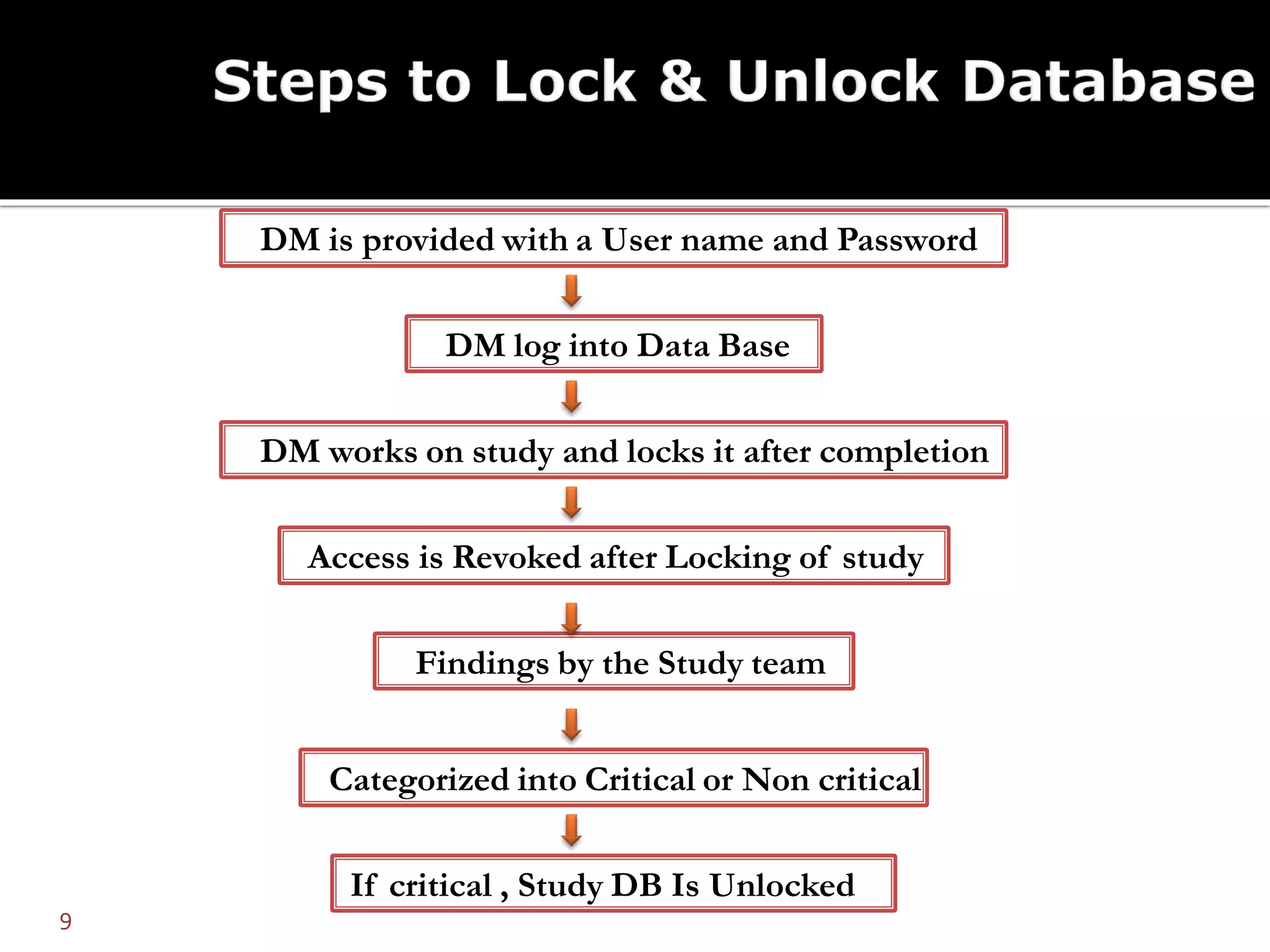
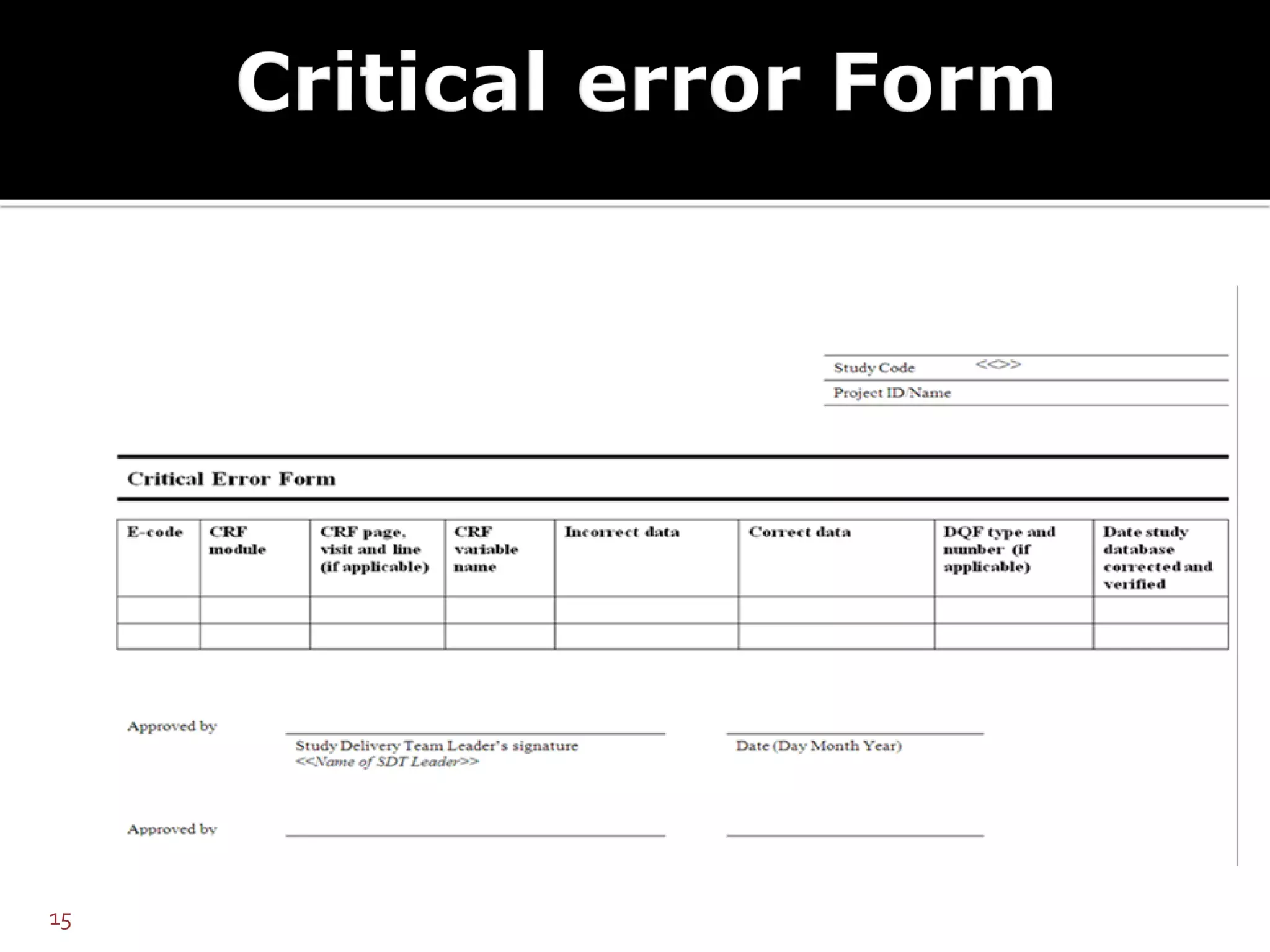
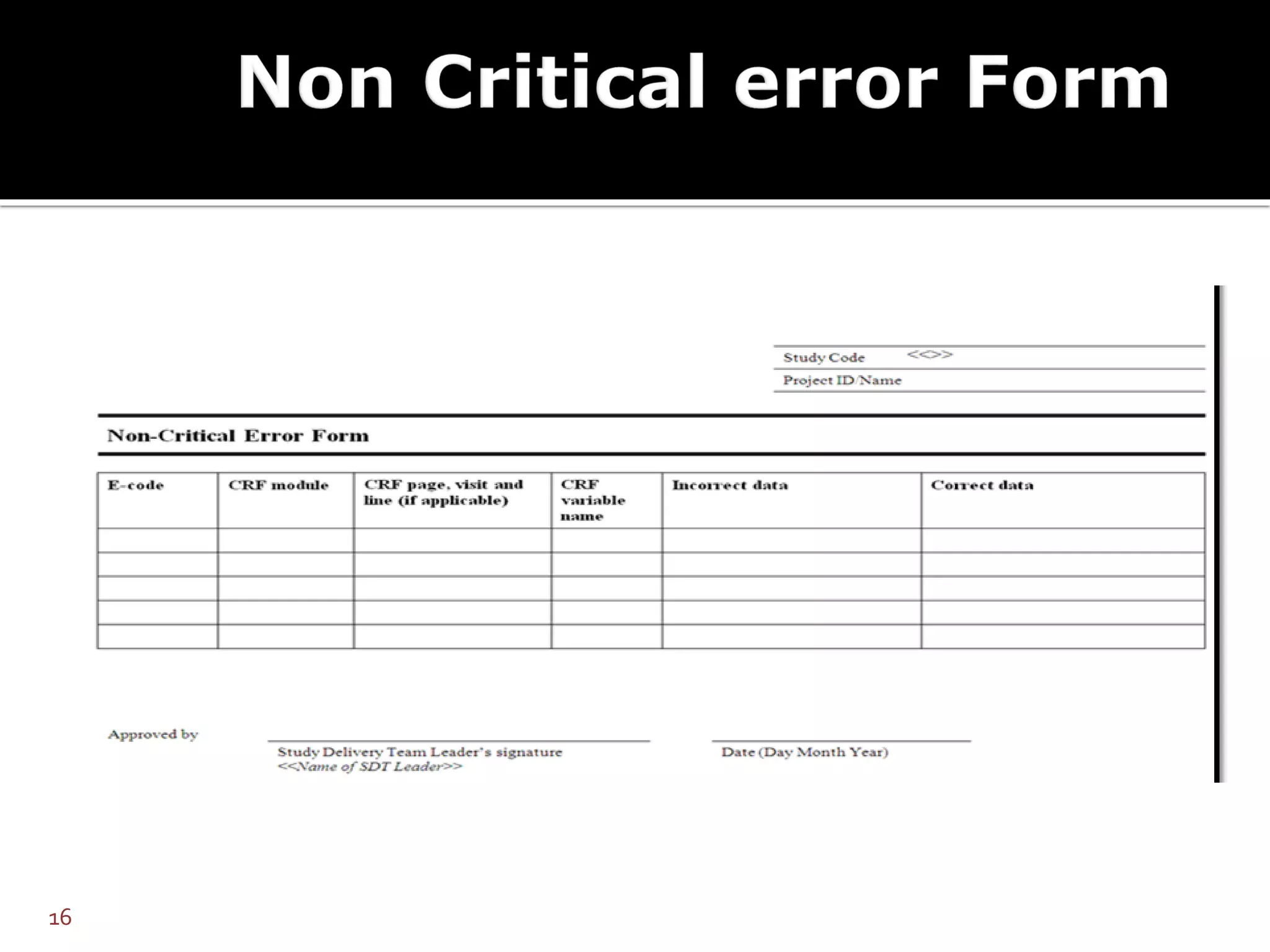
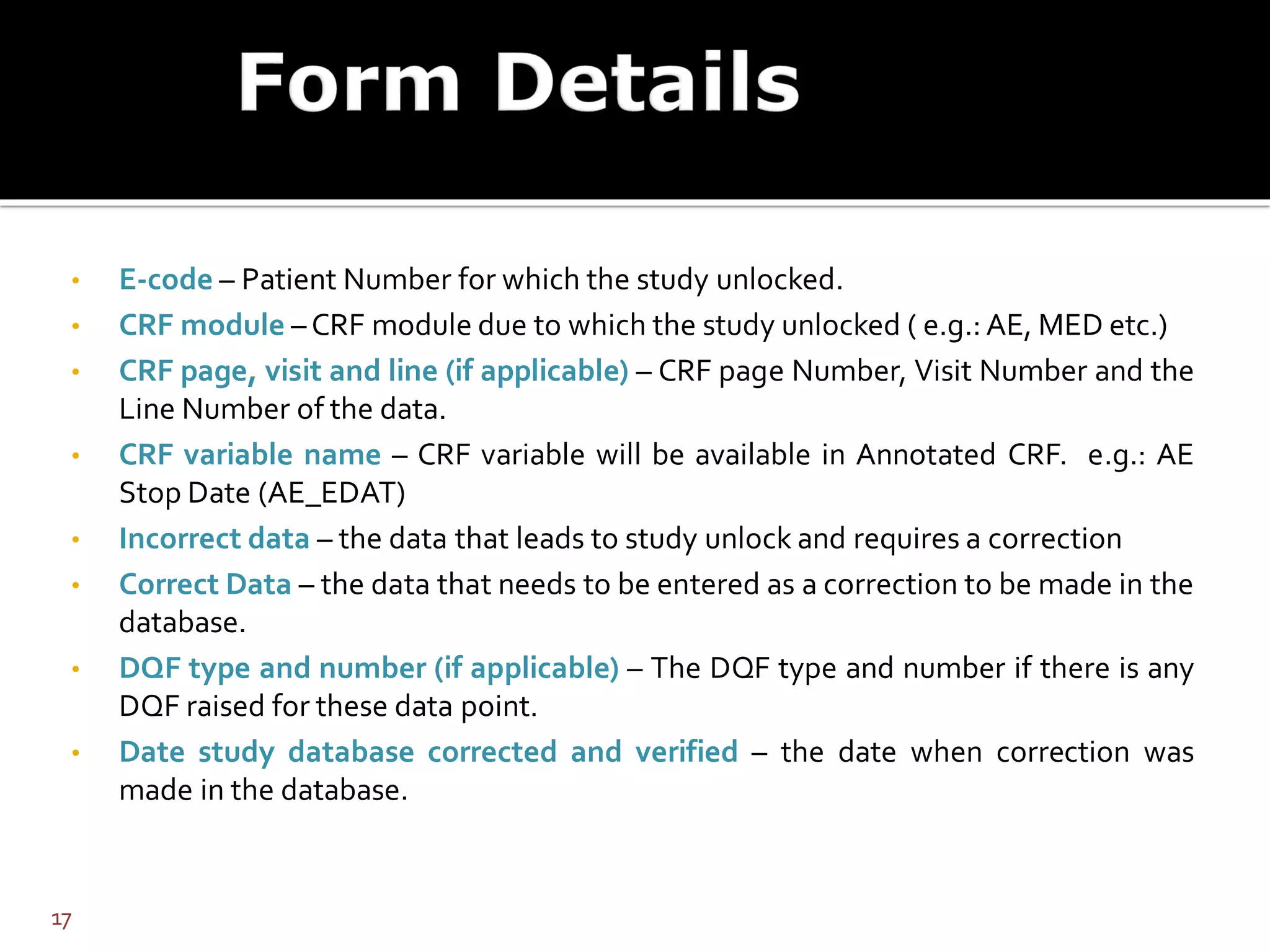
The document discusses database lock and unlock procedures. Database lock denotes completion of data collection and signals that no further changes can be made to trial data, making it ready for analysis. Database unlock allows for selective changes, usually to address critical errors found post-lock. Procedures should define how errors are categorized, handled, and documented. Unlocking requires approval and strict controls to prevent unauthorized changes.