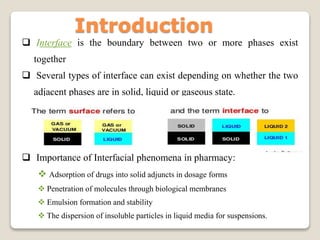
1. Interfacial phenomena are important in pharmacy for drug adsorption, penetration through membranes, emulsion formation and stability, and suspension of insoluble particles.
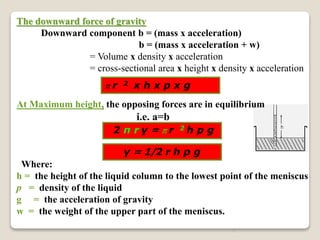
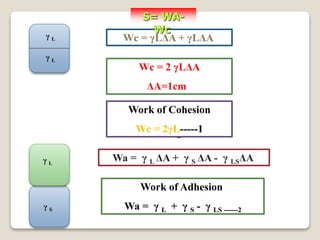
2. Surface tension is the inward force at the liquid interface, while interfacial tension exists between immiscible liquids. Temperature, additives, and molecular interactions influence surface/interfacial tensions.
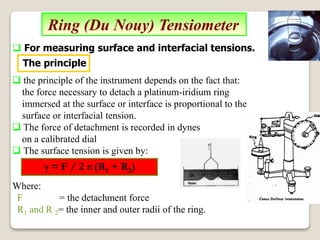
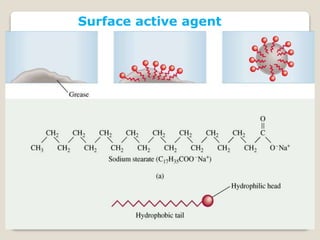
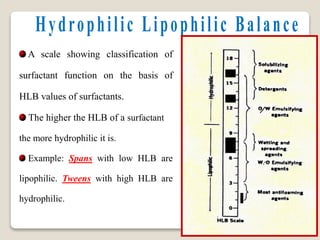
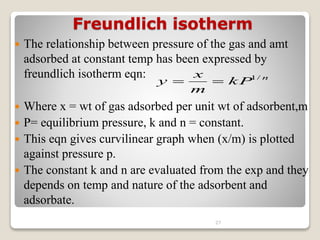
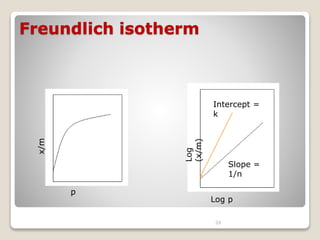
3. Several methods measure these tensions, including the capillary rise, Du Nouy ring, and drop weight methods. Surface-active agents are amphiphilic molecules that adsorb at interfaces and are used as wetting, solubilizing, and emulsifying agents in pharmaceutical formulations.
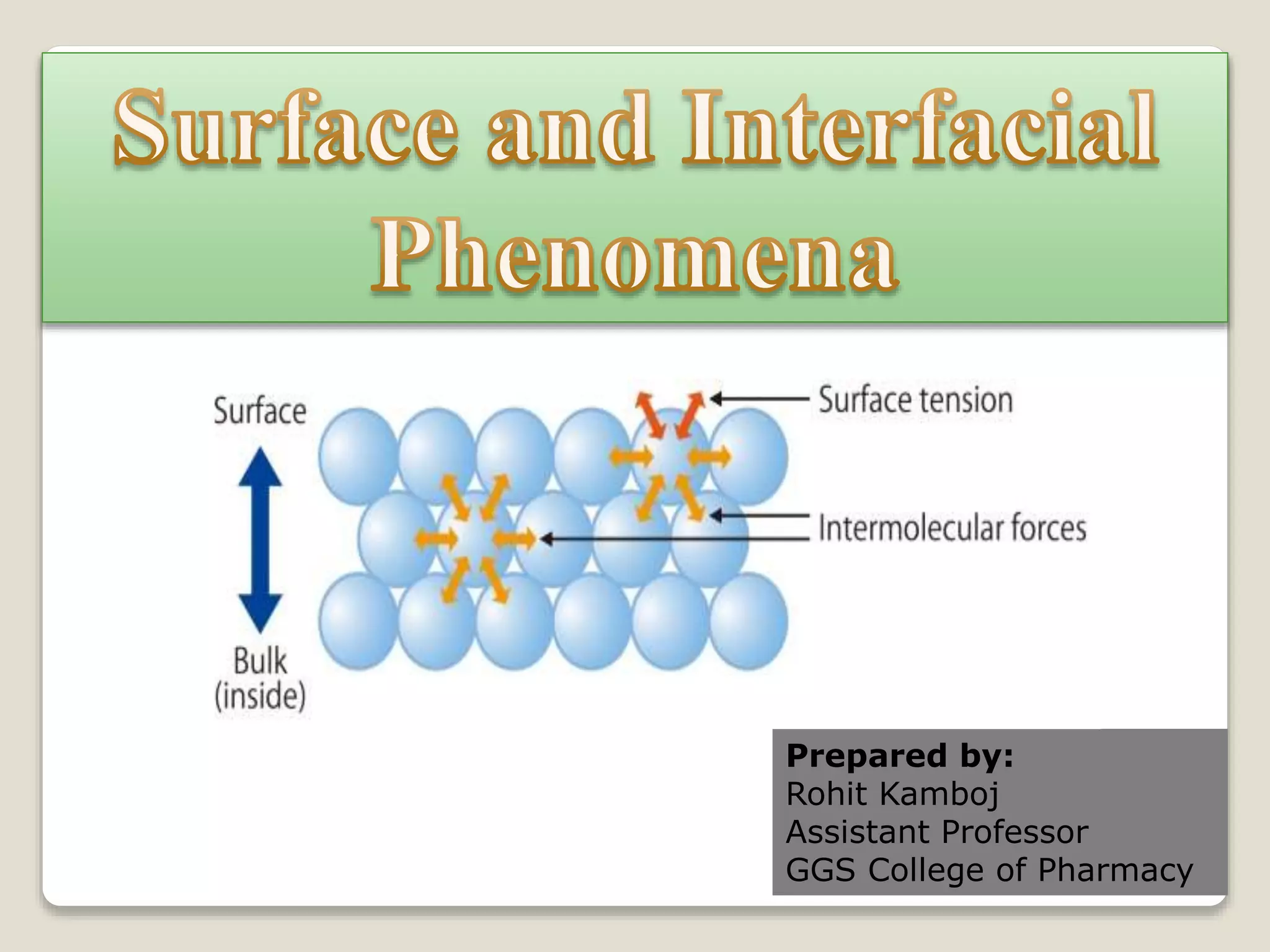

![Surface Tension
Thus SURFACE TENSION [γ ]
is the force per unit length that
must be applied parallel to the
surface so as to counterbalance
the net inward pull and has the
units of dyne/cm.
INTERFACIAL TENSION is the force
per unit length existing at the interface
between two immiscible liquid phases and
has the units of dyne/cm.
If two liquids are completely miscible, no
interfacial tension exists between them.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/surfaceandinterfacialphenomena-200417163249/85/Surface-and-interfacial-phenomena-4-320.jpg)