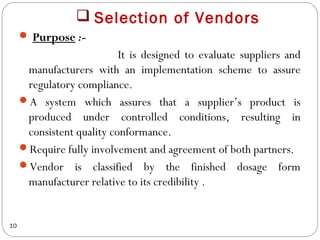
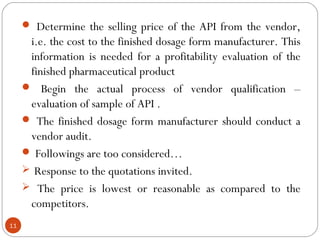
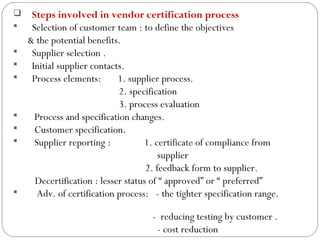
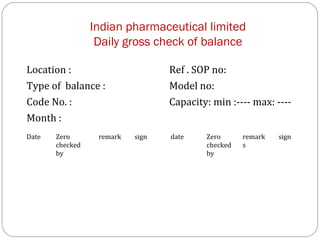
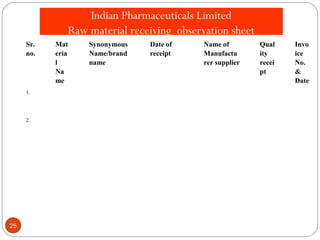
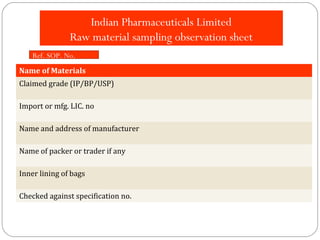
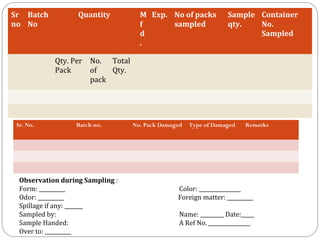
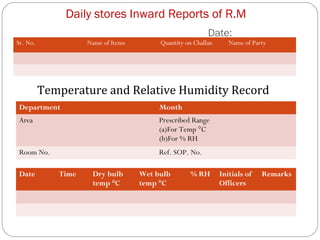
Raw materials include all materials used in manufacturing a finished product, whether present in the final product or not. They must meet defined purchase specifications. Key steps in purchasing raw materials include requisition, supplier selection, quotation, order placement, receipt, and payment. Proper storage conditions must be maintained based on product requirements. Vendors are selected and qualified to ensure a consistent supply of materials meeting quality standards. Receipt, storage, and sampling of materials are controlled through standard operating procedures.