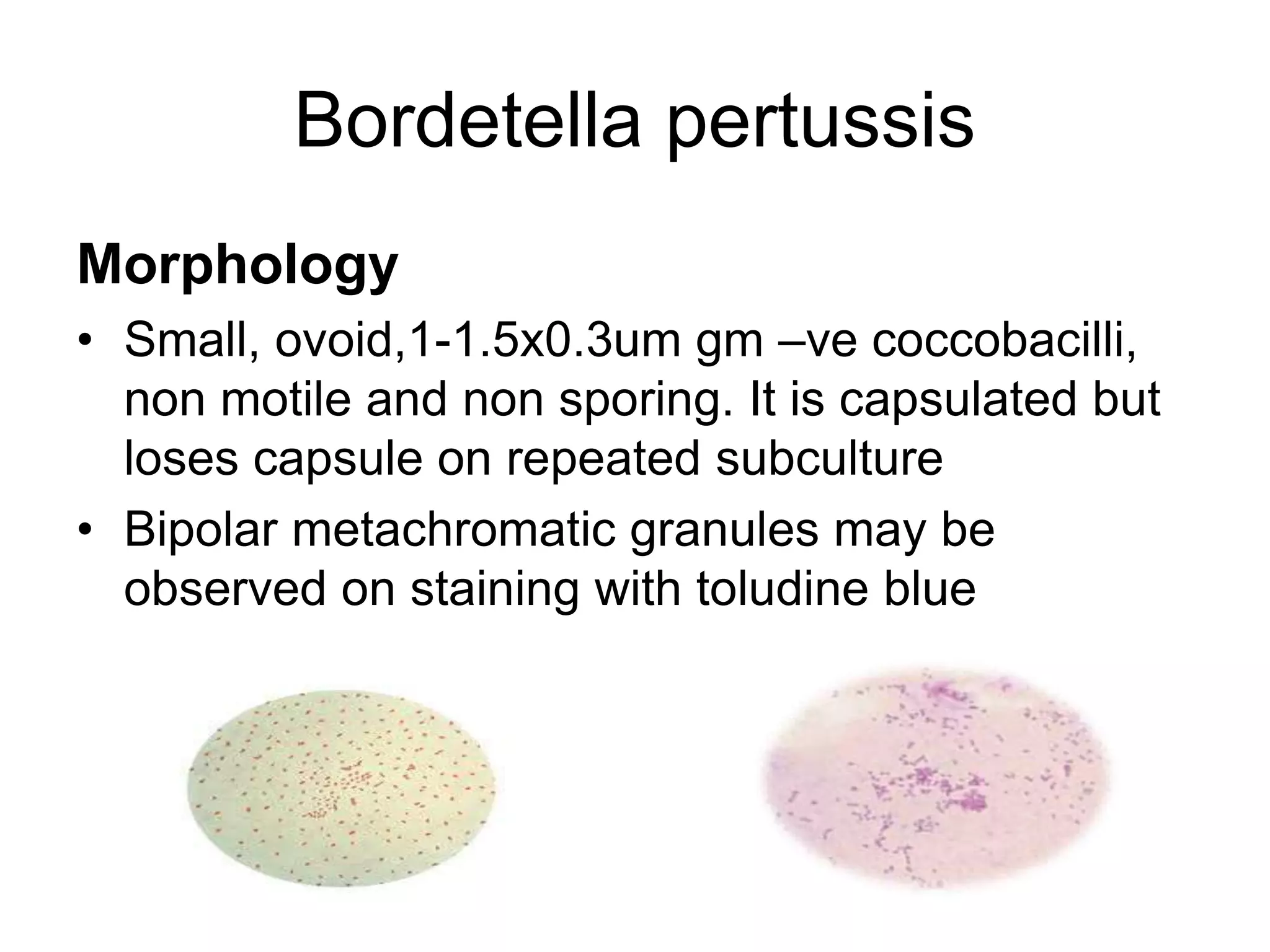
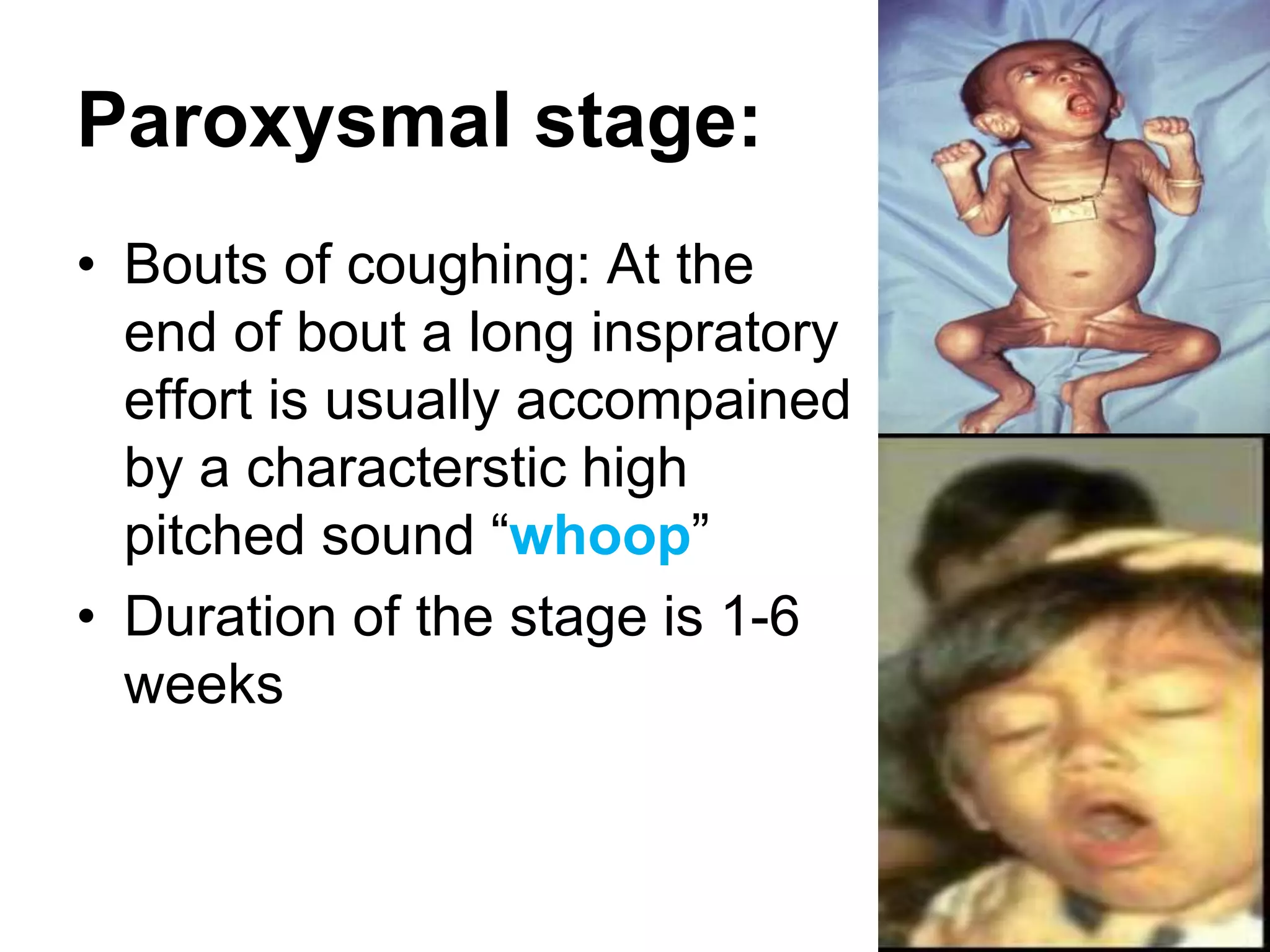
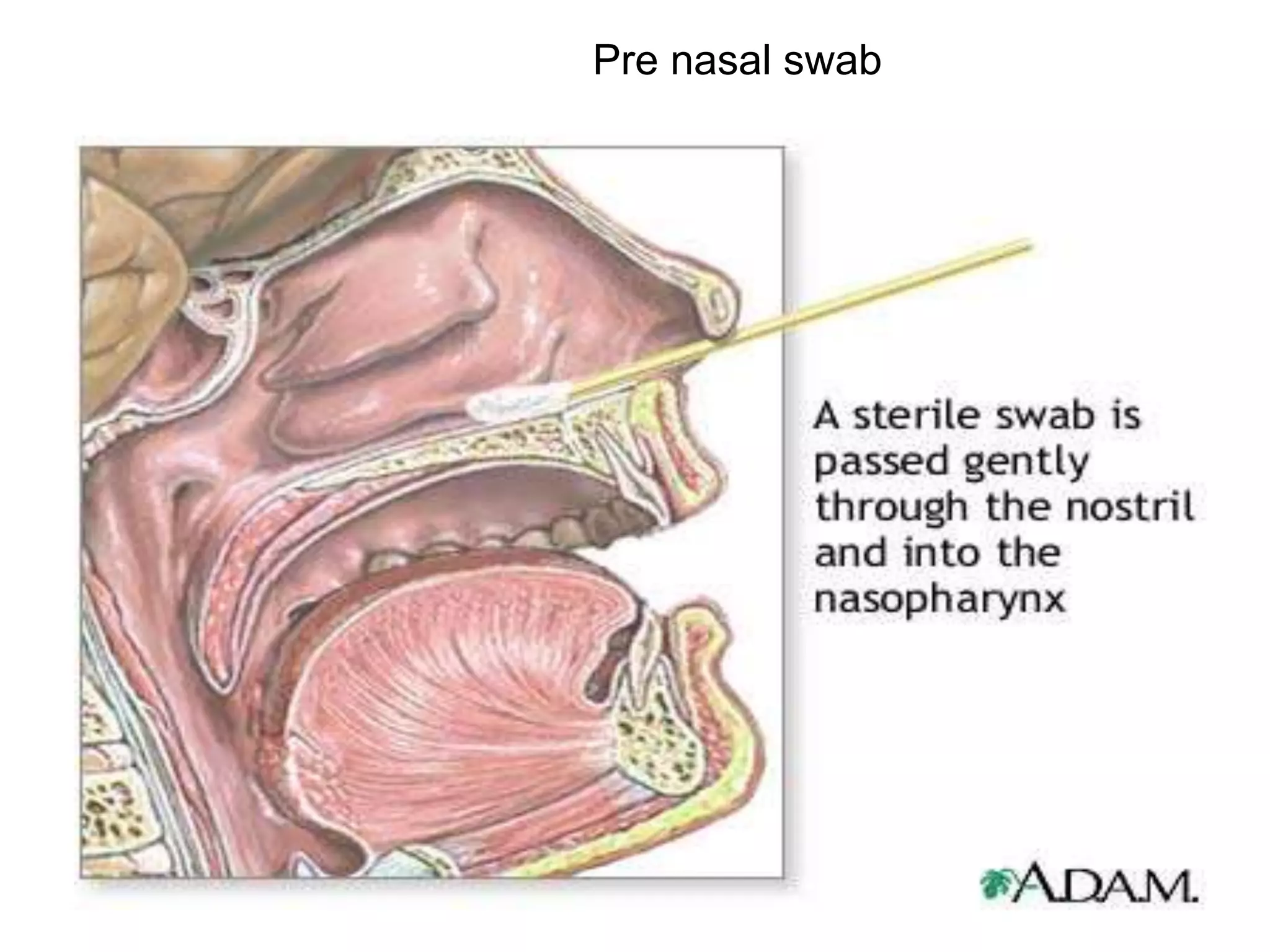
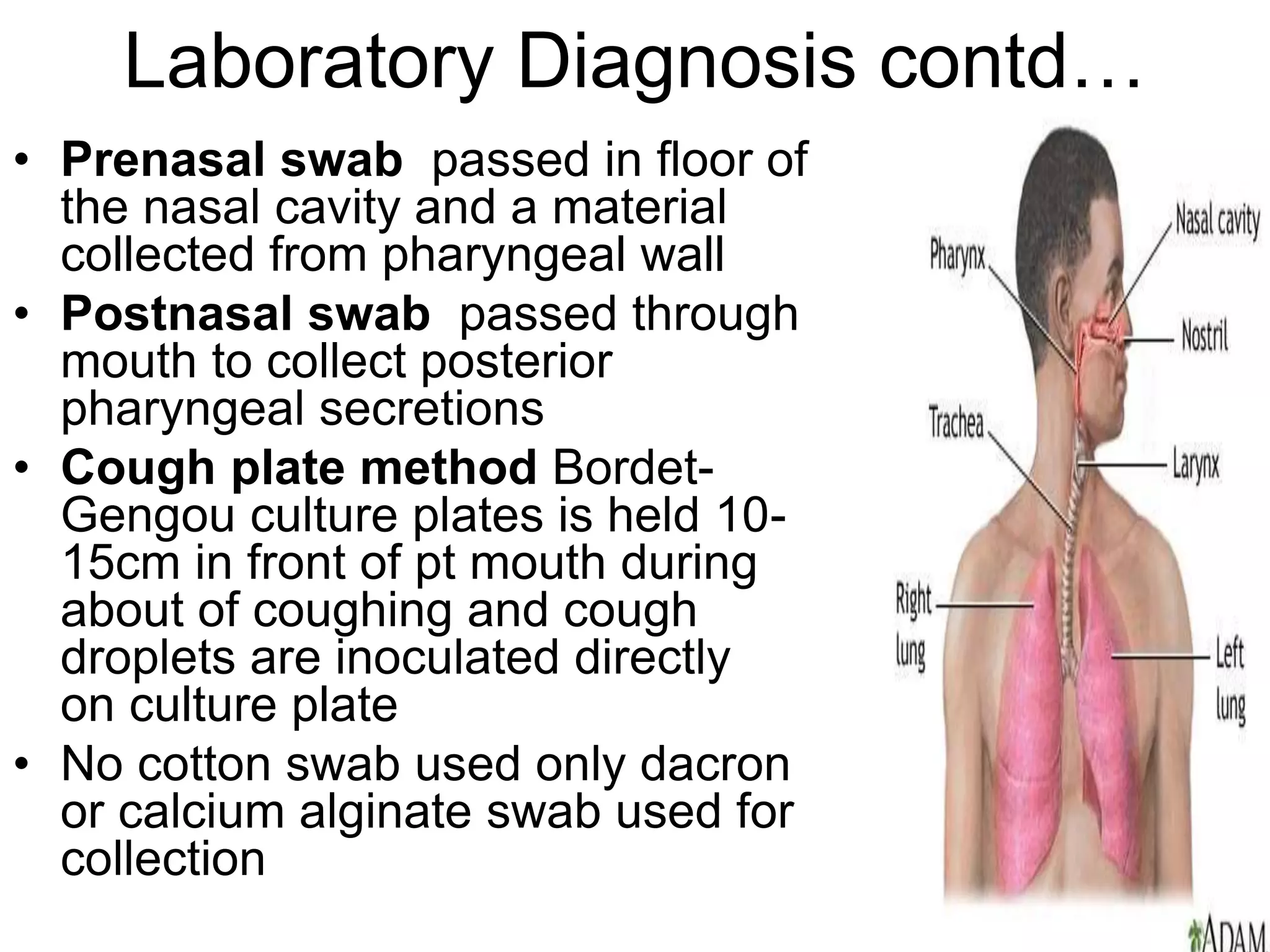
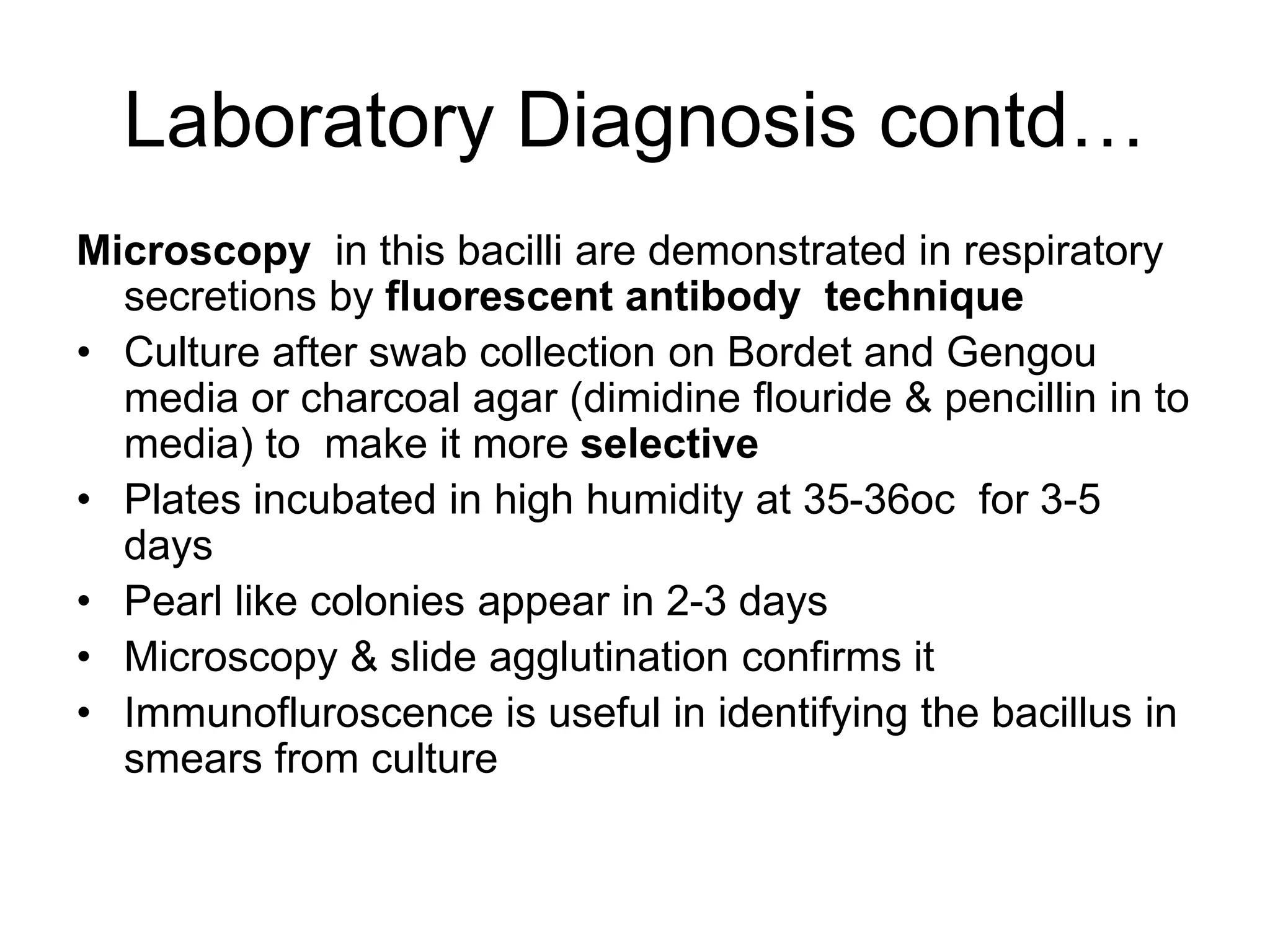
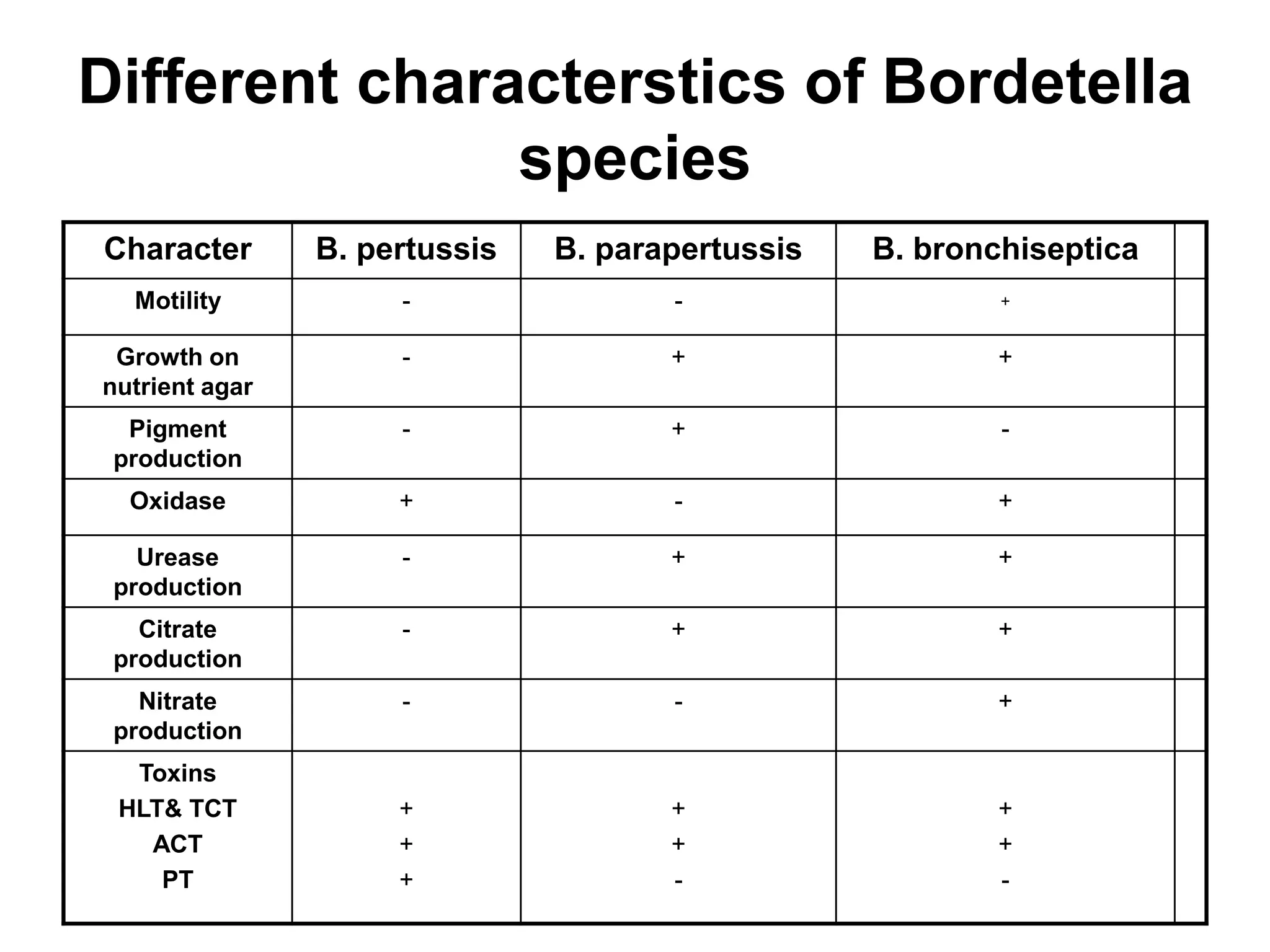
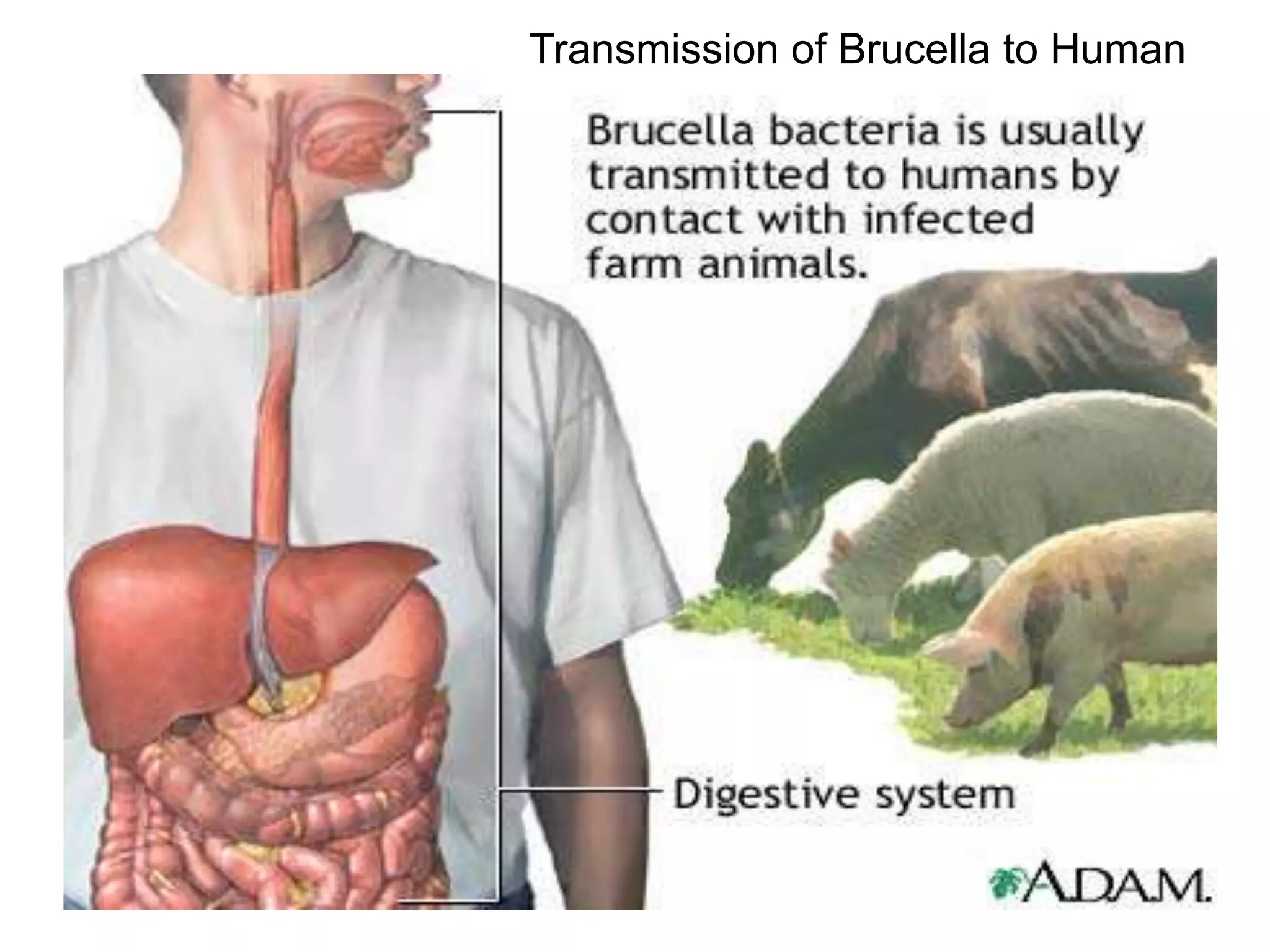
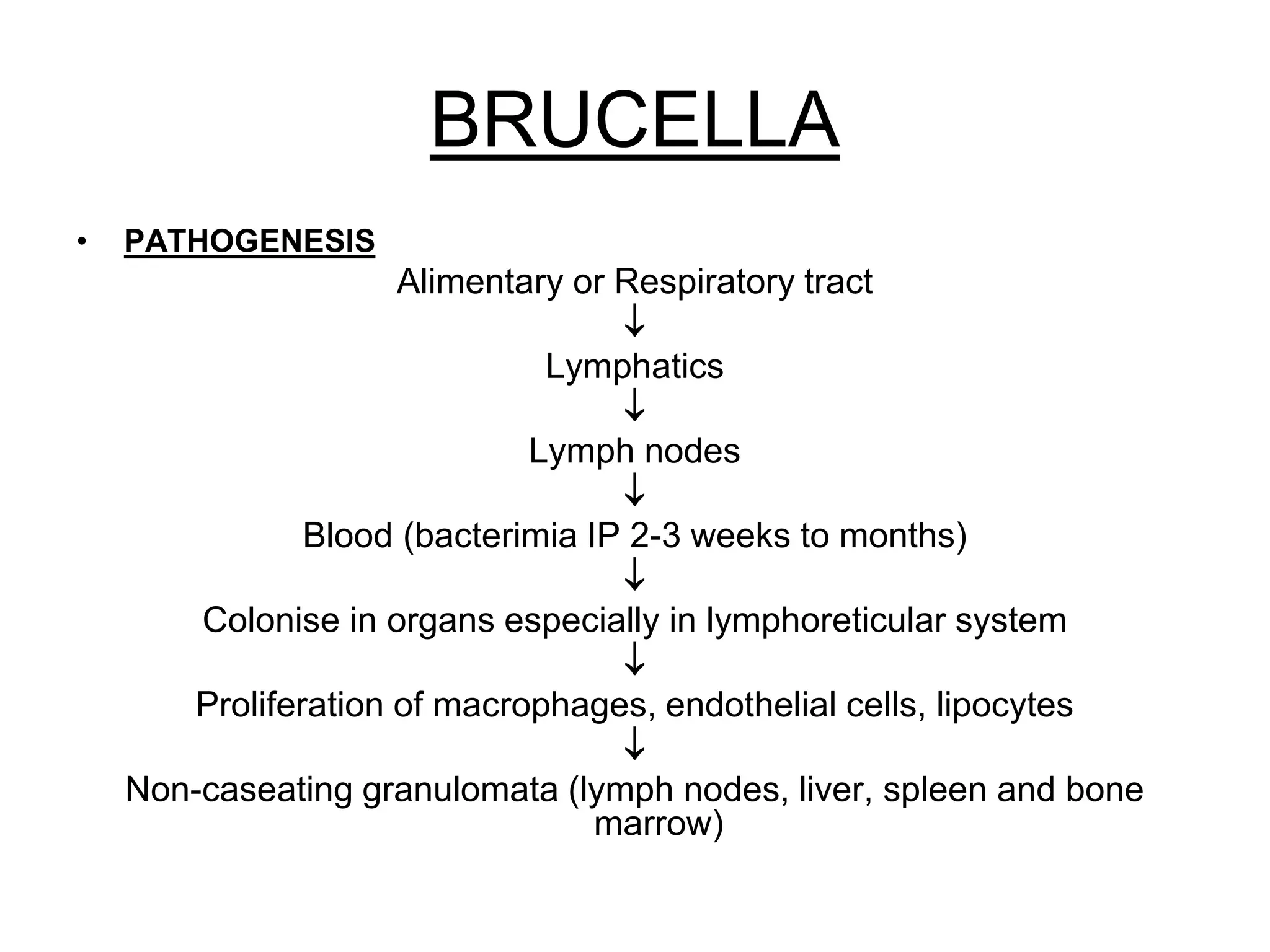
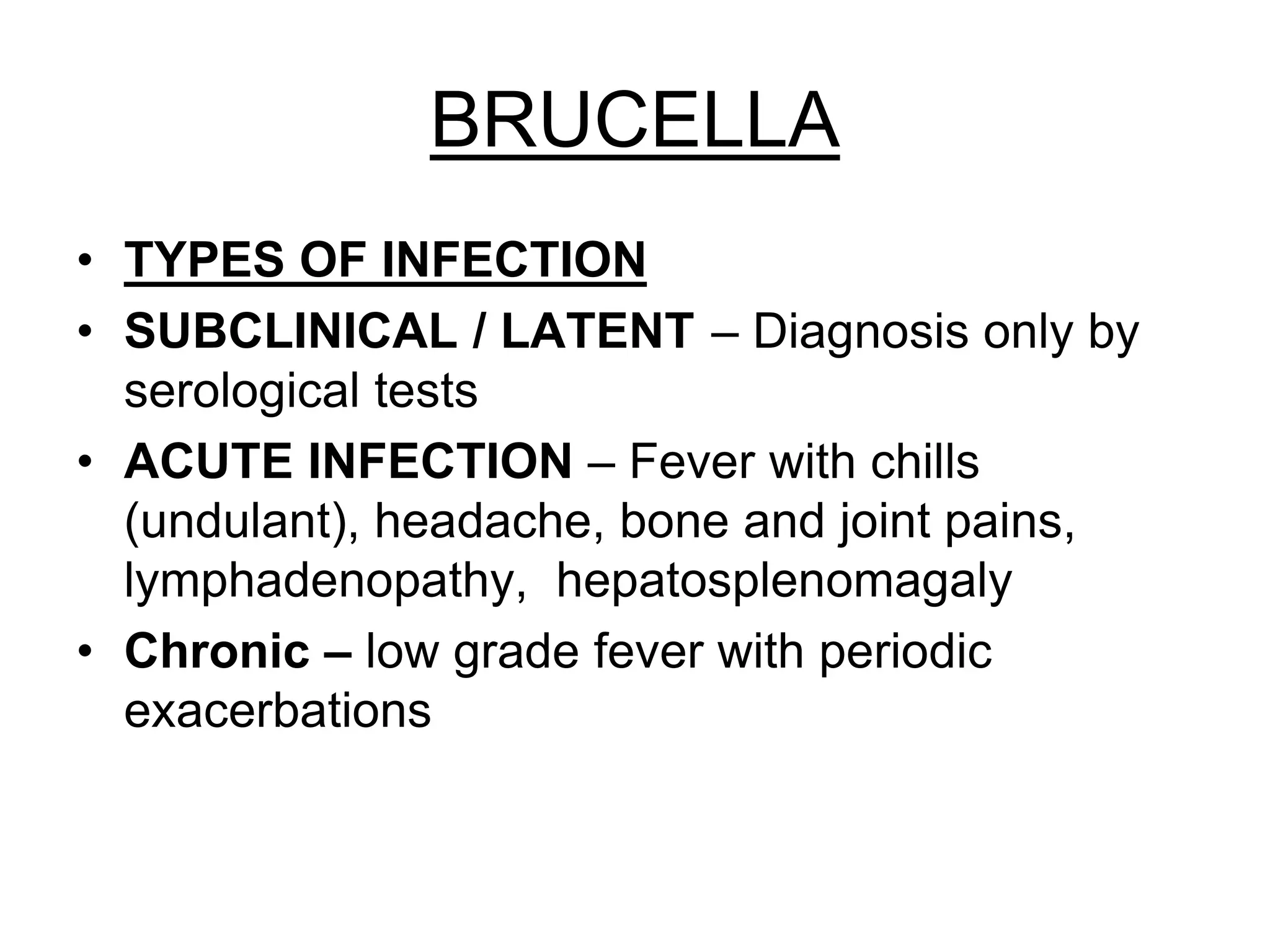
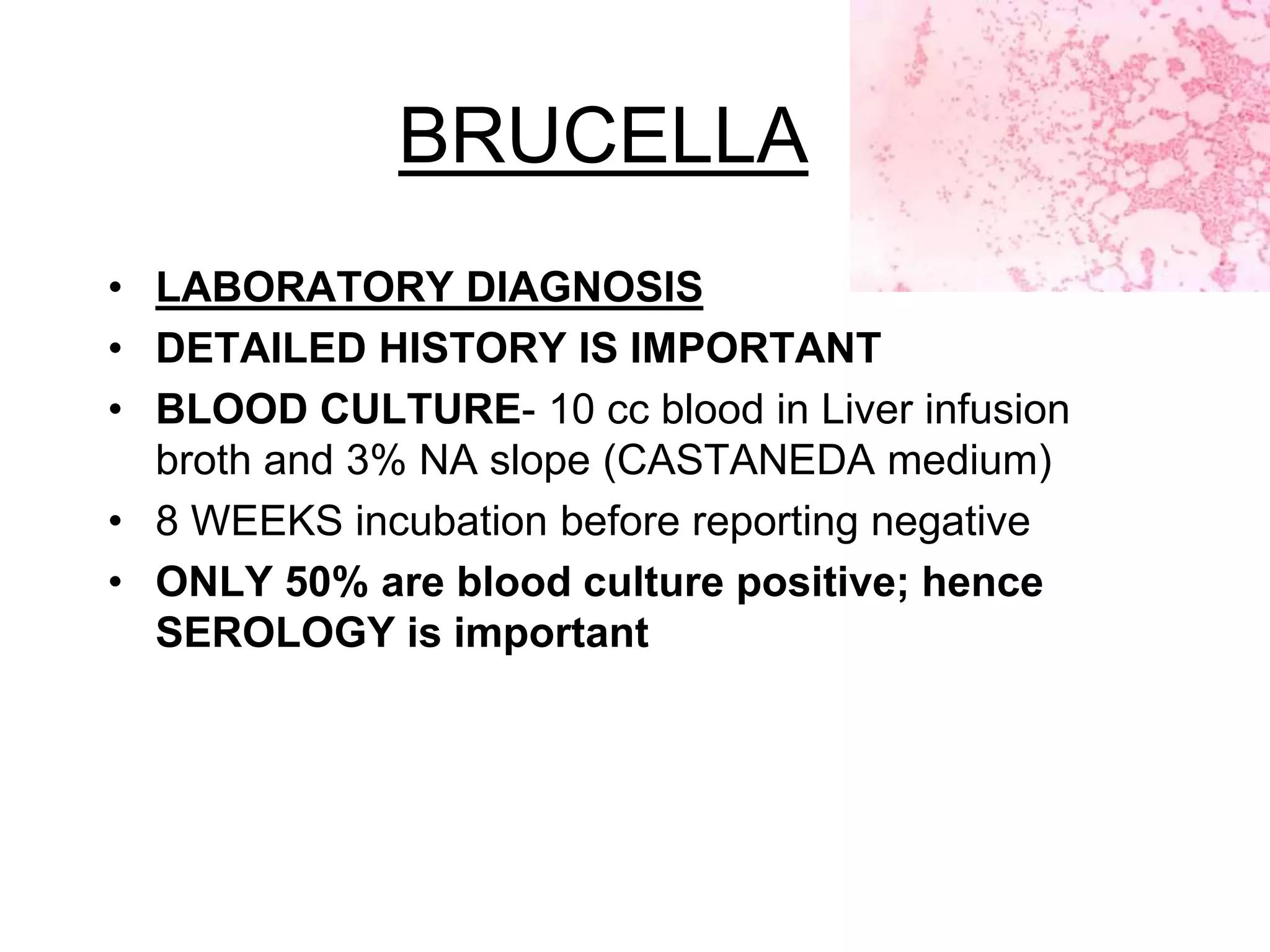
The document outlines the history and characteristics of Bordetella, including its pathogenic species such as Bordetella pertussis, which causes whooping cough, and the diagnostics and treatments for infections. It details the laboratory identification methods and the epidemiology of brucellosis, a zoonotic disease caused by Brucella species, including transmission routes and clinical manifestations. Treatment protocols and preventive measures against both Bordetella and Brucella infections are discussed in depth.