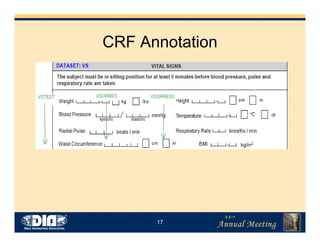
This document discusses the implementation of CDISC SDTM. It notes that the FDA plans to require SDTM as a federal regulation, giving it legal force. Successful implementation requires mapping source data to SDTM domains and validating the results. The data manager plays a key role in mapping and quality control. New roles like mapping specialist and data integration specialist are needed to perform tasks like developing SDTM domains and executing conversion jobs. Widespread adoption of SDTM is expected to provide significant benefits through automation and standardization.