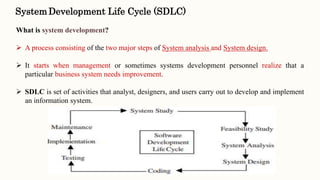
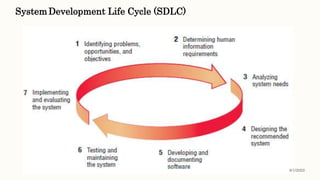
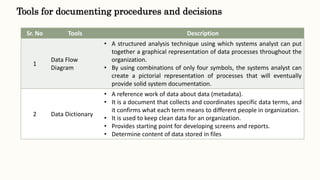
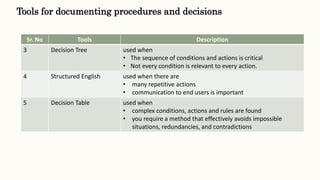
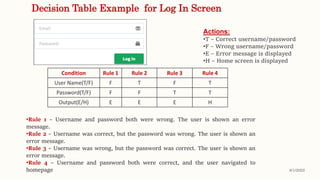
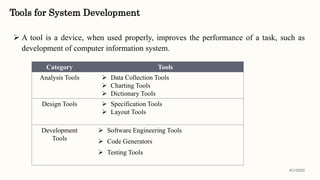
This document discusses classical systems development methodology. It describes the classical systems development life cycle (SDLC) which includes 7 phases: preliminary investigation, determination of system requirements, design of system, development of software, system testing, implementation and evaluation, and system maintenance. It also discusses tools and techniques used in each phase like fact finding techniques, documentation tools, and decision models.