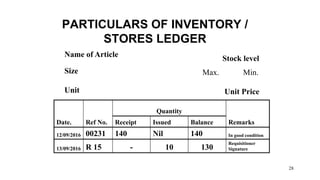
This document discusses procurement and inventory management. It defines key terms like procurement, supply, custody, accounting, and disposal. It also covers types of inventory like consumable and non-consumable, classification based on intended use, and functions of inventory management including receipt, storage, retrieval, issuing, records keeping, and control. Inventory is accounted for by recording stock movements and balances. Different inventory costs like purchase, ordering, holding and shortage costs are also outlined.