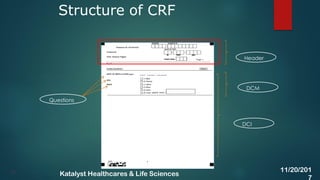
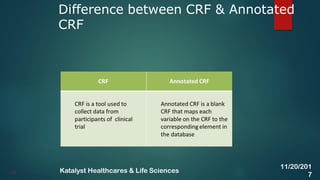
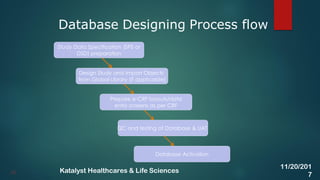
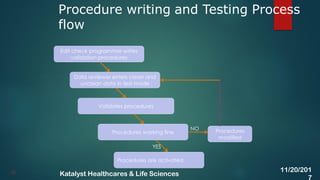
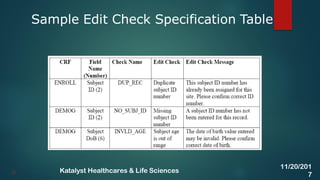
The document discusses the key activities involved in clinical study setup for data management, including designing case report forms (CRFs), developing the study database, programming validation and derivation procedures, and conducting user acceptance testing (UAT). It provides an overview of the study setup process and outlines the objectives, requirements, responsibilities, and deliverables for each setup activity.