This document discusses various aspects of managing medical stores and warehouses, including objectives, activities, design principles, systems, classification, storage, and handling of materials. The key points are:
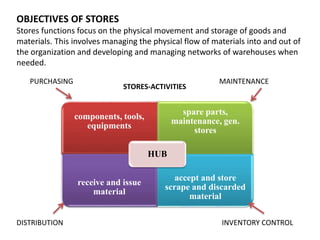
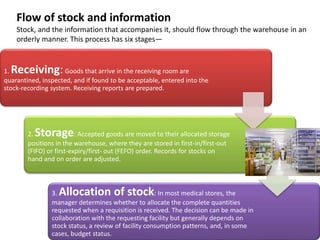
1. The objectives of medical stores are to receive, store, and distribute materials to meet user demands while minimizing waste through proper inventory control and storage methods.
2. Effective materials management involves planning, purchasing, receiving, inventory control, standardization, and disposal. Computerized stock records and communications between facilities are important.
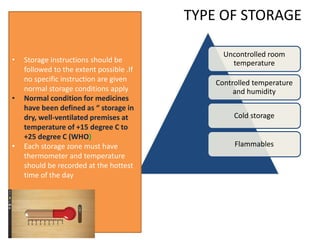
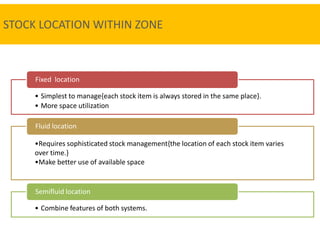
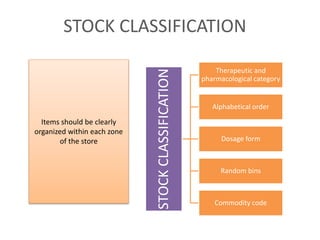
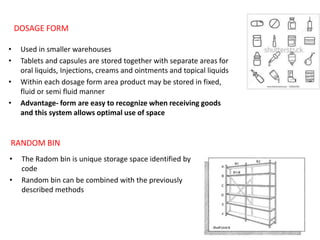
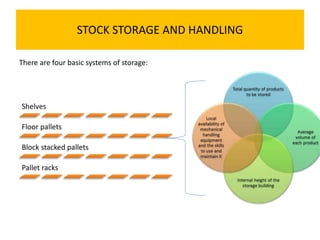
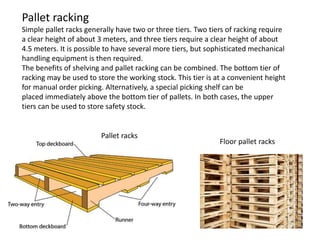
3. Proper warehouse design considers product movement, handling technology, storage plans, and future expansion. Classification systems and fixed, fluid, or semi-fluid location methods determine how items are organized within zones and