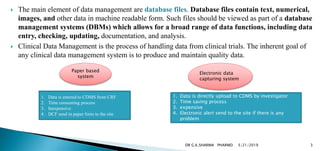
1. A clinical data management system (CDMS) is used to manage data from clinical trials by storing data entered in case report forms (CRFs) by investigators.
2. Data management involves planning, collection, entry, validation, manipulation, backup and documentation of data to create a high quality database. Commonly used CDMS tools include Oracle Clinical, ClinTrial, Macro and eClinical Suite.
3. Open source CDMS tools include OpenClinica, openCDMS, TrialDB and PhOSCo which are free. All CDMS tools ensure an audit trail and management of discrepancies according to roles and user access levels.