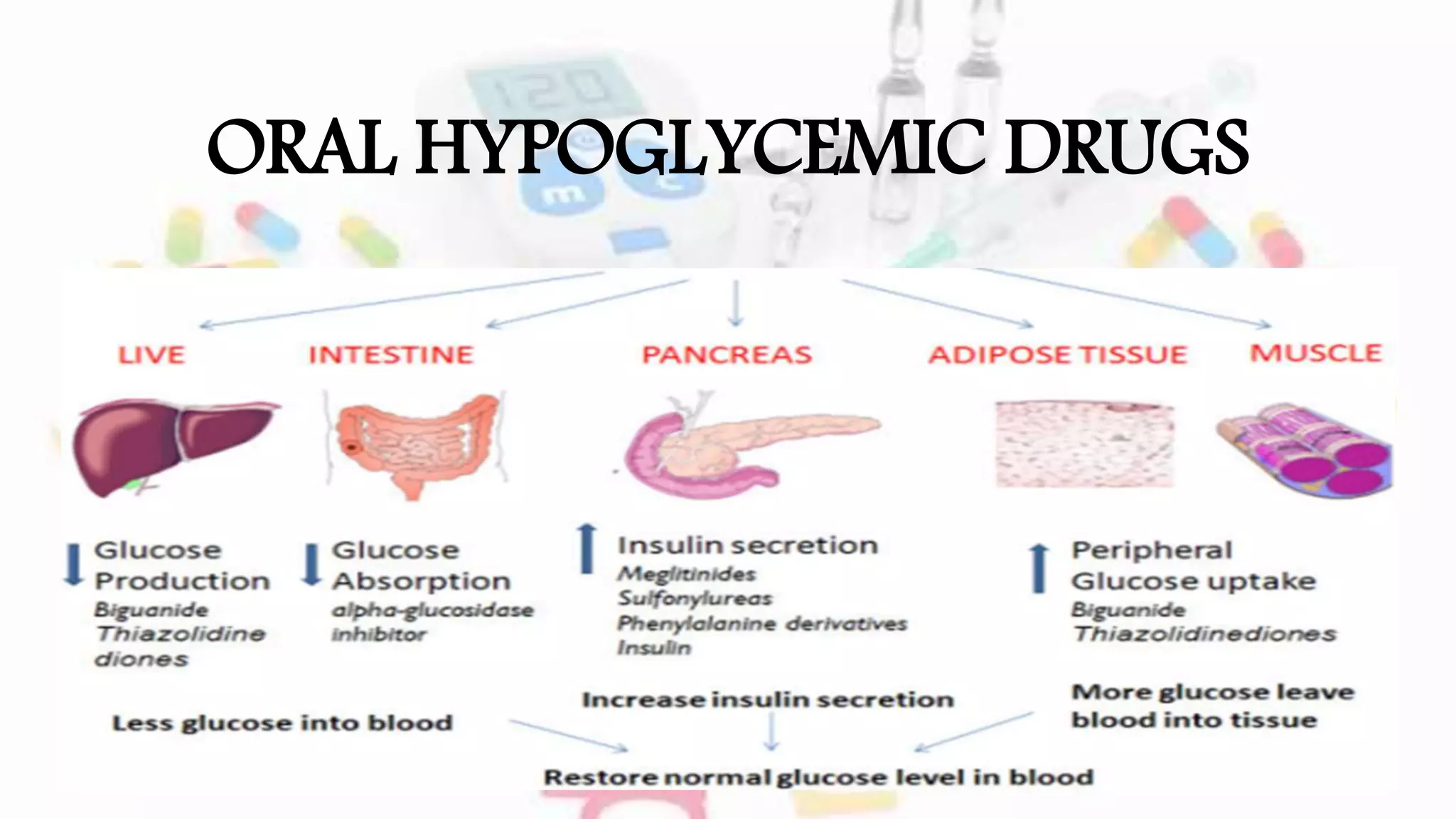
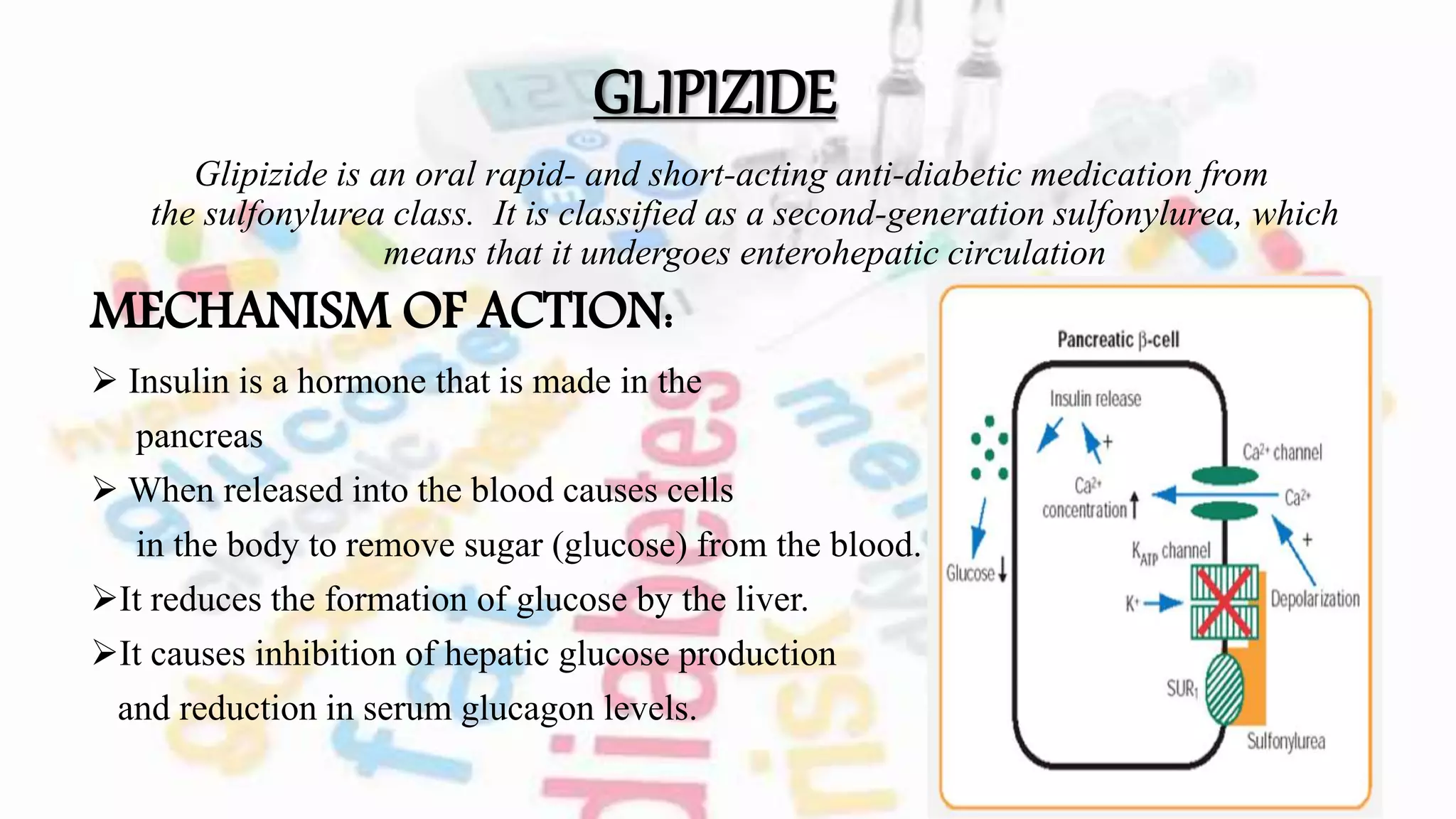
The document discusses oral hypoglycemic agents used to manage diabetes, outlining classifications such as sulfonylureas and glinides. It details mechanisms of action, dosages, and contraindications for specific drugs like tolbutamide, glipizide, repaglinide, and nateglinide, emphasizing safety considerations and potential side effects. Additionally, it describes the differences between drug classes and the importance of tailoring treatment based on individual patient factors.