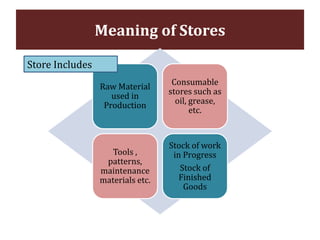
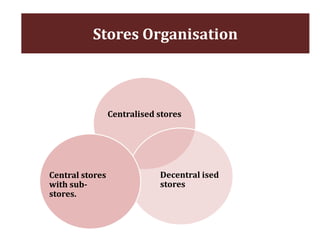
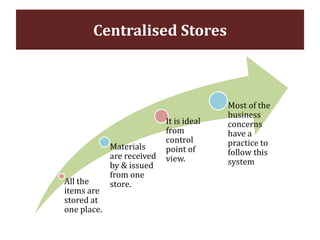
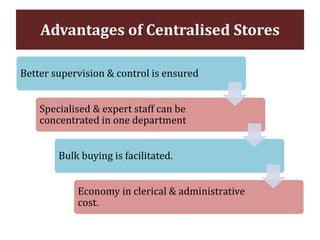
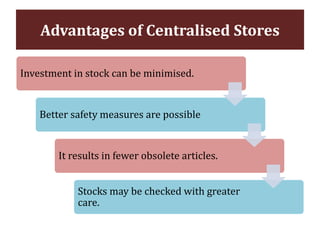
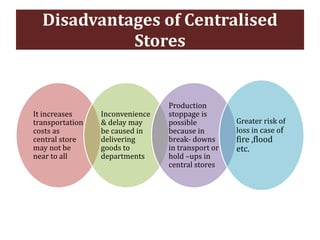
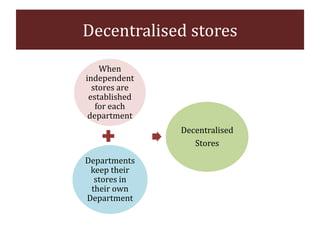
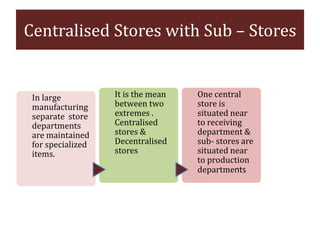
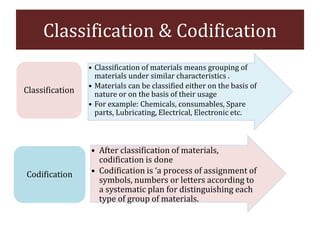
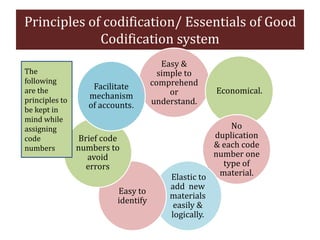
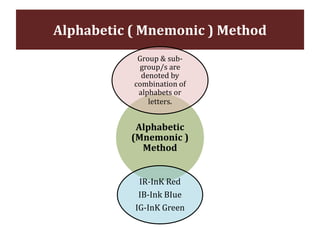
The document discusses stores organization and management. It describes different types of store systems like centralized stores, decentralized stores, and centralized stores with sub-stores. It highlights the advantages and disadvantages of each system. It also covers store classification, codification, stores ledger, and advantages of maintaining a stores ledger. Maintaining proper store records through classification, codification, and a stores ledger allows for better control, supervision and stock management.