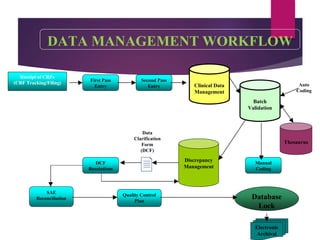
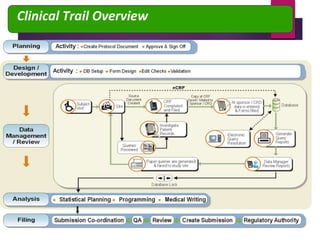
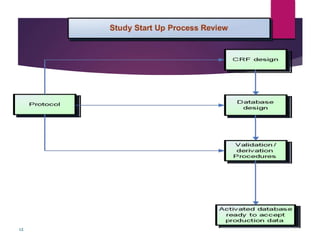
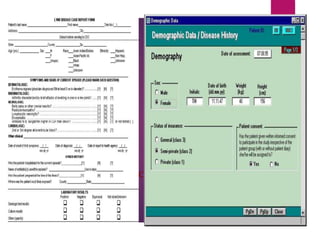
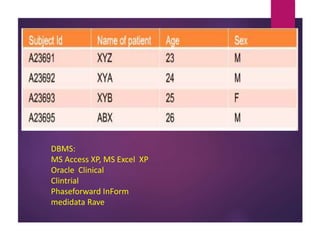
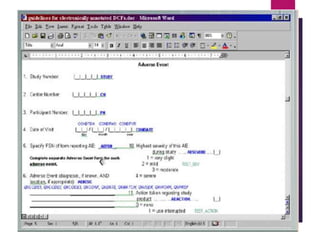
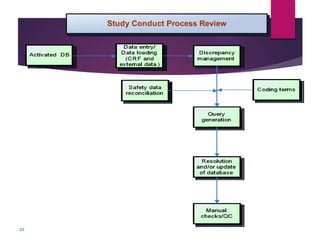
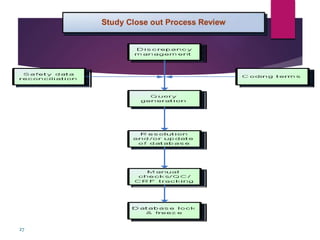
Clinical data management (CDM) is crucial for collecting, processing, and validating clinical trial data, ensuring its integrity for regulatory approval. It involves multiple roles, from data entry to quality control, and encompasses a systematic workflow including study setup, conduct, and closeout. CDM has evolved to prioritize the accurate and timely delivery of clean data for analysis, reflecting its importance in the overall clinical research process.