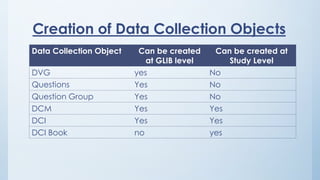
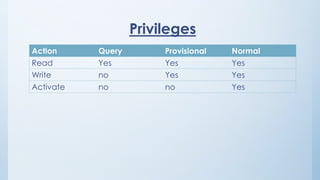
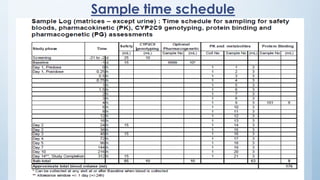
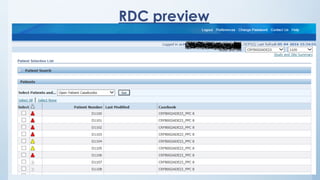
Teams involved in clinical trials include the clinical trials team, statistician team, study set up team, and data management team. These teams perform various functions like conducting trials, generating reports for regulatory authorities, developing electronic case report forms, and managing data and discrepancies.
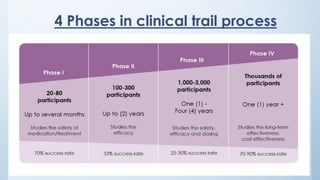
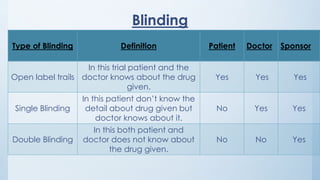
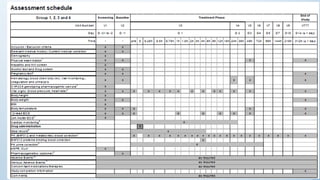
There are typically four phases in a clinical trial process: planning, implementation, analysis, and reporting. Clinical trials can be open label, single blinded, or double blinded depending on whether the patient and/or doctors are aware of the treatment given.