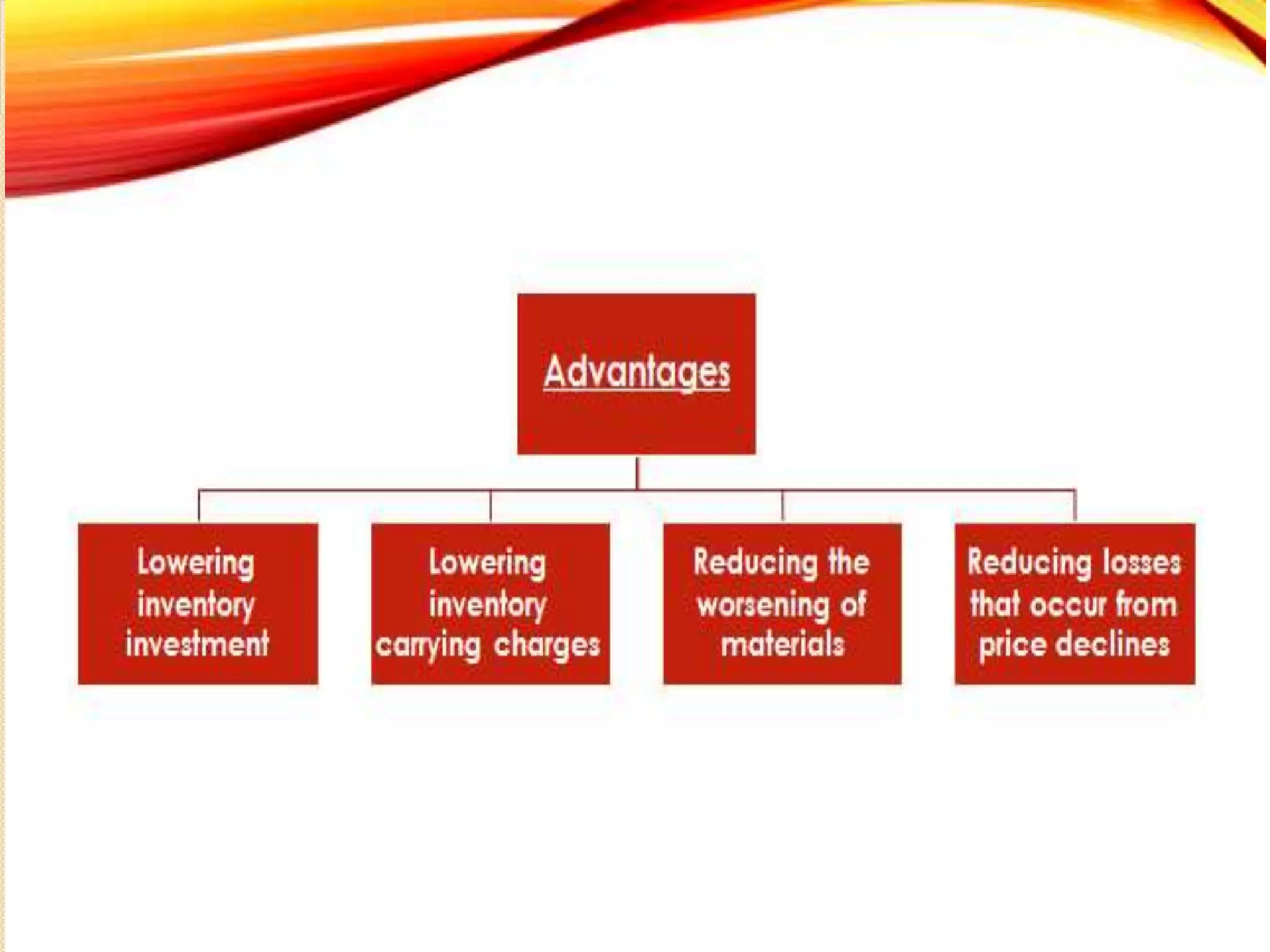
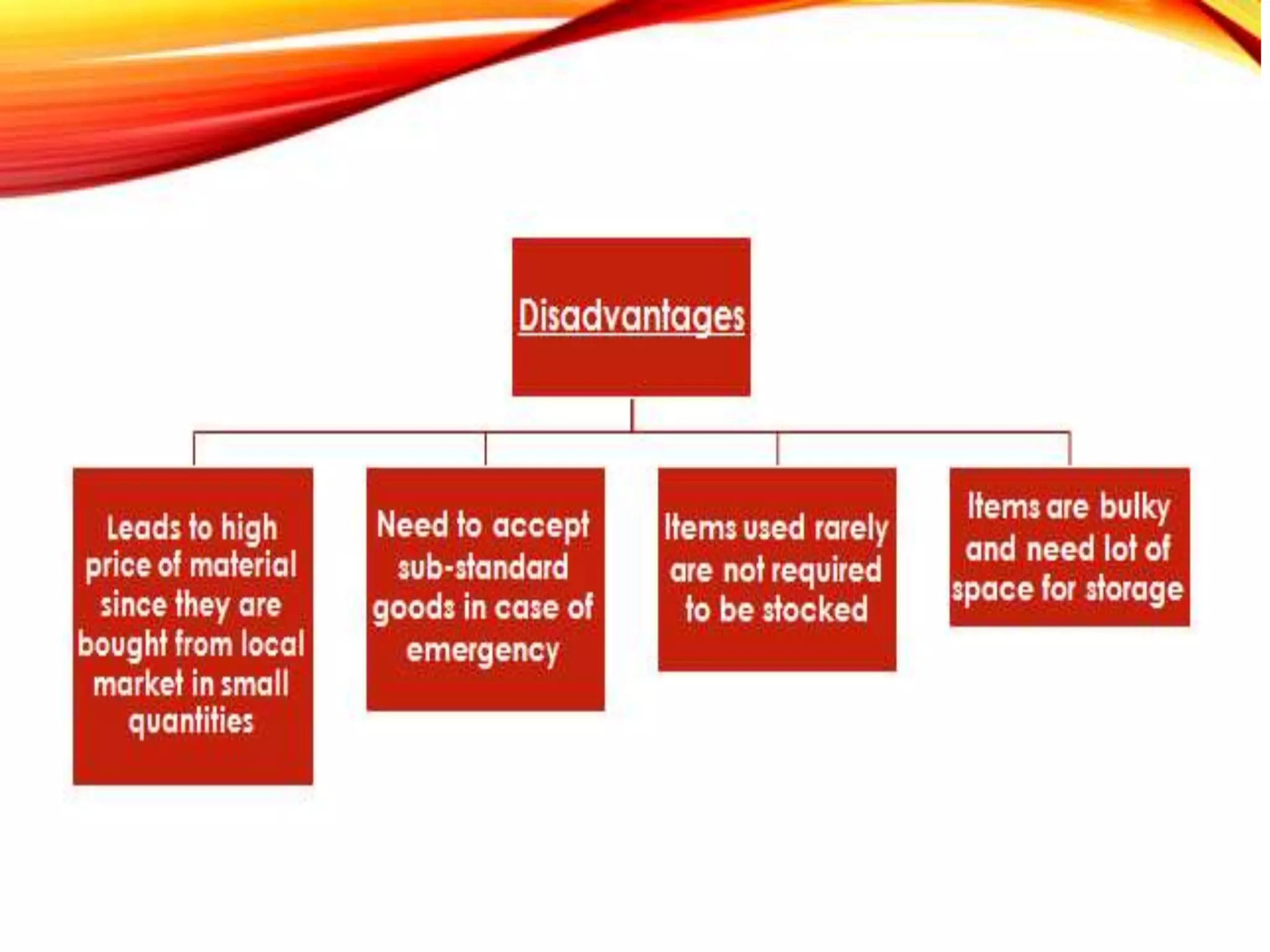
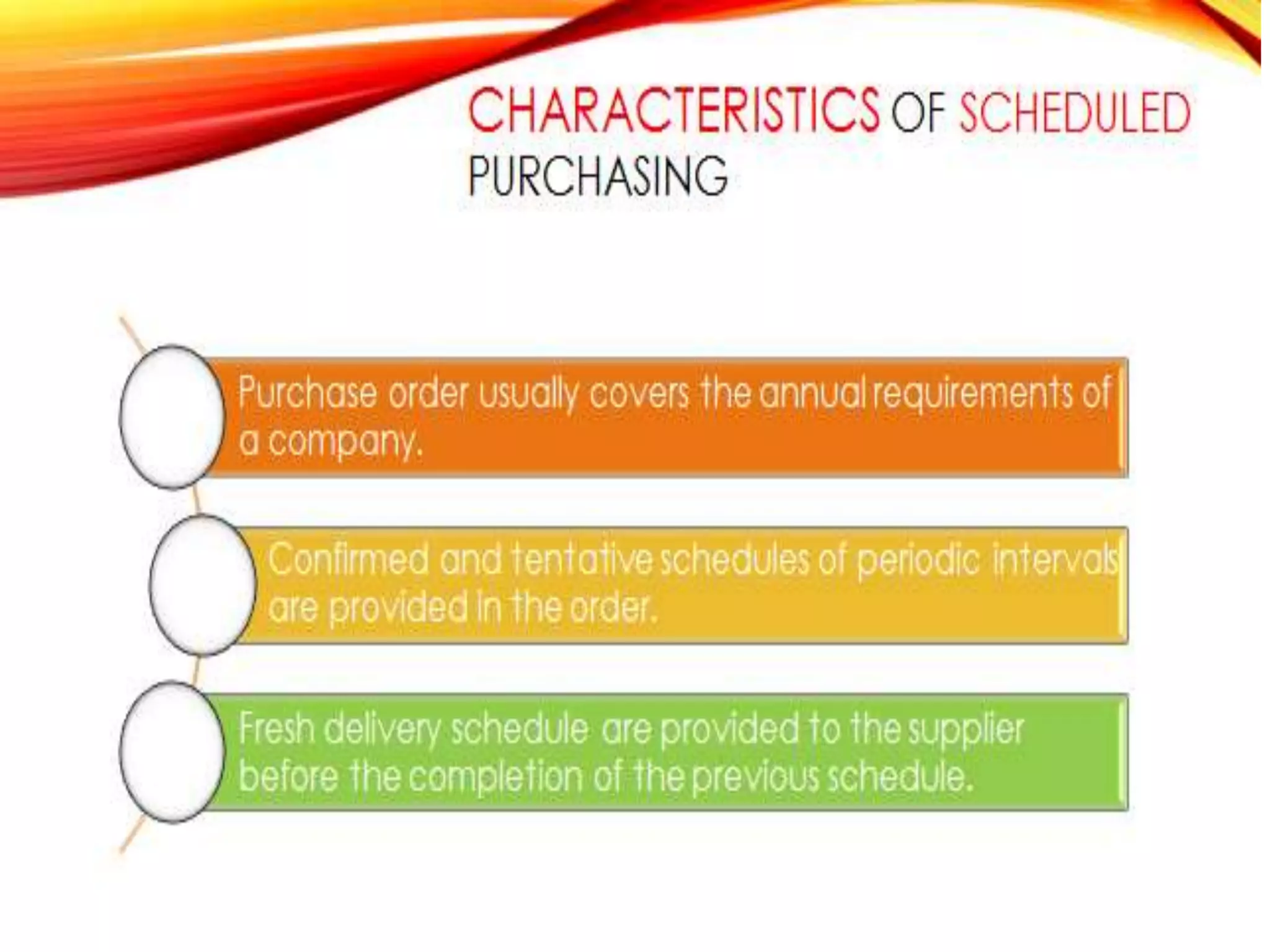
The document discusses purchase management and the purchasing process. It describes the key objectives of purchasing as ensuring the right materials are purchased at the right price, from the right suppliers, at the right time, and delivered to the right place. The main responsibilities of the purchasing department are learning material needs, supplier selection, price negotiation, quality monitoring, and ensuring delivery. The purchasing cycle begins with a purchase requisition and proceeds through supplier selection, purchase order placement, delivery, and payment. Methods for value analysis to reduce costs are also outlined.