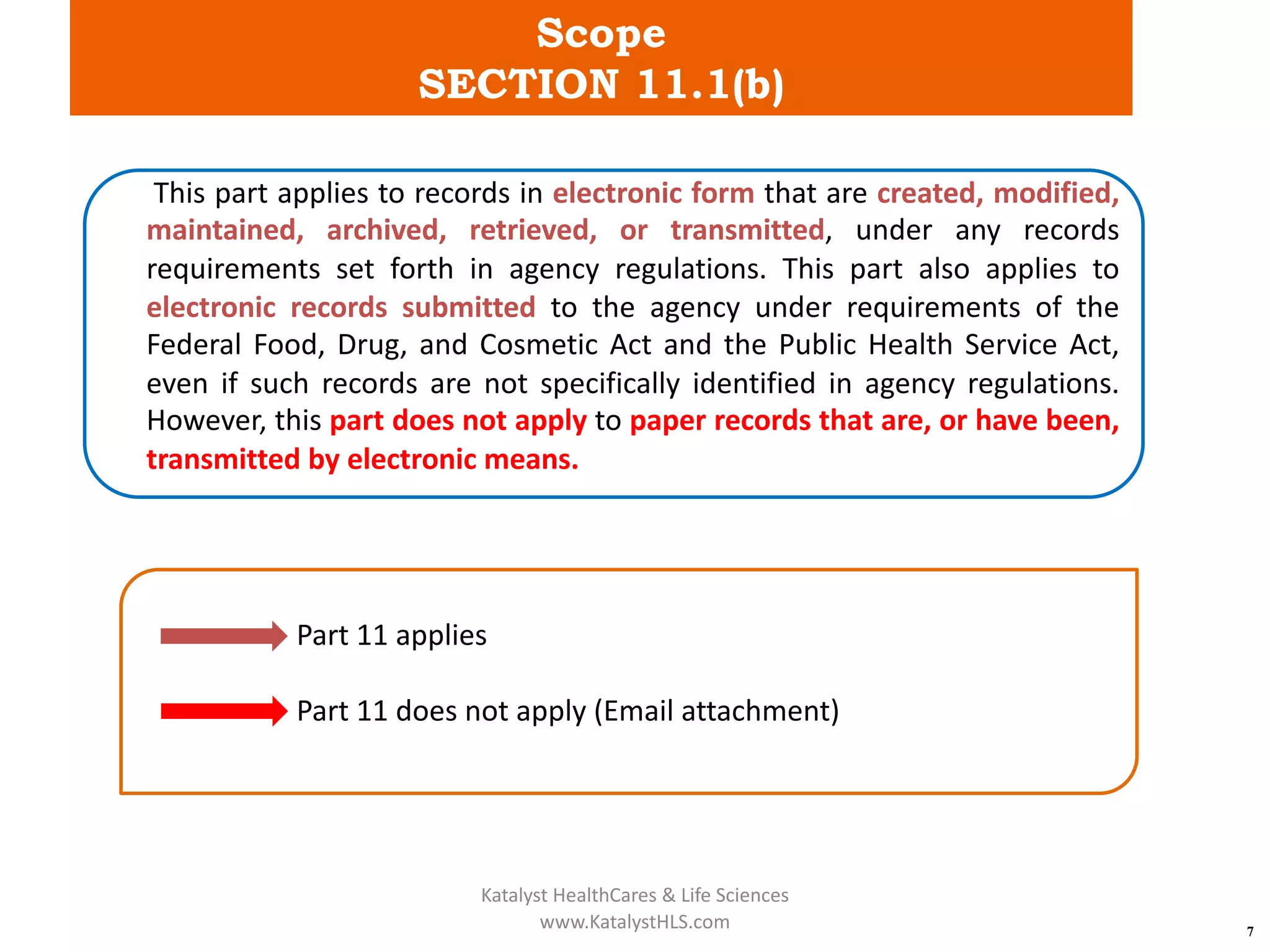
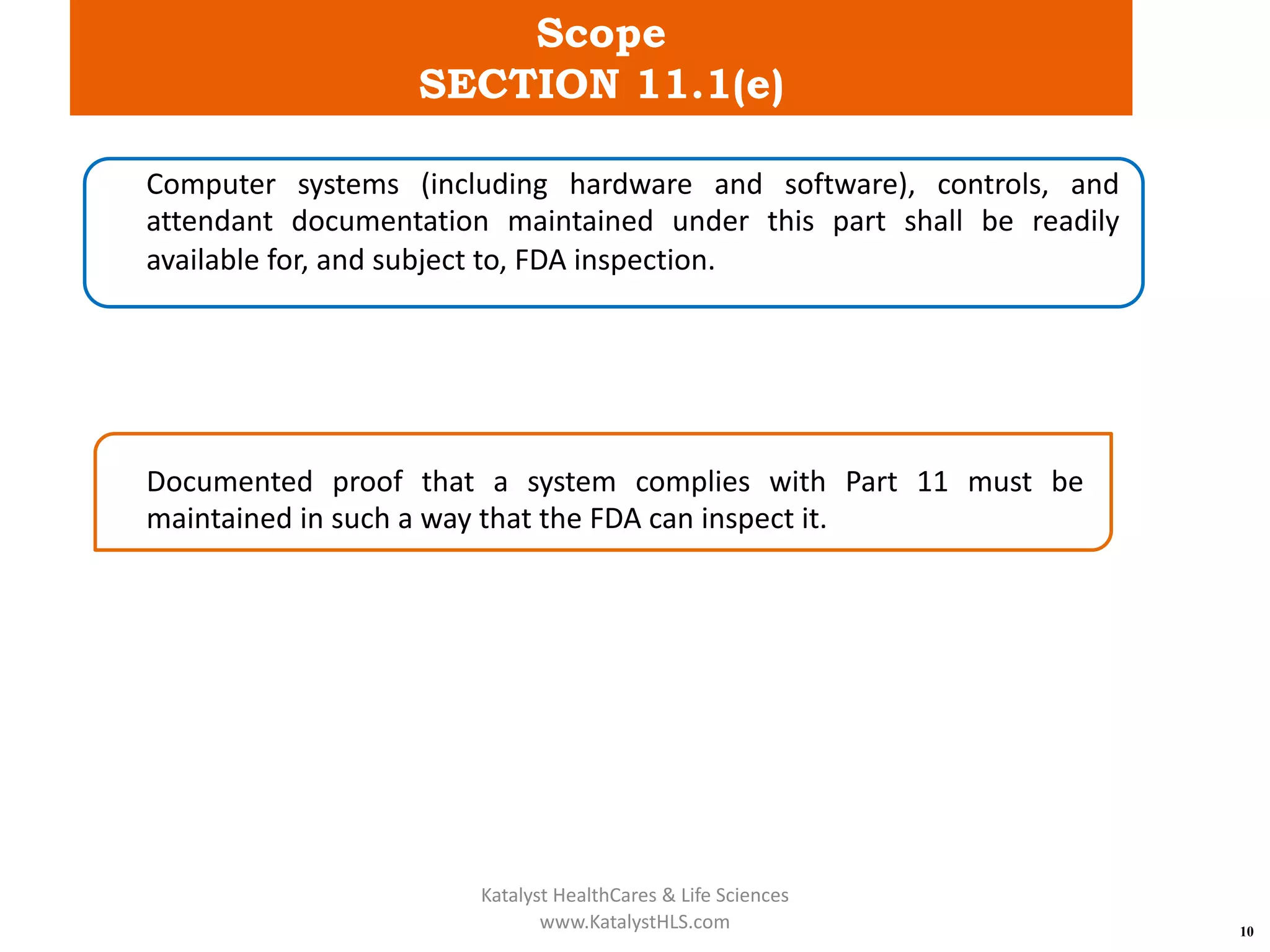
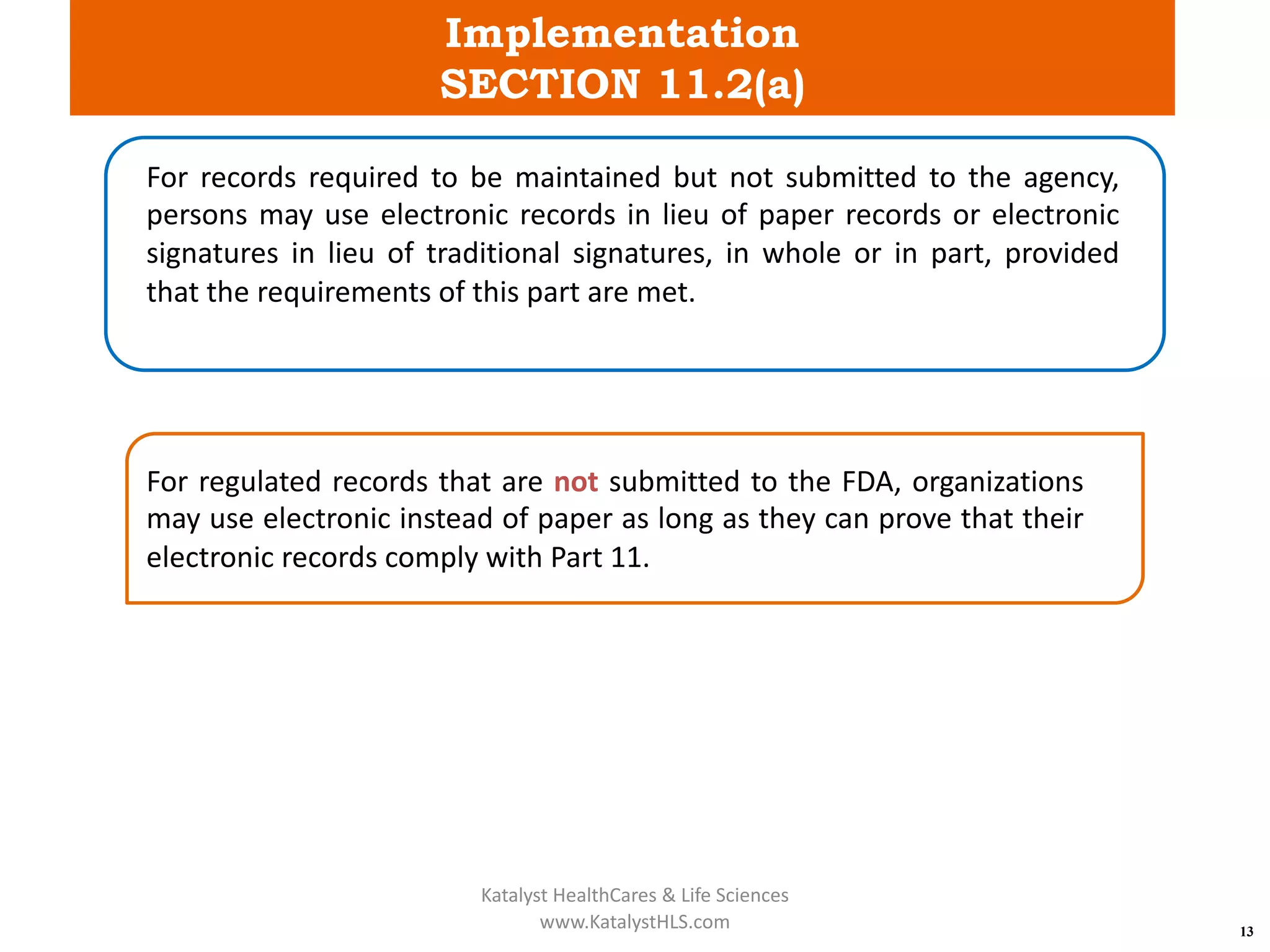
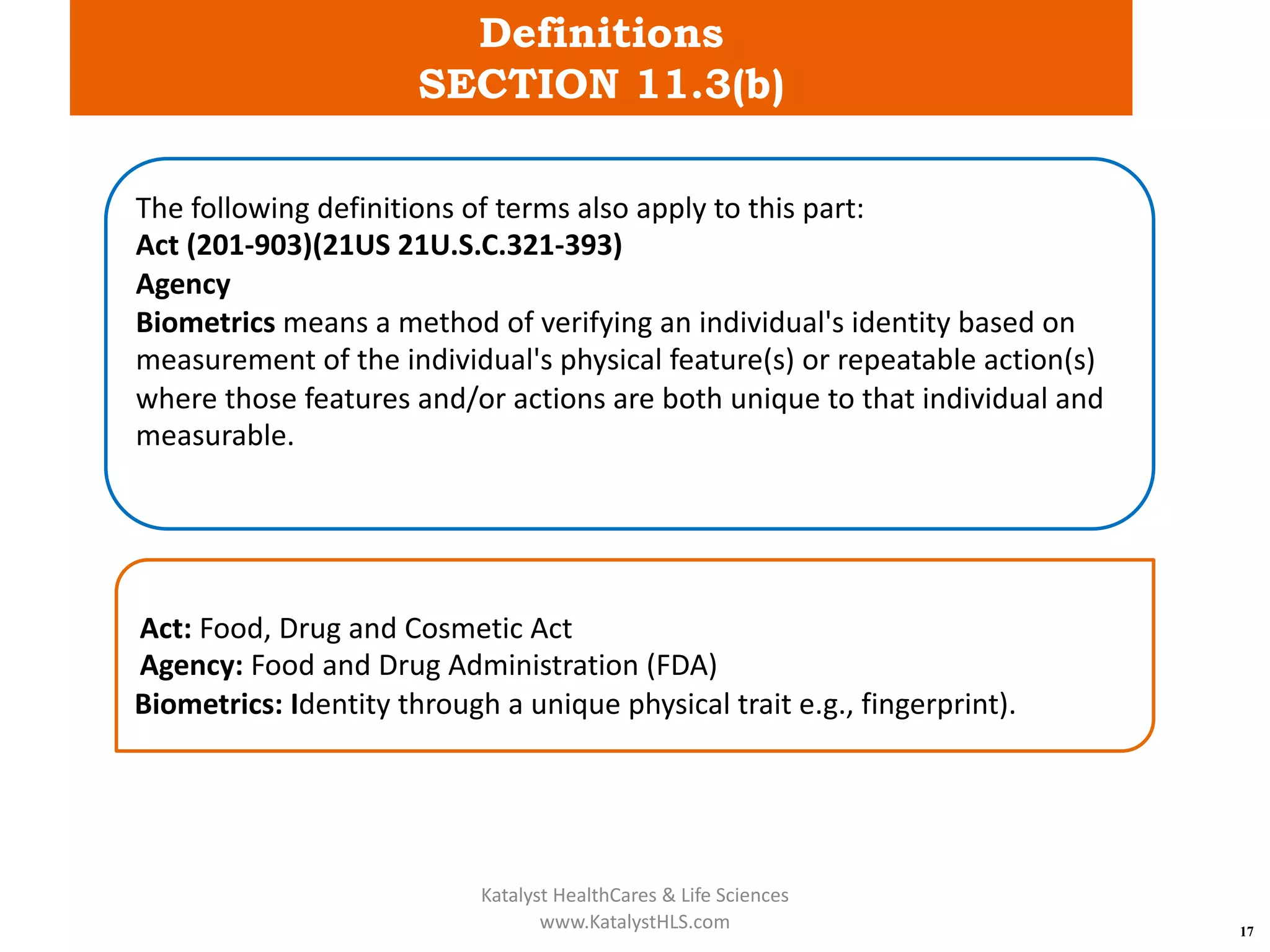
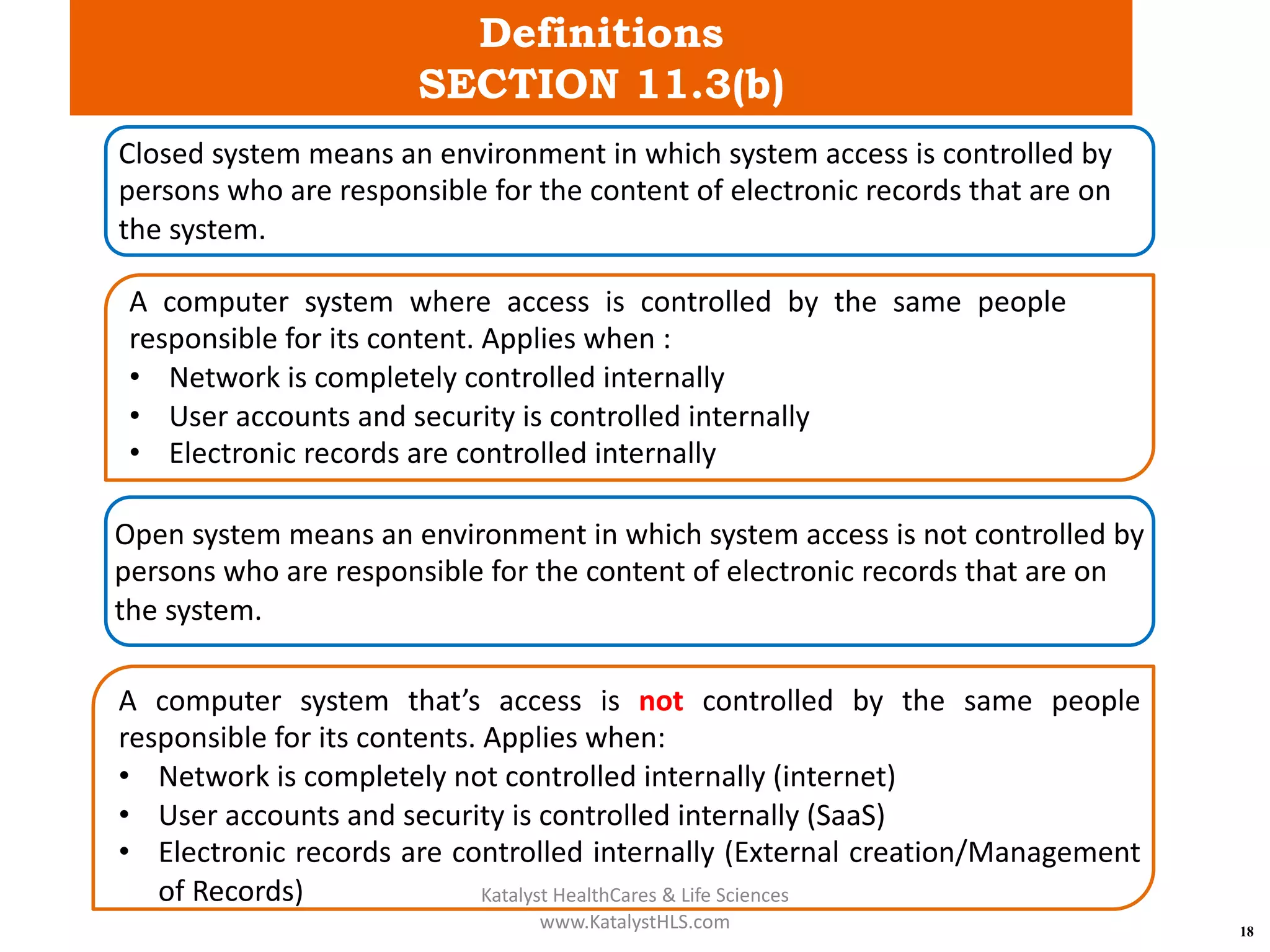
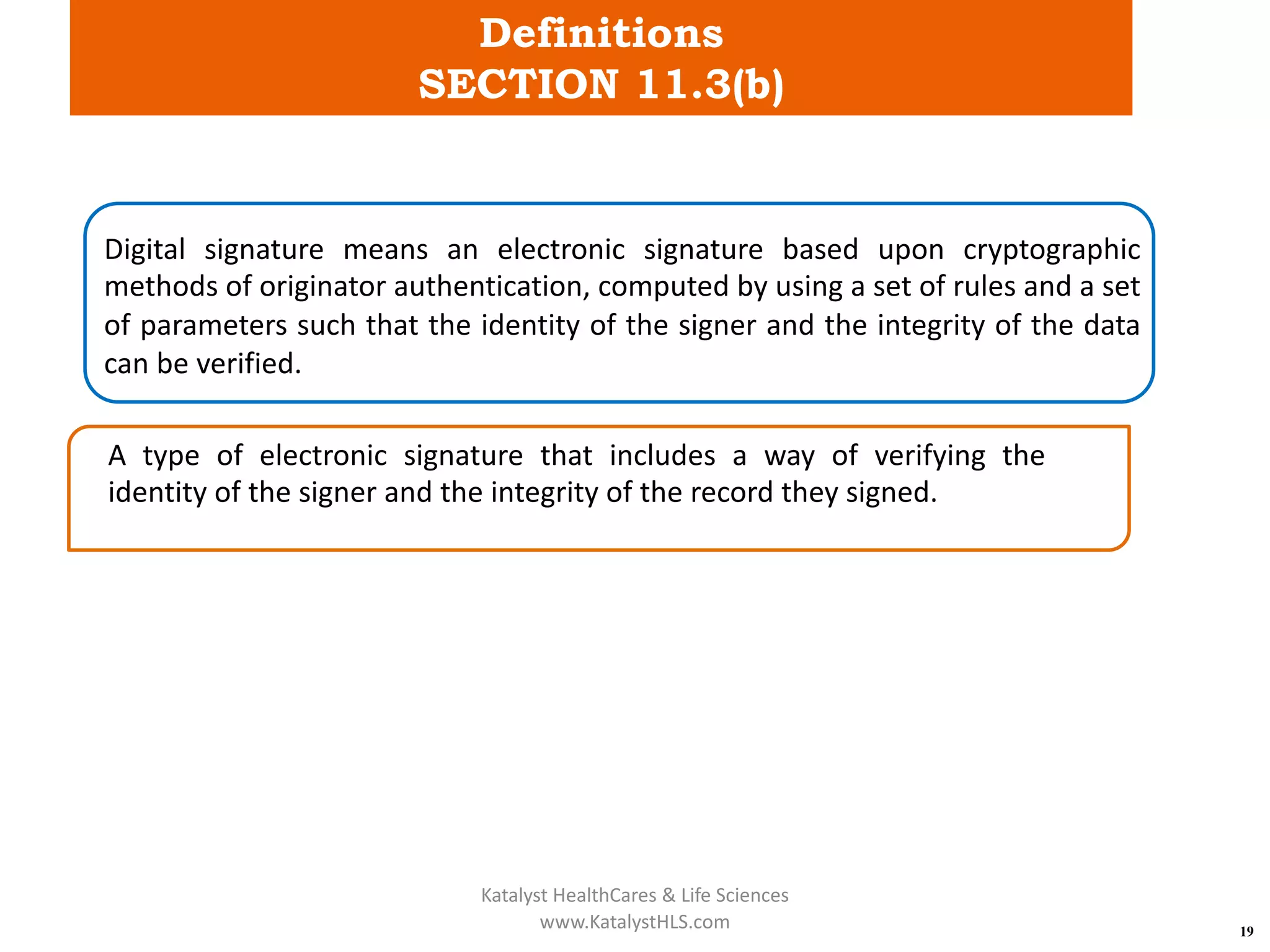
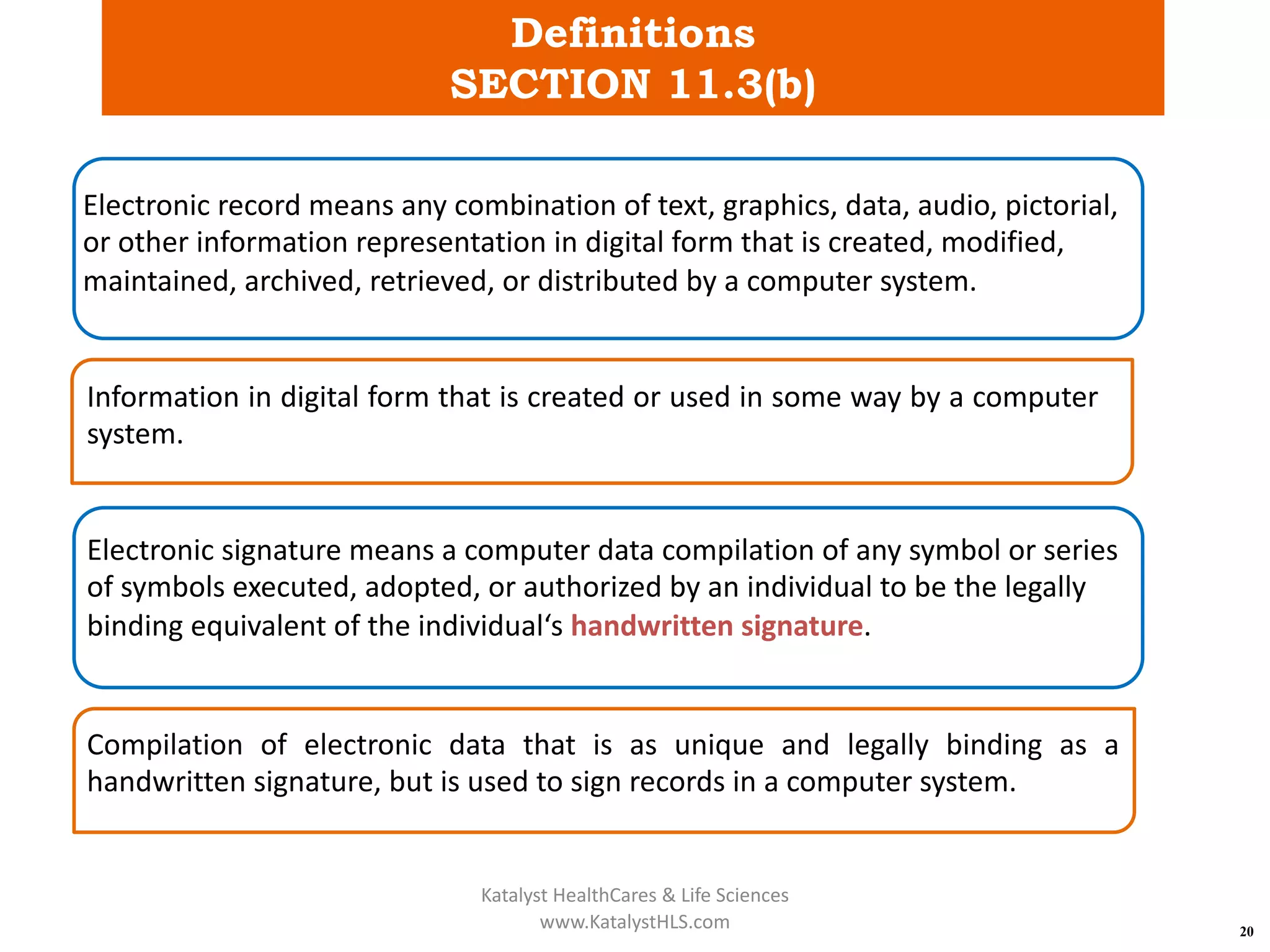
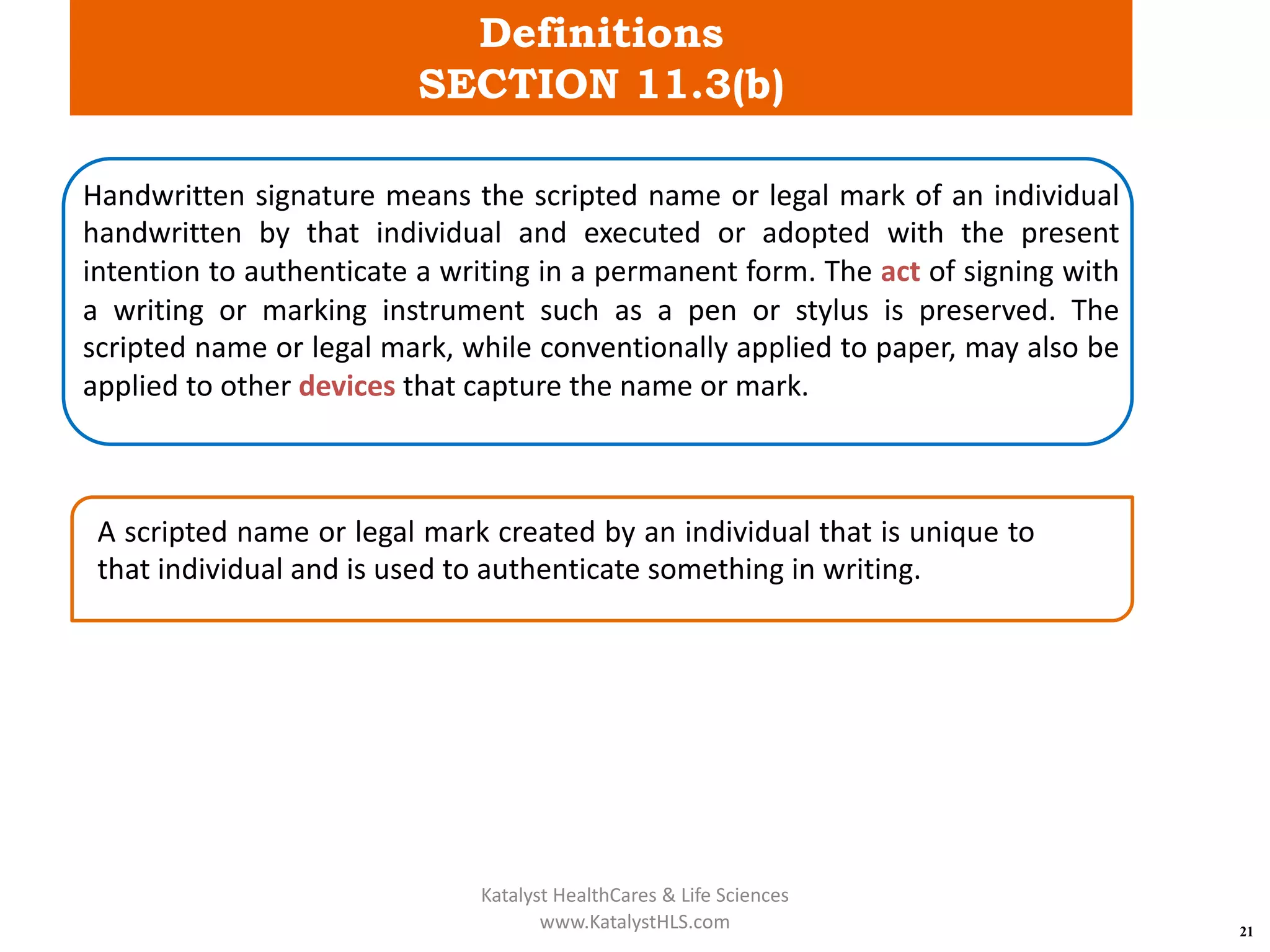
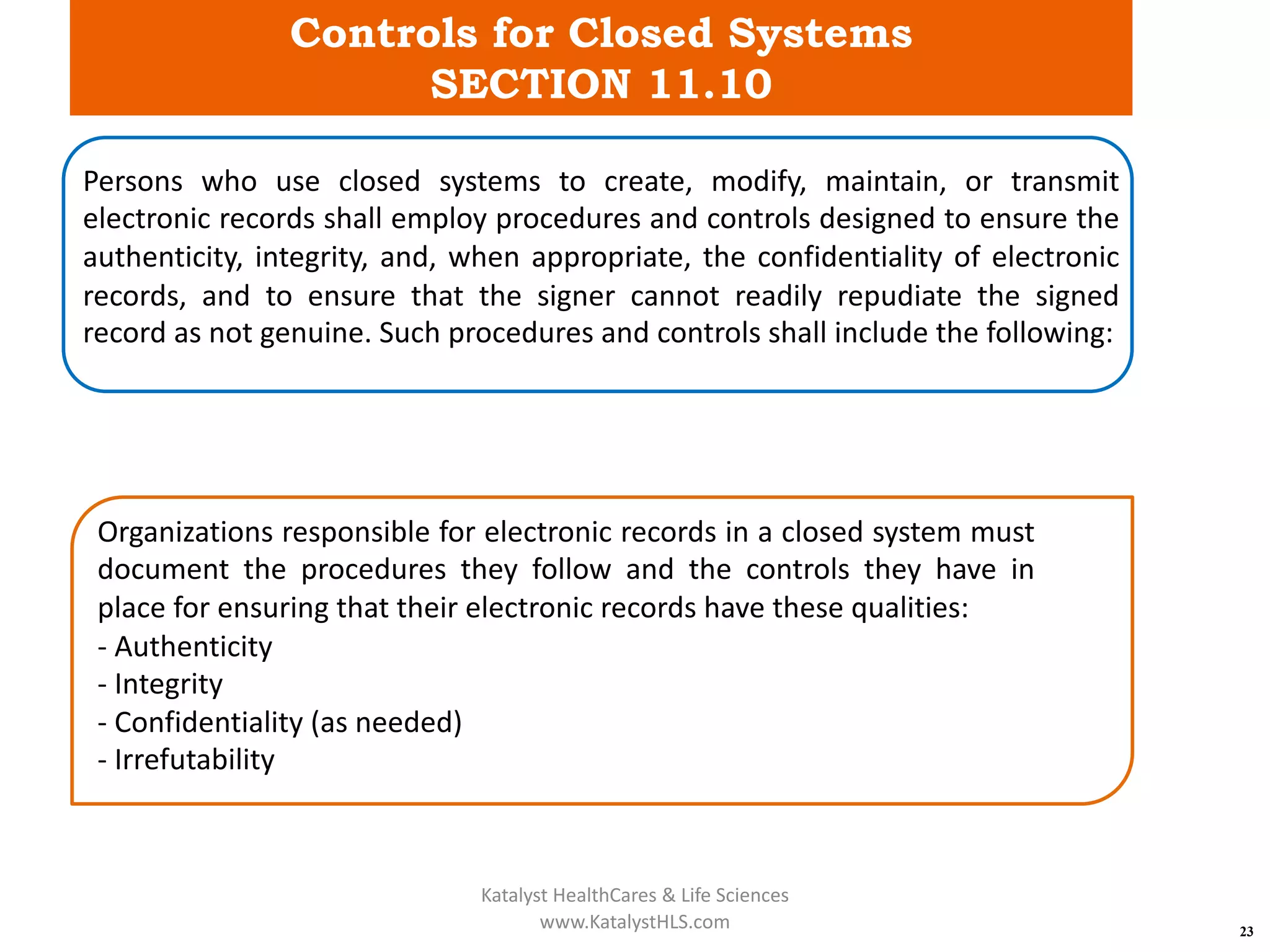
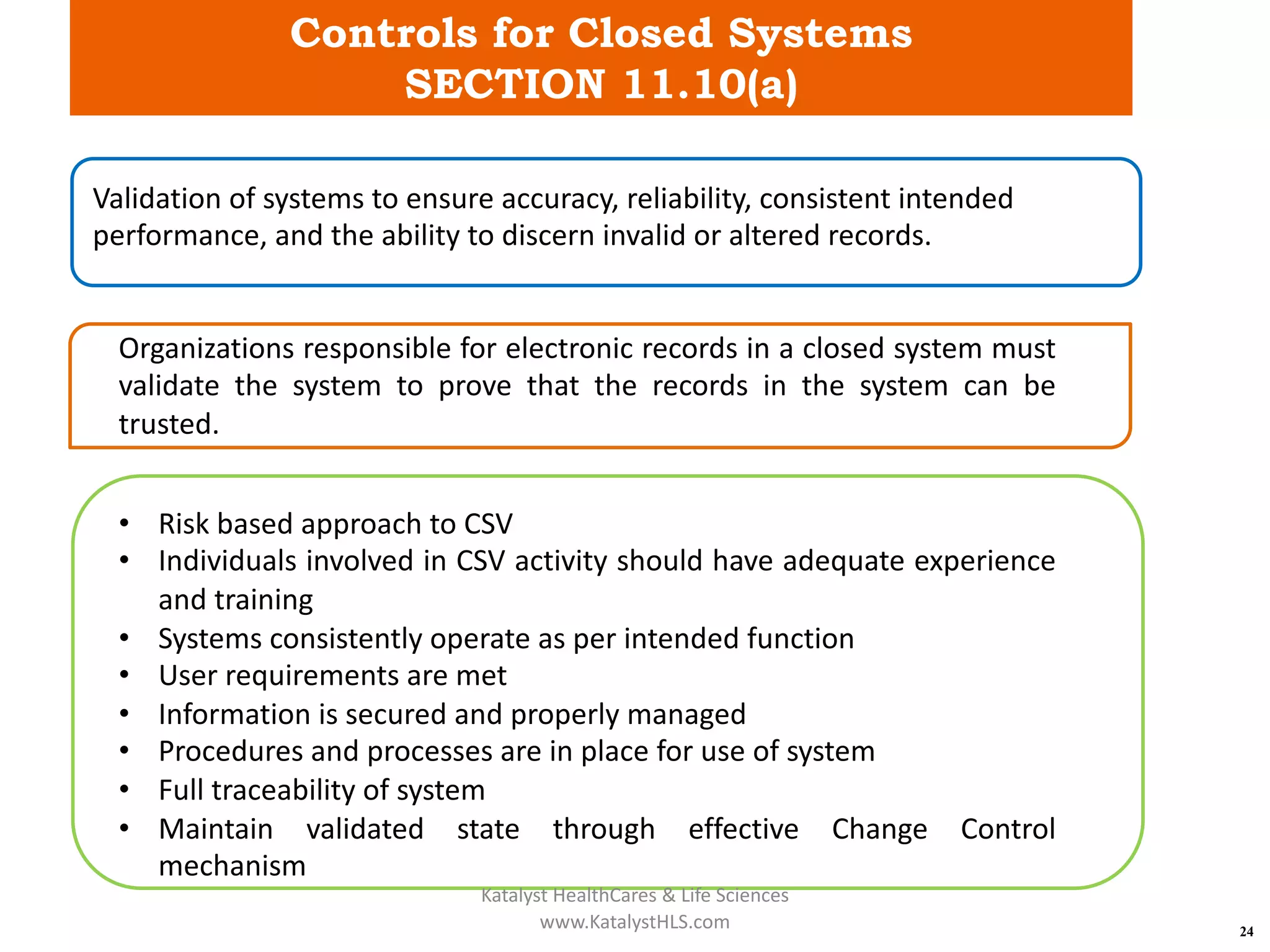
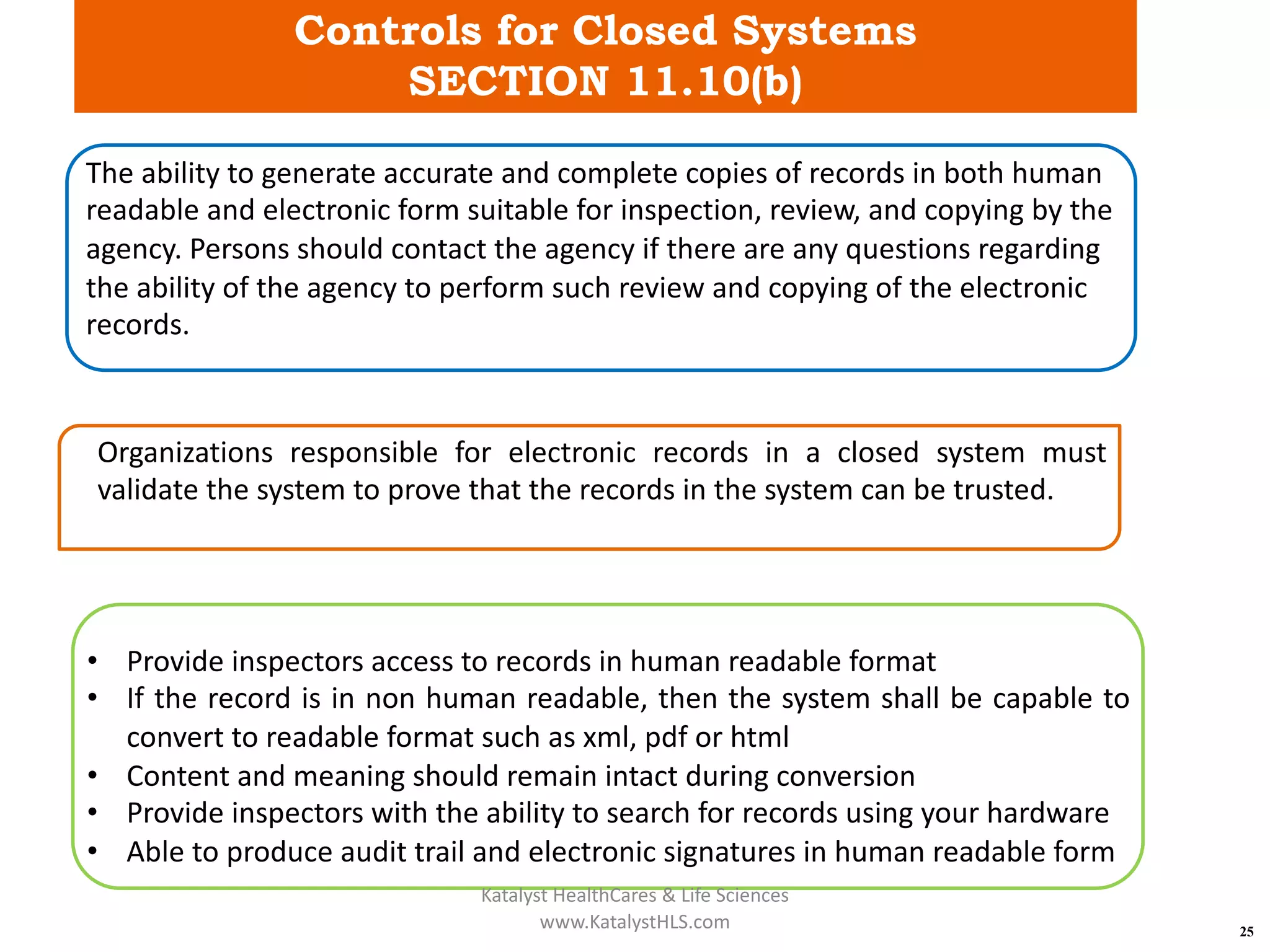
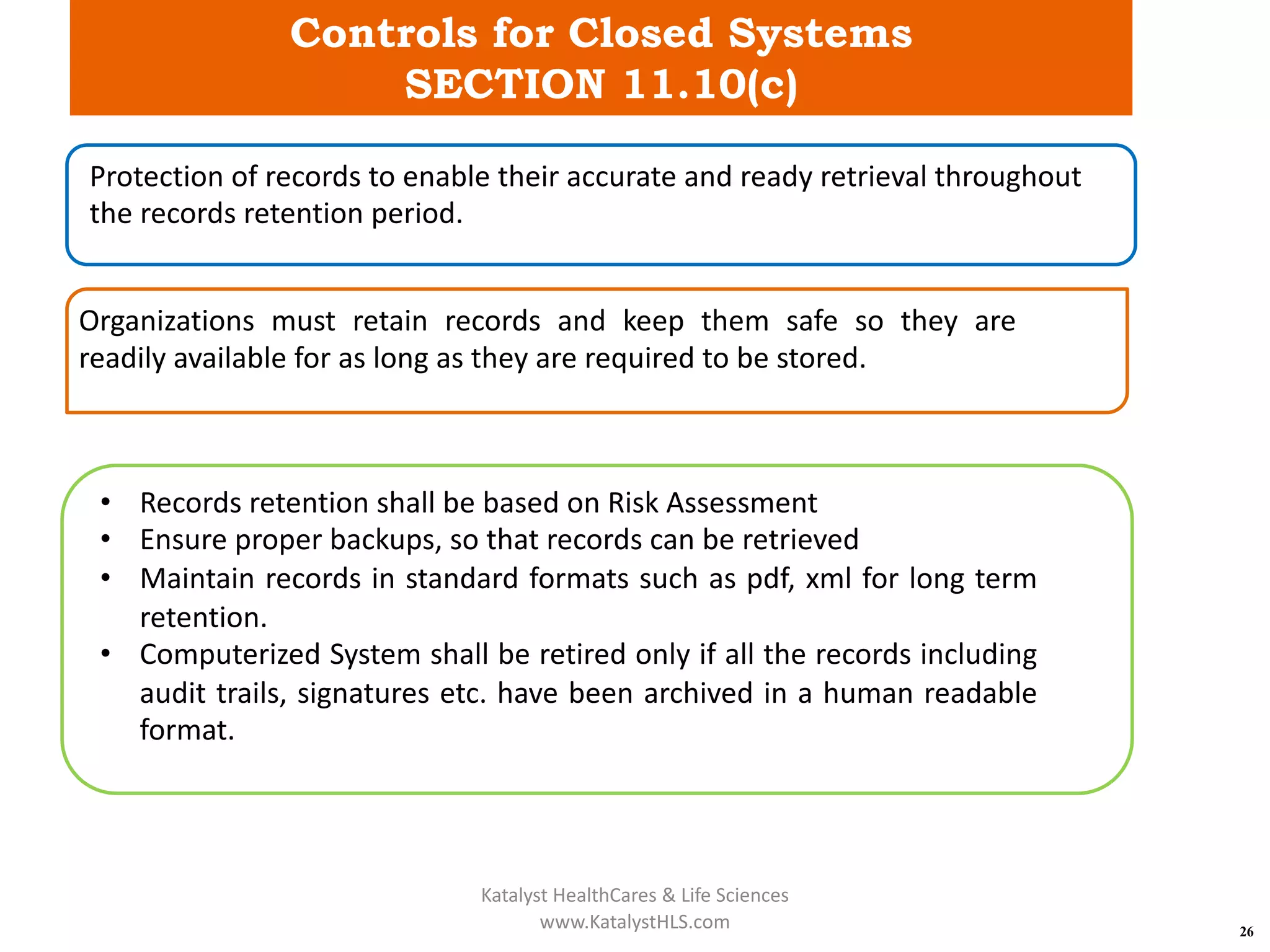
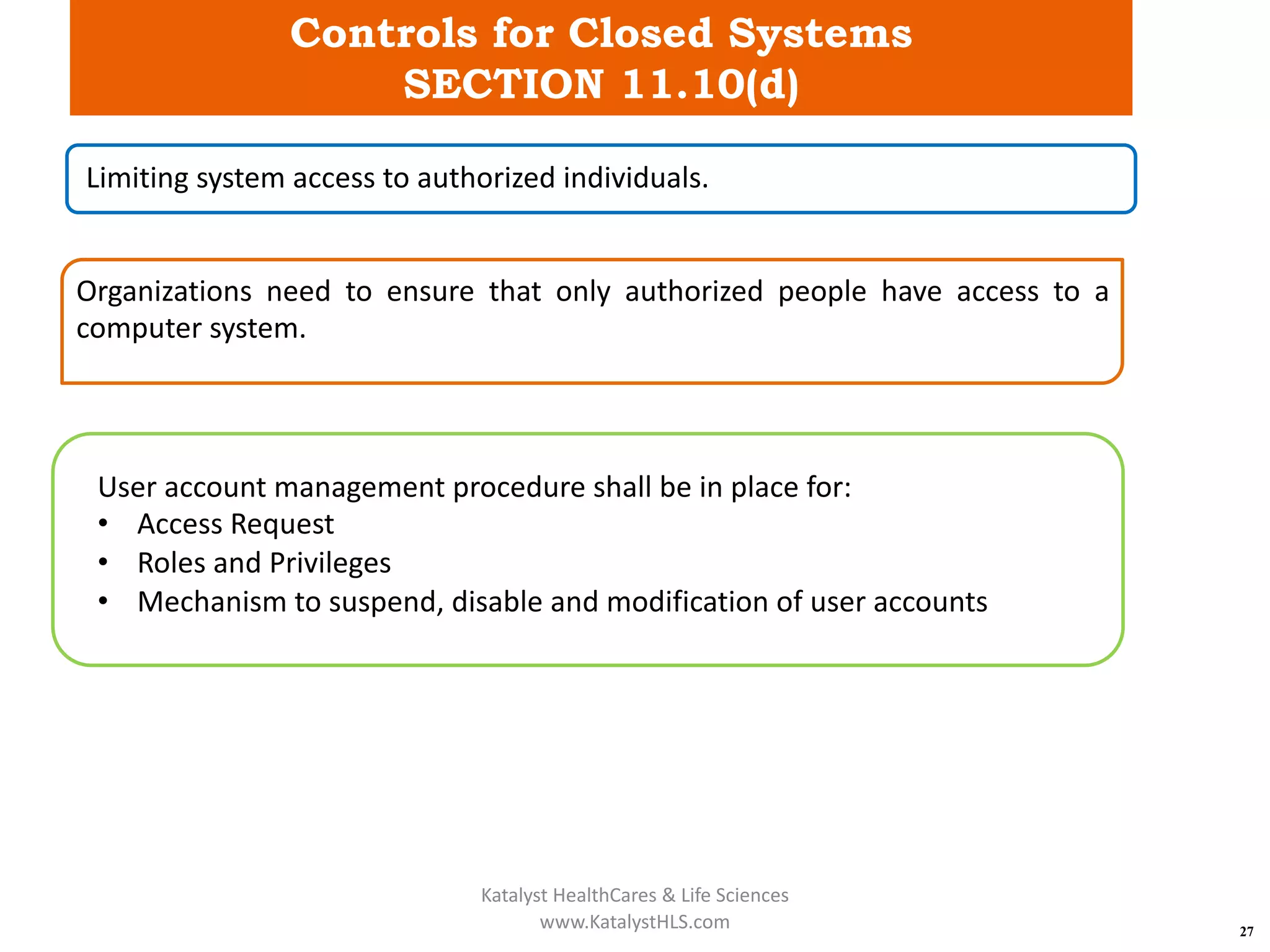
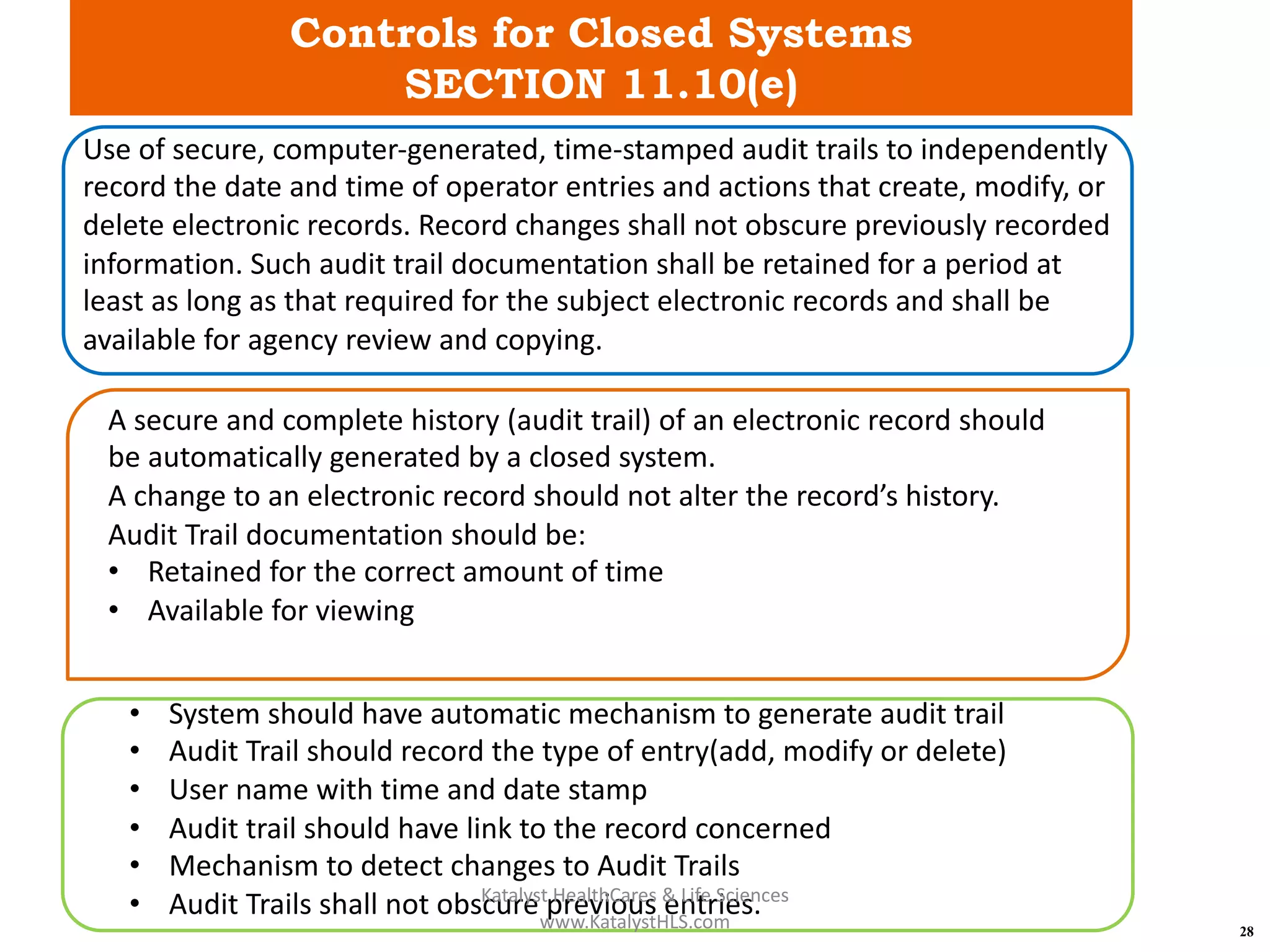
The document provides an overview of 21 CFR Part 11, which governs the use of electronic records and signatures in the FDA regulatory framework, ensuring they are equivalent to traditional paper records and handwritten signatures. Key sections include general provisions, electronic record and signature requirements, and implementation details, along with a detailed examination of controls for both closed and open systems. The document emphasizes the importance of system validation, security measures, and compliance with specified guidelines to maintain the trustworthiness and reliability of electronic records.