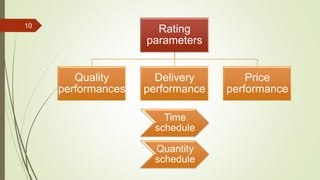
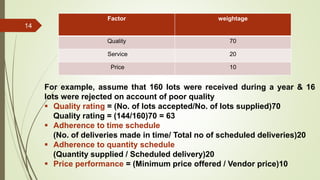
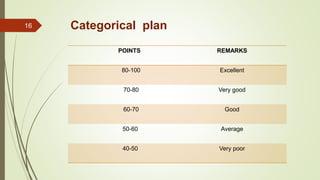
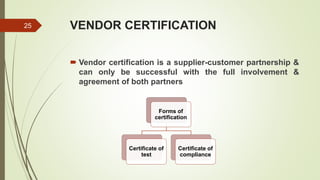
This document discusses vendor development and evaluation procedures. It explains that vendor development involves identifying, developing, and evaluating prospective suppliers to ensure materials are procured at the right quality, quantity, price, and time. The key steps include vendor evaluation, rating vendors based on quality, delivery, price, and time performance, maintaining an approved vendor list, and certifying vendors. Periodic re-evaluation and monitoring of current suppliers is important for effective vendor management.