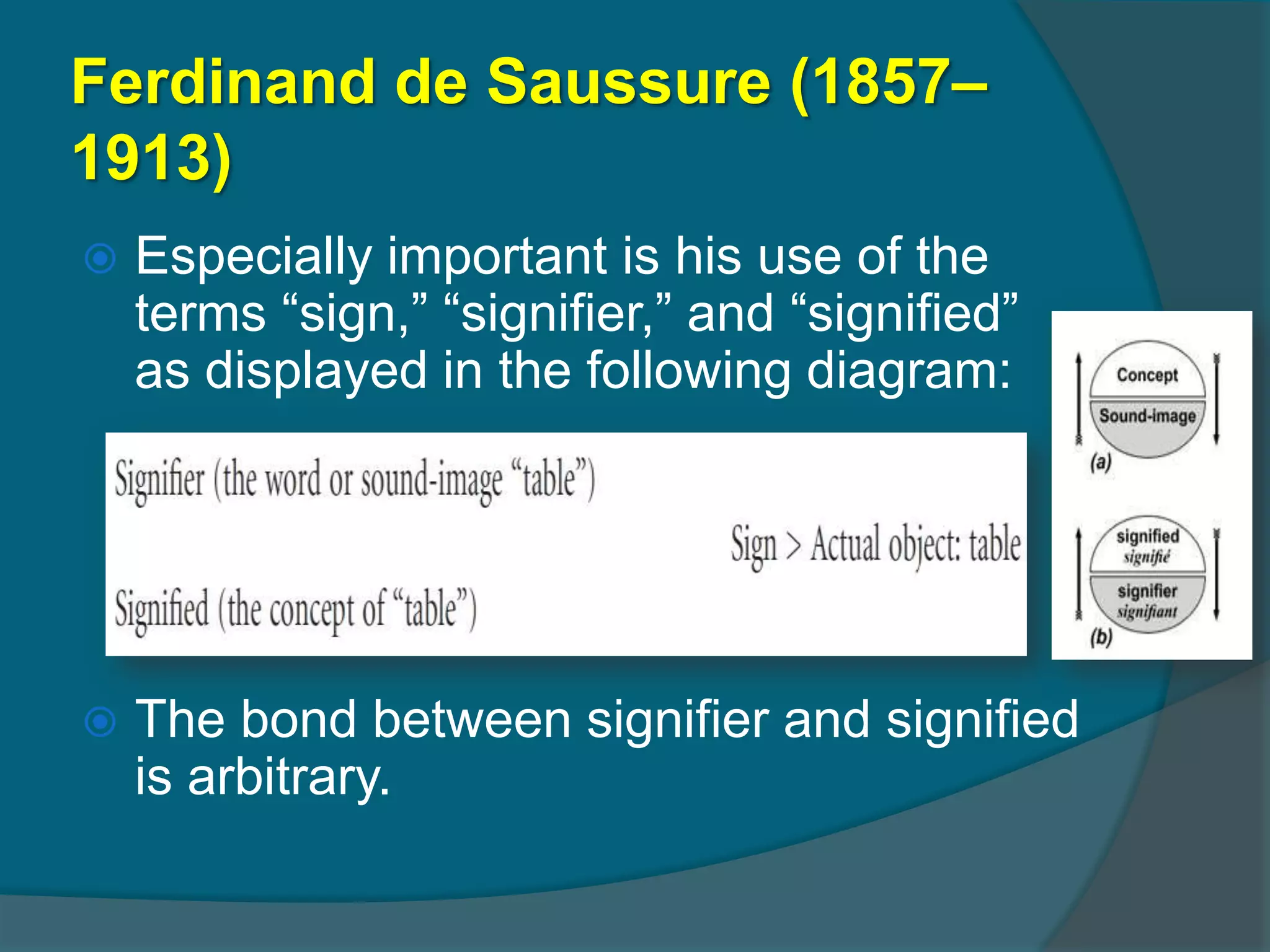
Structuralism seeks to identify the underlying systems and conventions of literature. Key figures include Ferdinand de Saussure and Roland Barthes. Saussure viewed language as a social institution and structure that could be studied synchronically. He introduced concepts like the sign, signifier, and signified. Barthes extended structural analysis and semiotics to broader cultural phenomena, helping transition structuralism to post-structuralism.