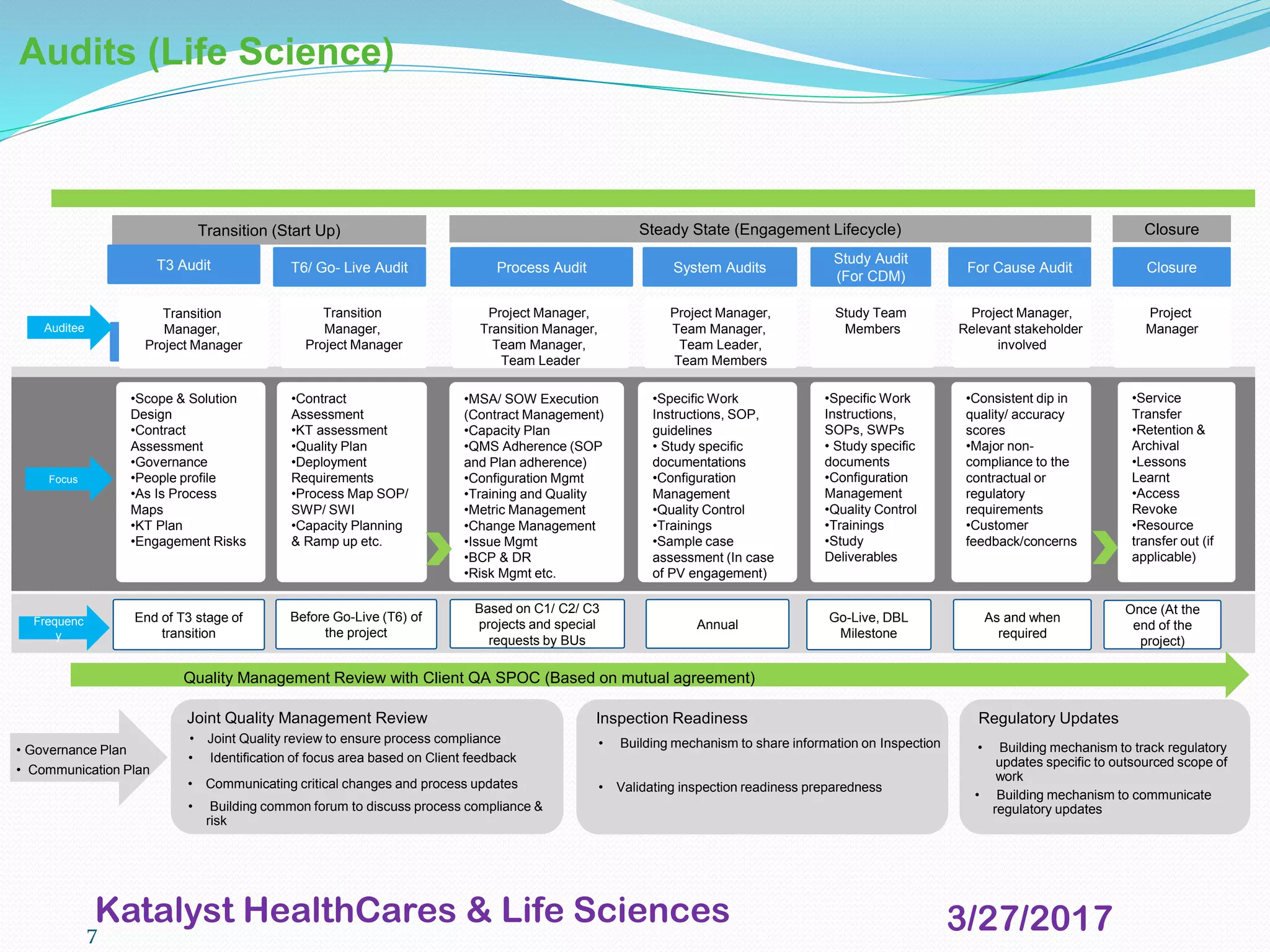
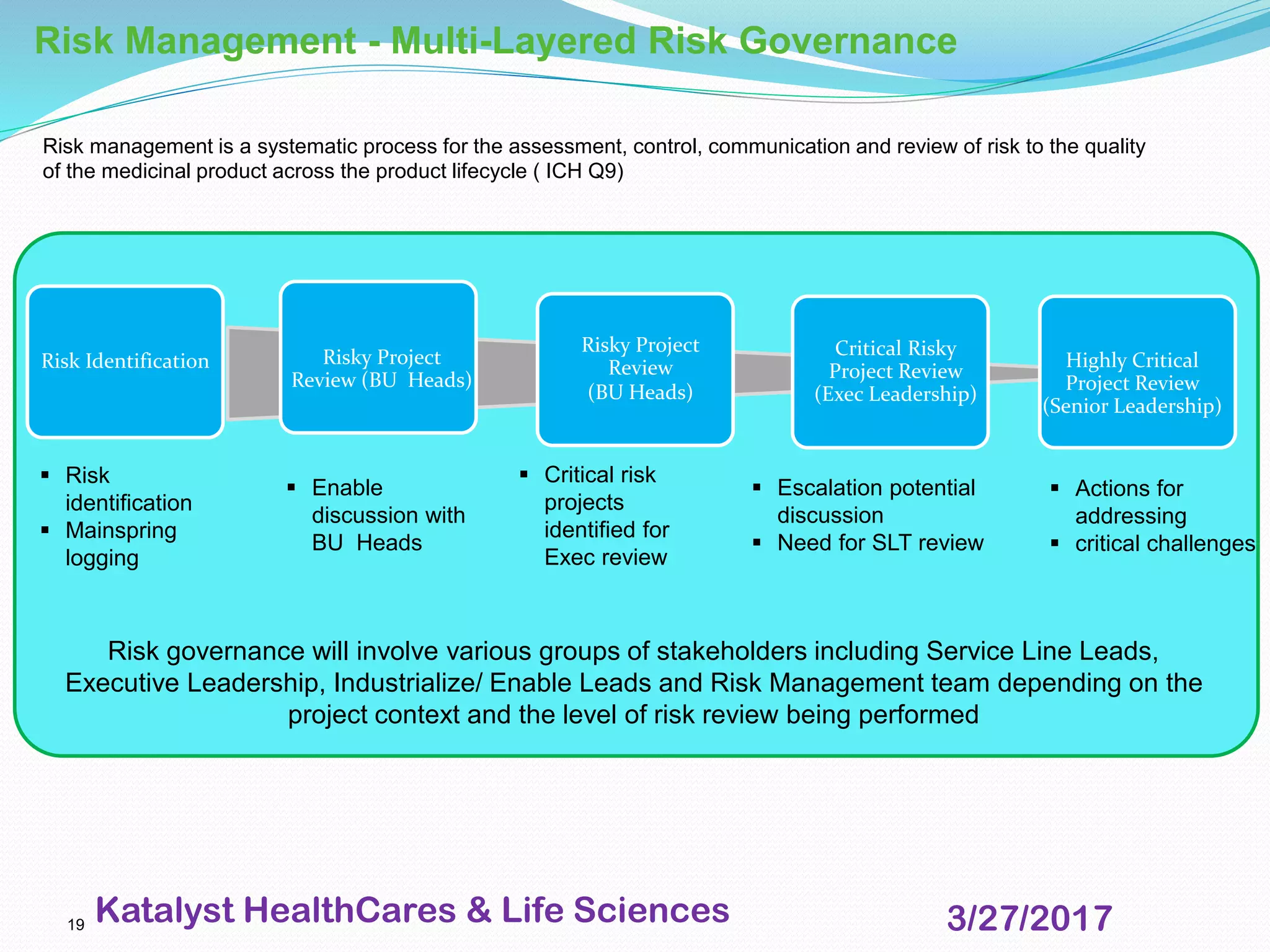
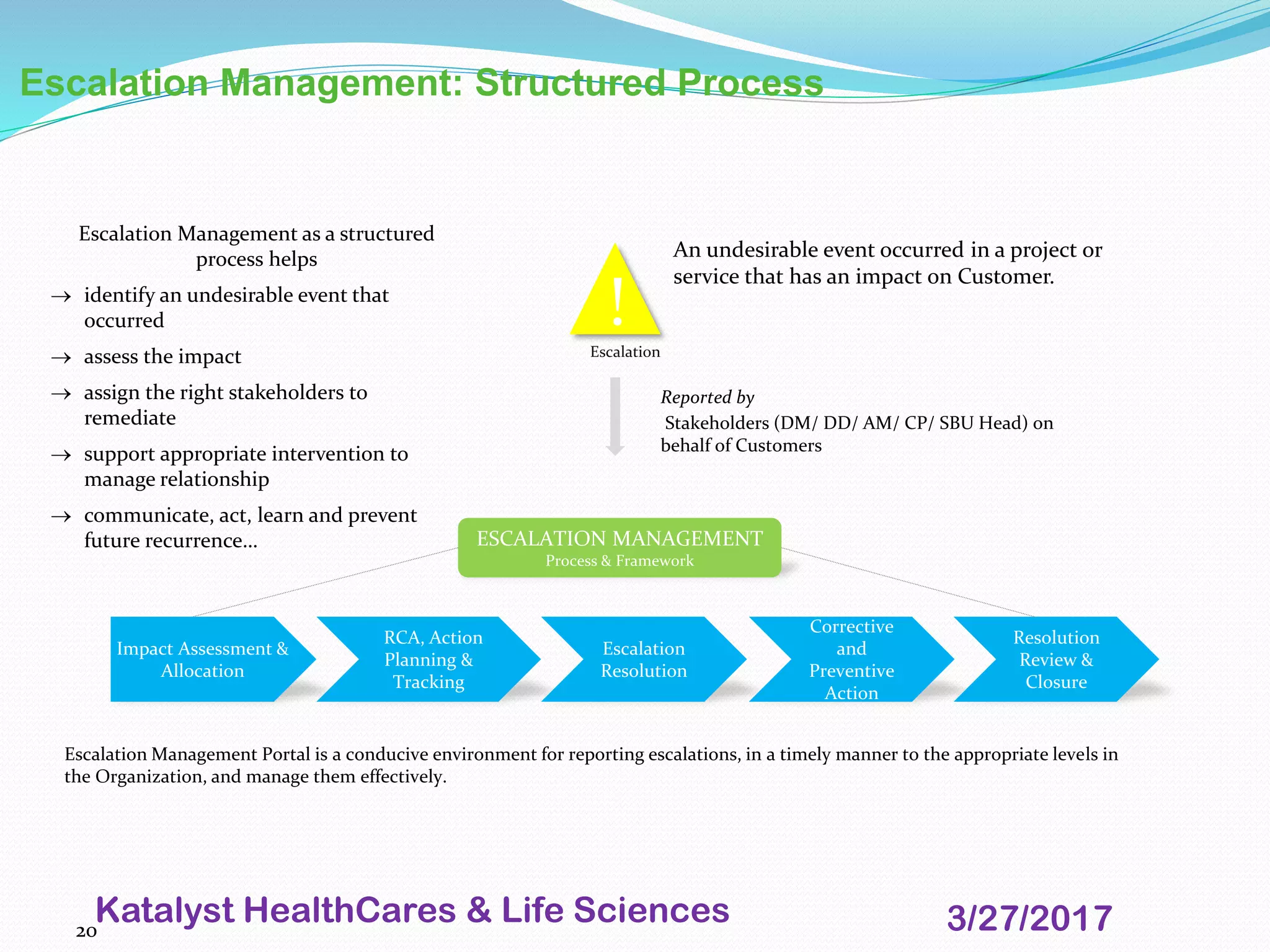
This document provides an overview of audits and inspections for quality management in life sciences. It defines audits and inspections, describes types of each, and outlines focus areas. Key aspects of audits covered include classification of findings, root cause analysis, corrective action processes, audit tools, and dos and don'ts. Good documentation practices, risk management, and escalation management processes are also summarized. The purpose is to educate on quality policy, audits, inspections, and related quality management topics in life sciences.