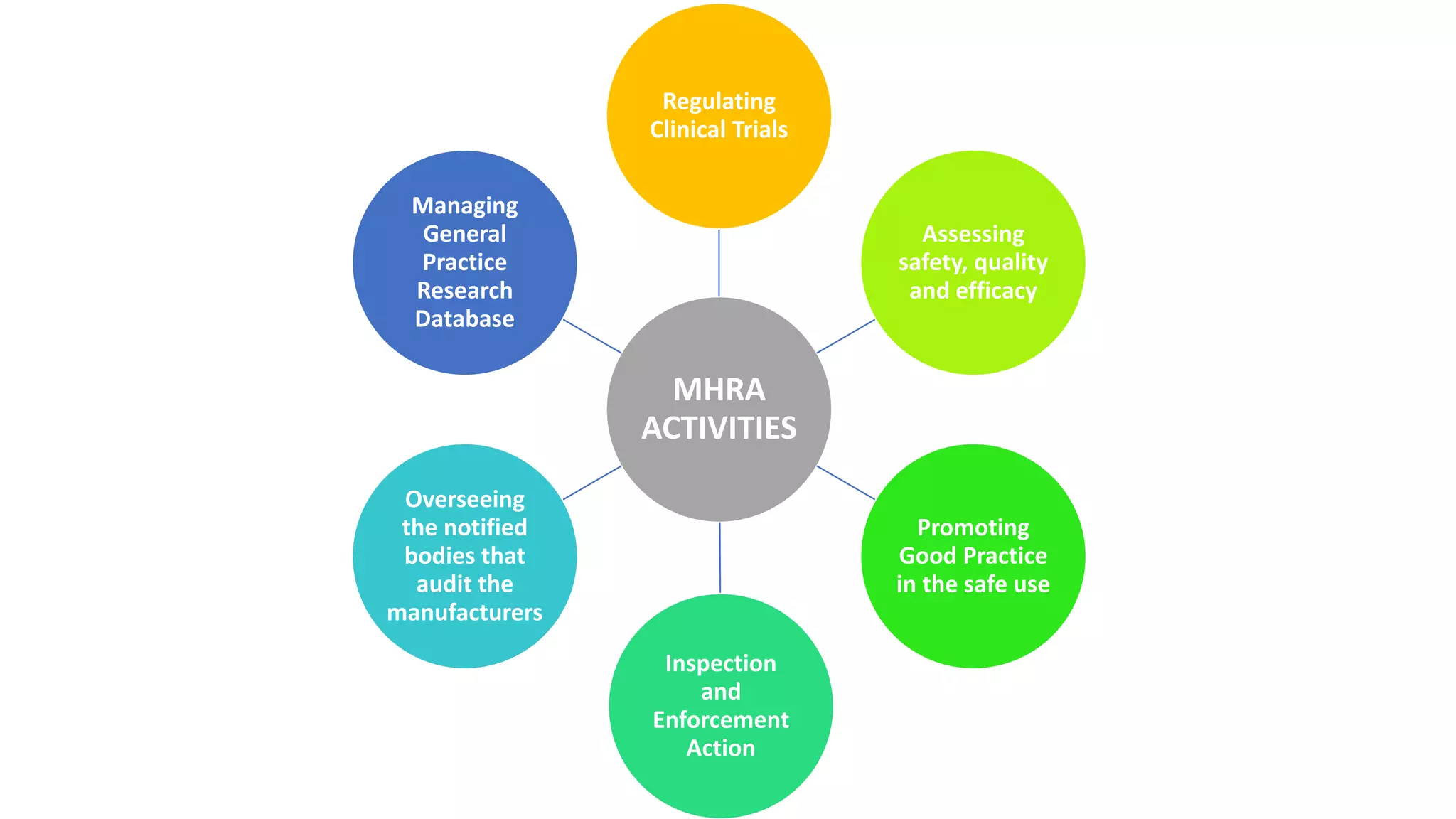
The MHRA is a UK government agency responsible for regulating medicines and medical devices. It was formed in 2003 by merging the Medical Control Agency and Medical Devices Agency. The MHRA aims to protect public health by regulating products to ensure acceptable safety and efficacy profiles. It also aims to educate the public about risks and benefits of products. The MHRA board is composed of a non-executive chairman, six non-executive members, and the agency's chief executive officer. Key functions of the MHRA include regulating clinical trials, assessing safety and efficacy of products for marketing authorization, inspecting manufacturers, and enforcing statutory guidelines.