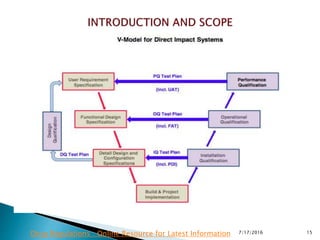
This presentation provides information on computerized system validation from the World Health Organization (WHO). It discusses the purpose and principles of validation to ensure performance of computer systems. Key points covered include validation protocols and reports, evaluating vendor systems, requirements specifications, functional specifications, and maintaining validated systems. The presentation is intended to provide pharmaceutical professionals with latest guidance on computerized system validation.