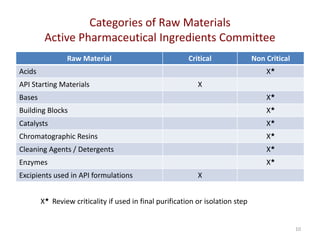
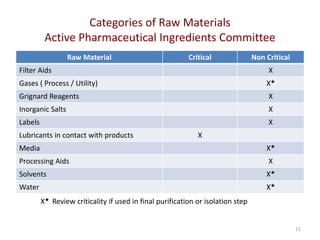
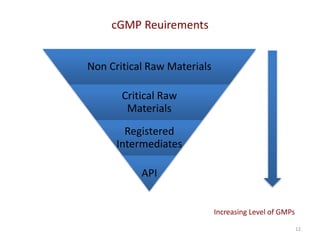
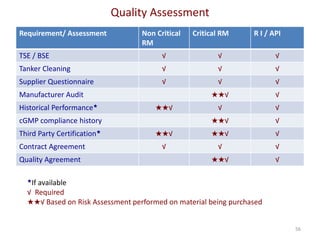
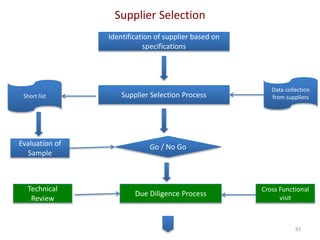
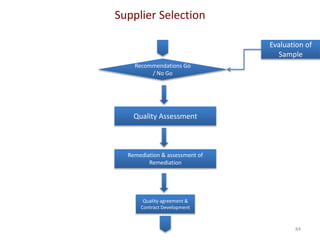
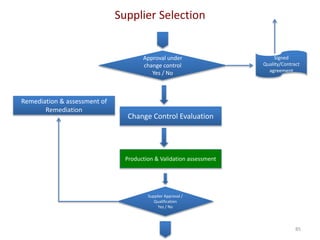
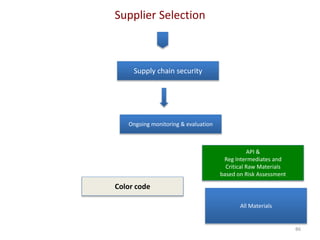
The document discusses supplier selection and quality assurance processes in the pharmaceutical sector, emphasizing the importance of due diligence, regulatory compliance, and risk assessment. It outlines key selection criteria for critical raw materials and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) along with a systematic approach to supplier evaluation, quality assessment, and continuous monitoring. Additionally, it highlights potential challenges and necessary documentation needed throughout the supply chain to ensure compliance and overall product quality.