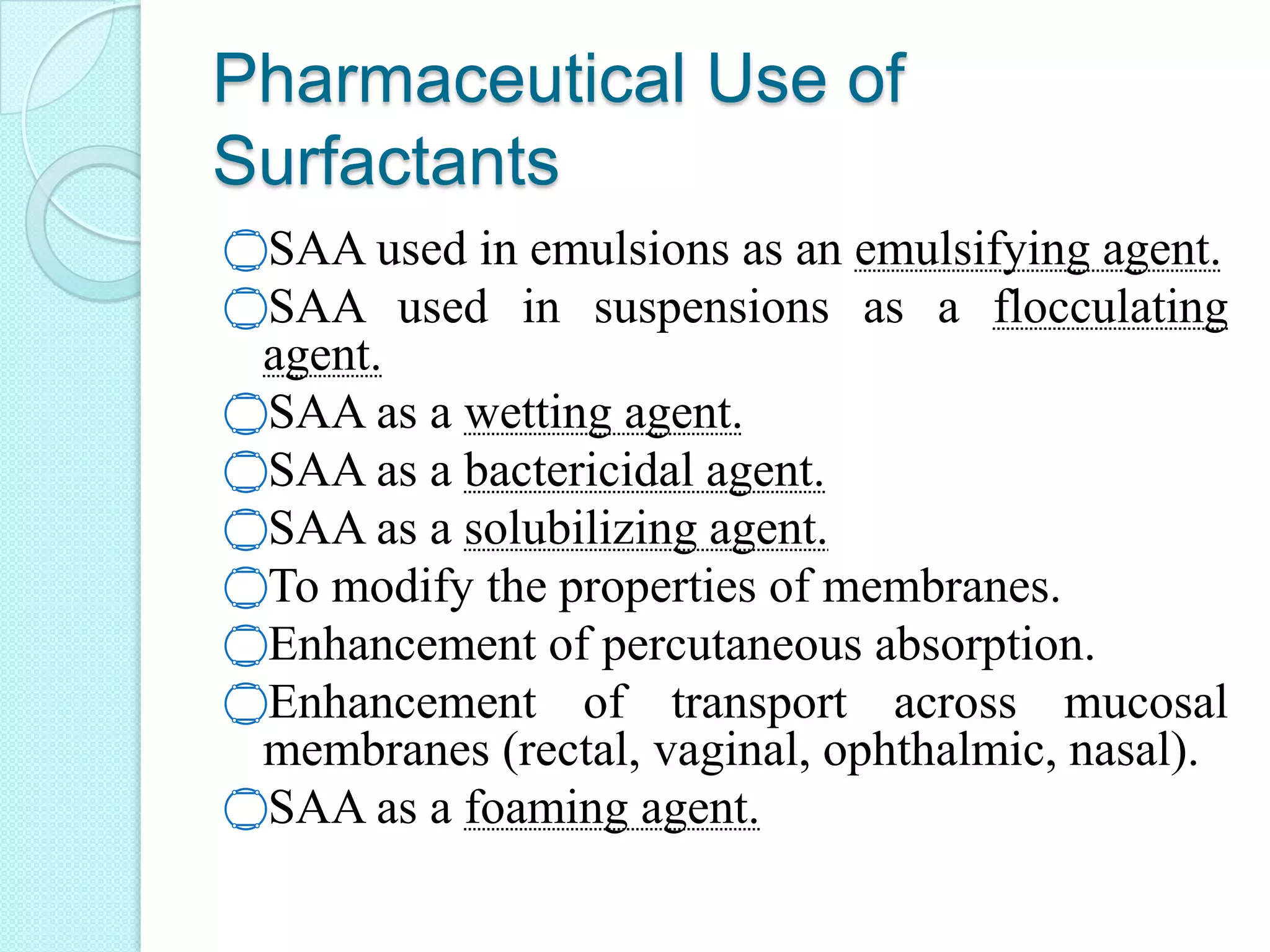
This document defines surfactants as substances that lower surface tension and interfacial tension when dissolved in a medium. Surfactants are amphiphilic molecules with both hydrophobic tails and hydrophilic heads. They are classified as ionic (cationic, anionic, amphoteric) or non-ionic. Common examples include soap, detergents, emulsifiers, and foaming agents. Surfactants are used pharmaceutically as emulsifying agents, flocculating agents, wetting agents, solubilizing agents, and to modify membranes and enhance absorption and transport across mucosal tissues.