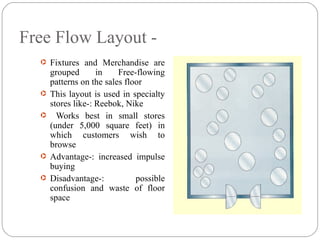
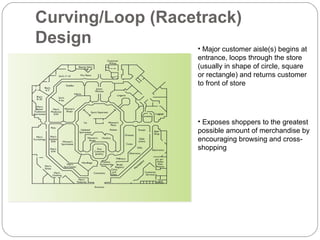
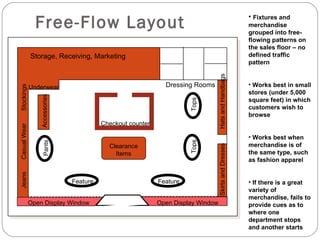
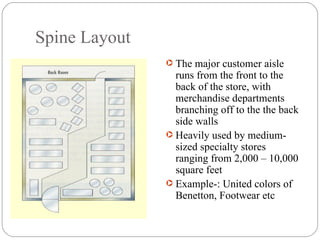
The document discusses various components of store design including store exterior, interior, layouts and image. It describes factors like location, signage, displays, and circulation patterns that affect the exterior and interior of a store. Different types of layouts - free flow, grid, loop and spine are explained along with examples. Store image and online retailing are also briefly covered.