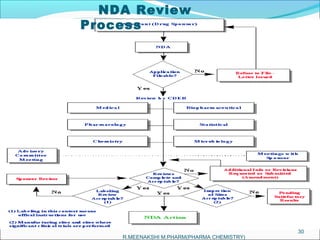
This document provides an overview of the new drug application (NDA) process for obtaining approval to market a new pharmaceutical drug in the United States. It describes the history of NDAs, the application requirements, FDA review process, possible outcomes, and an example of a drug that was initially not approved but later was approved after further use and review in other countries. The overall purpose of the NDA process is to ensure new drugs meet standards of safety and effectiveness before being approved for use and sale.