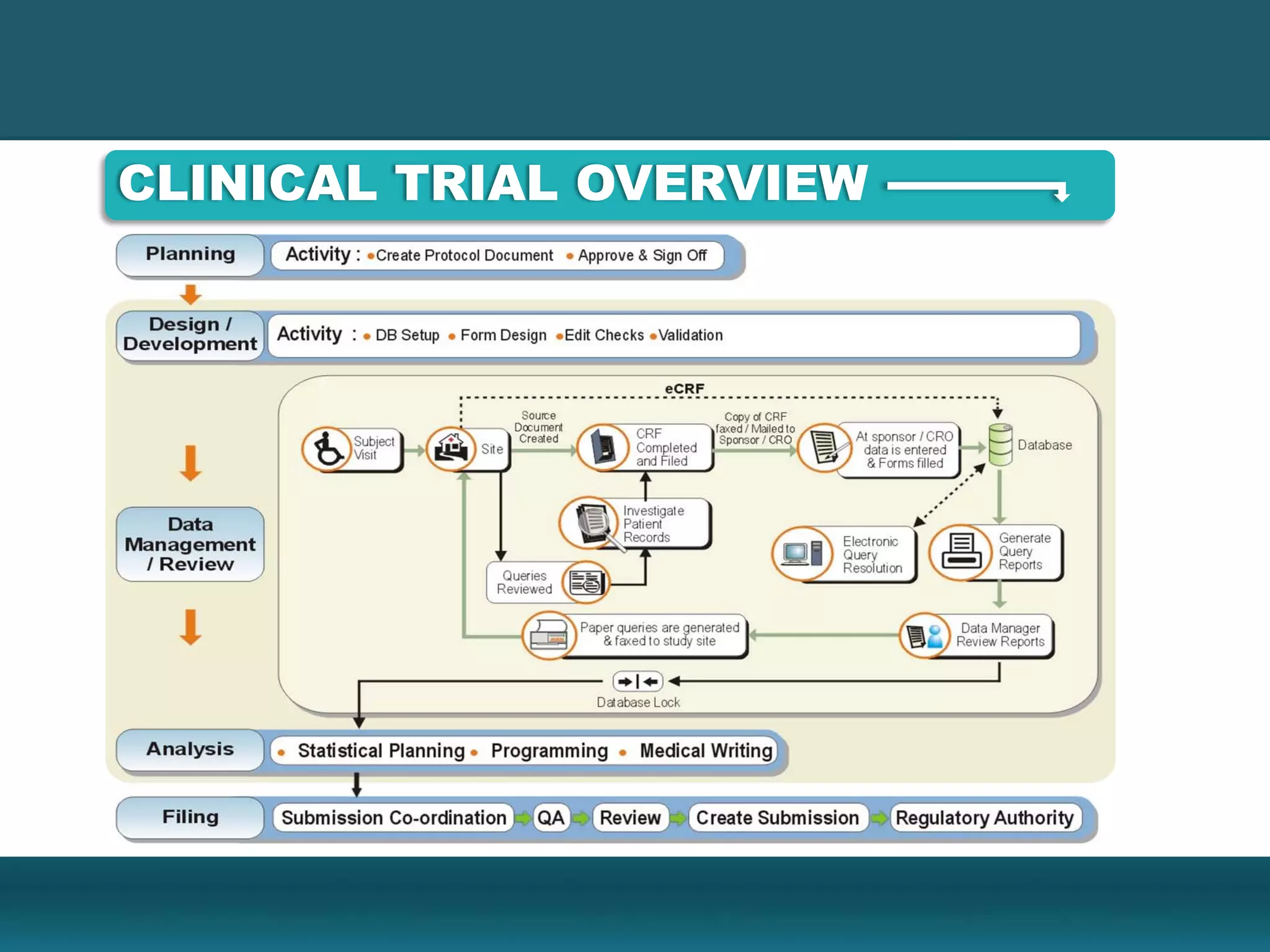
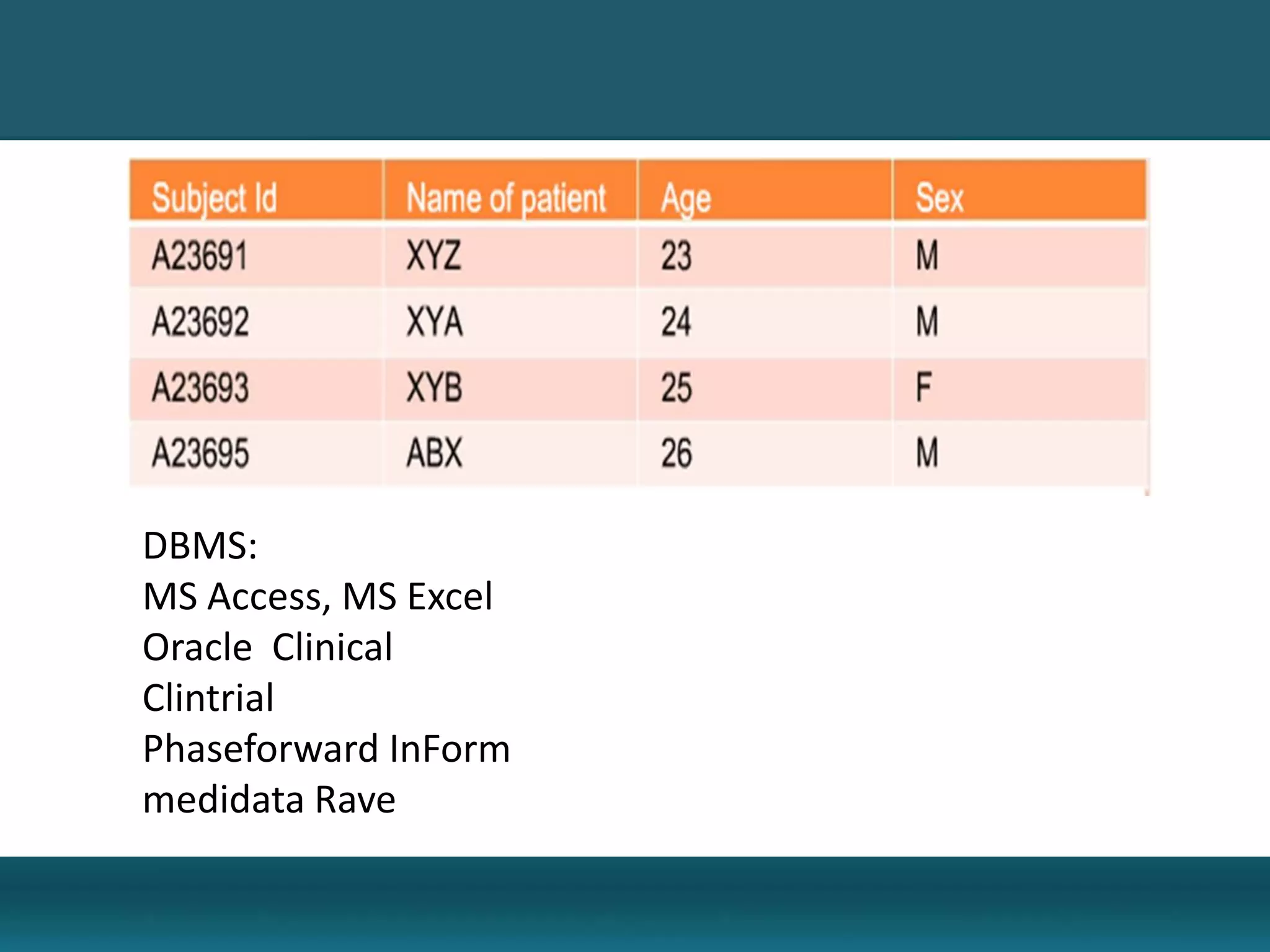
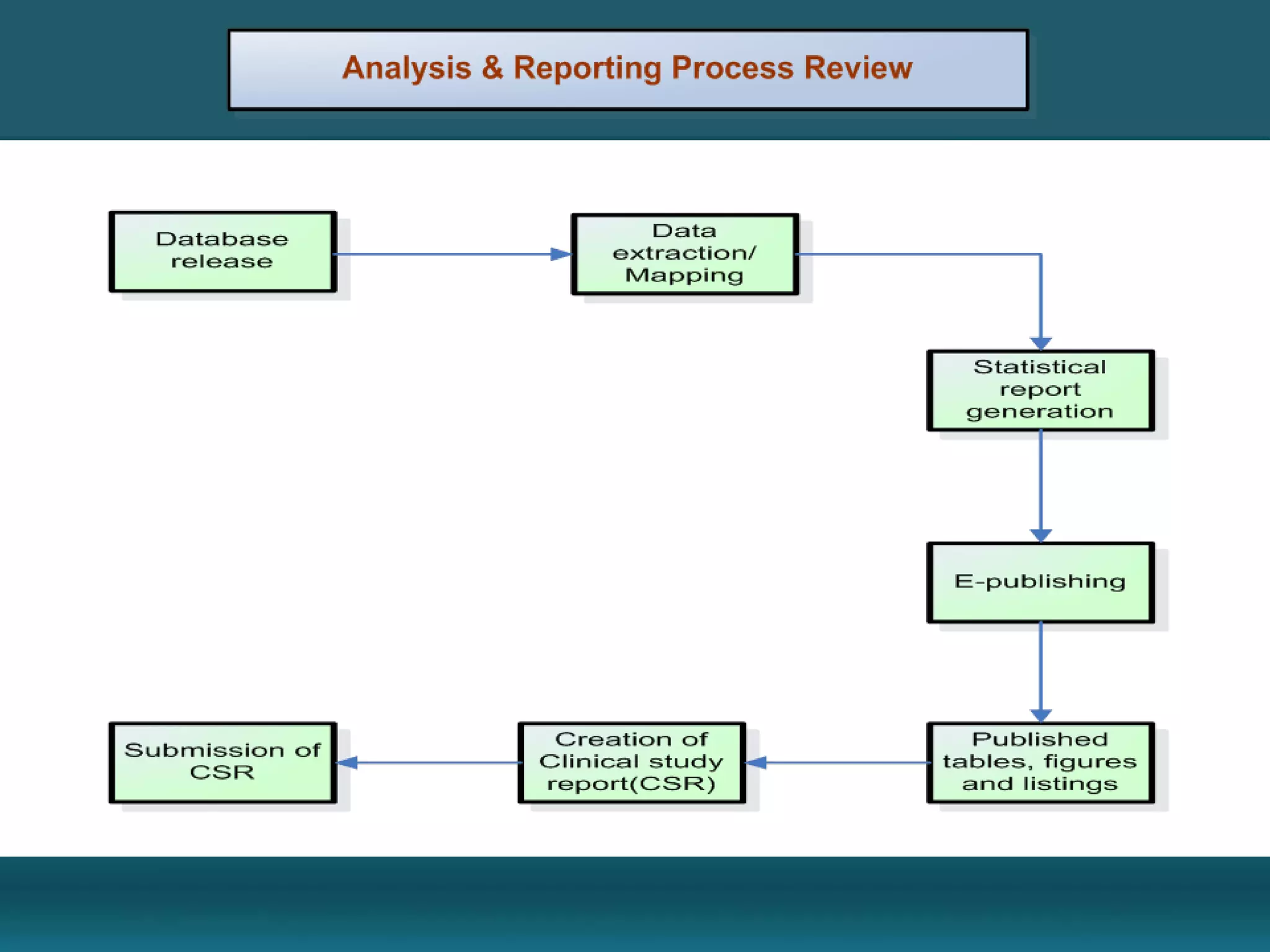
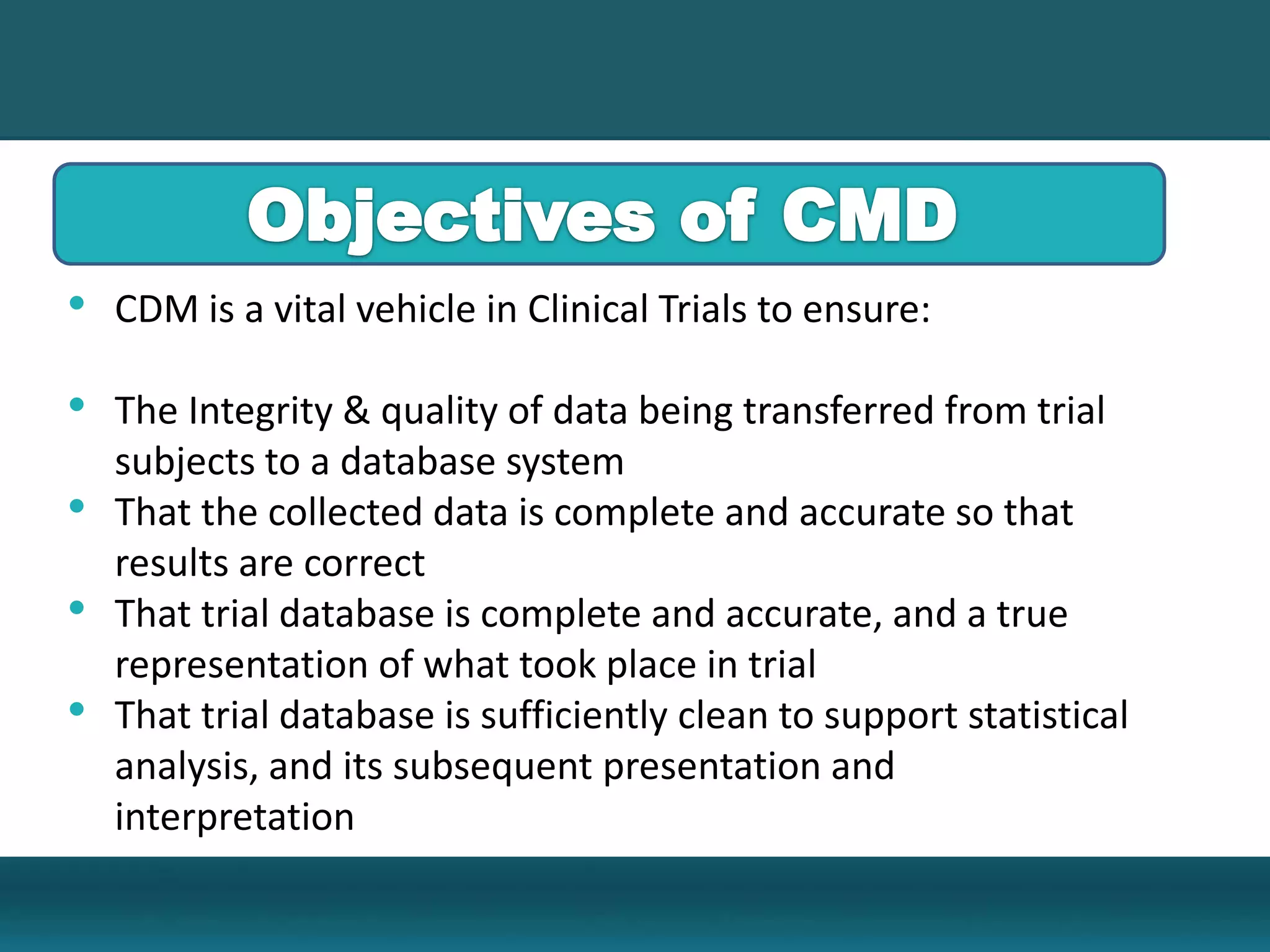
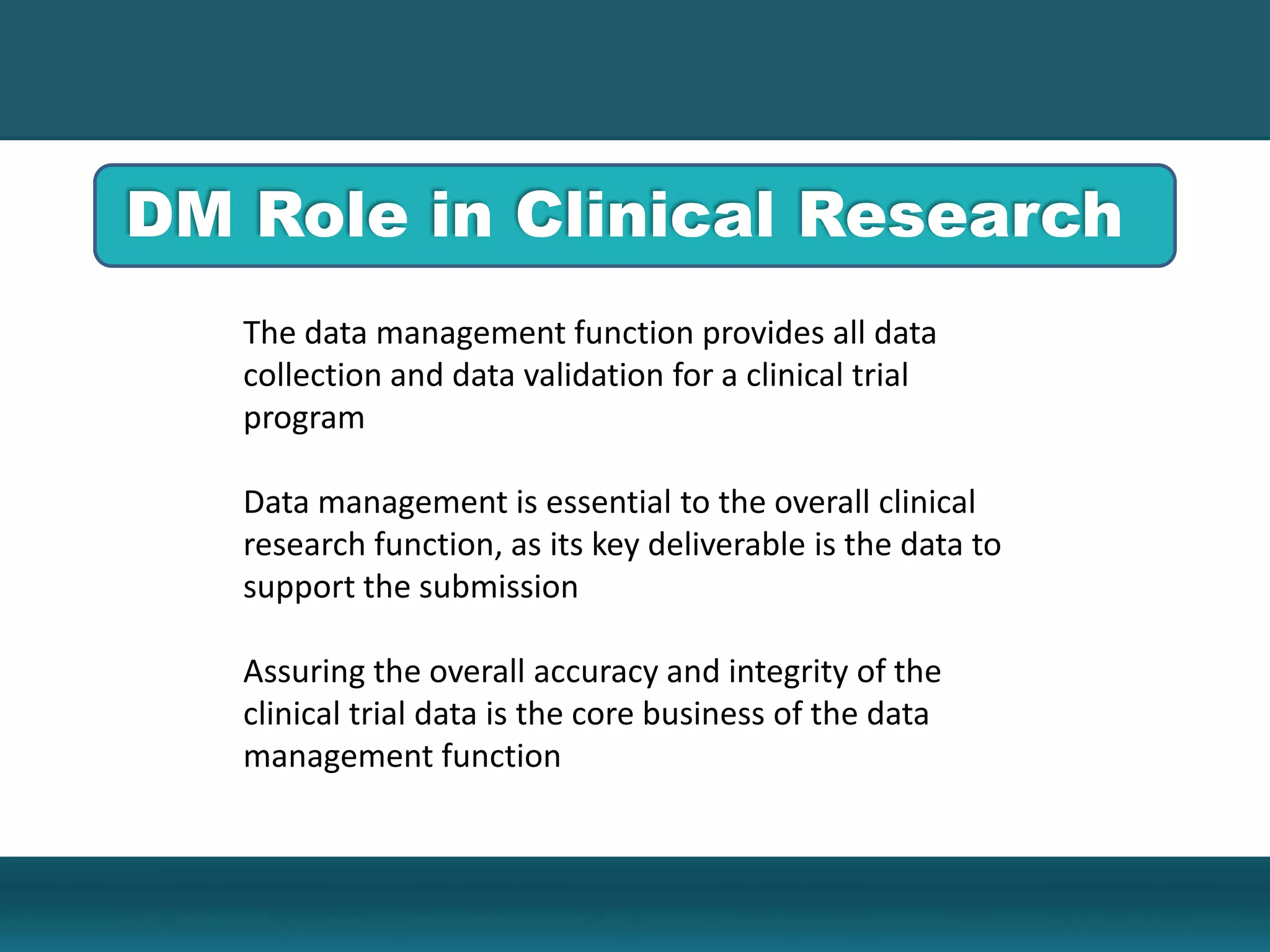
Clinical data management involves collecting, cleaning, and managing clinical trial data. It ensures data integrity and allows for statistical analysis. Key aspects include setting up electronic or paper case report forms, building and testing databases, entering and validating data, performing medical coding, reconciling safety data, conducting quality checks, and locking databases. The goal is to provide accurate and complete data to support regulatory approval of new drugs.