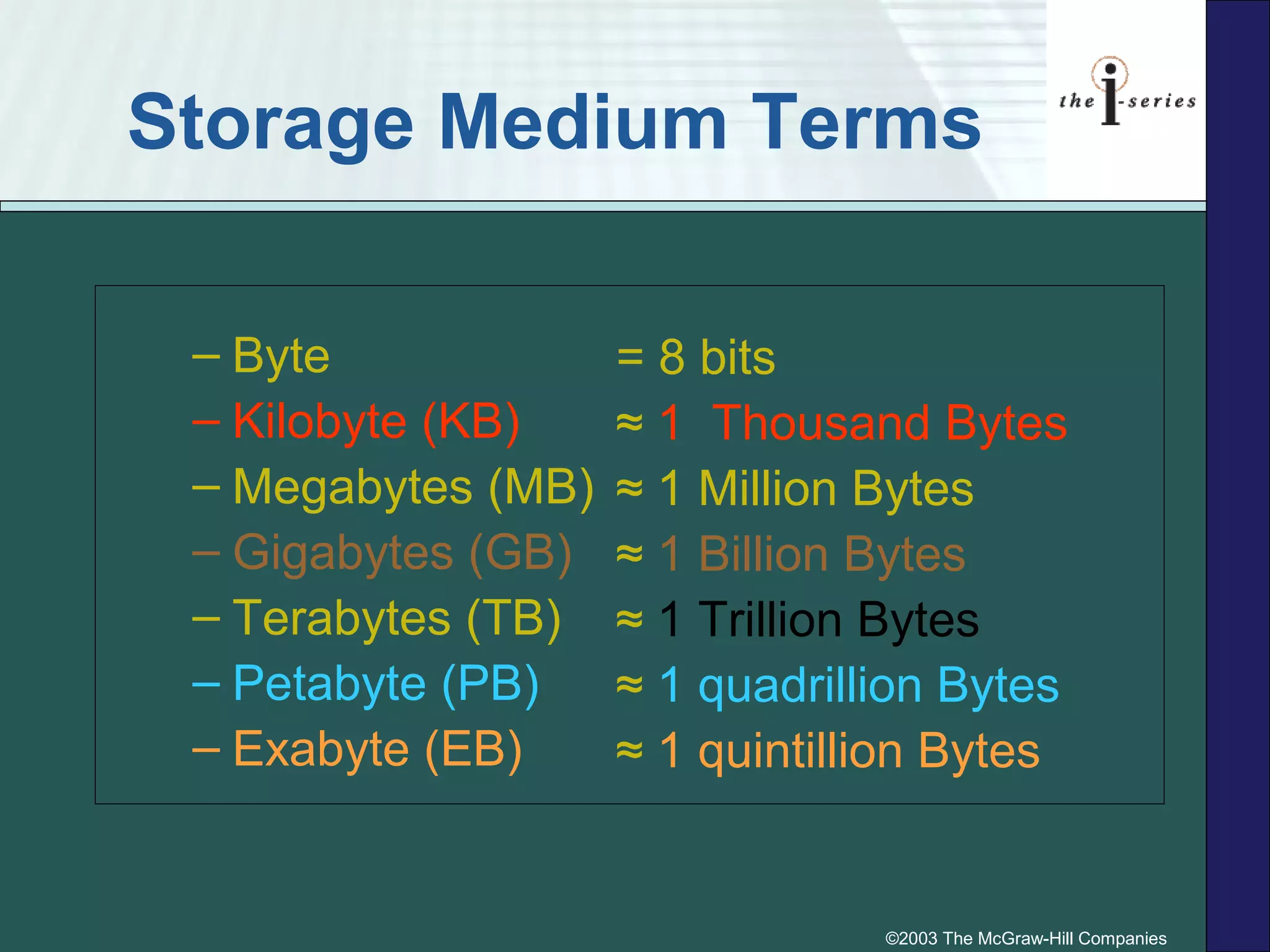
This document discusses different types of storage devices. It describes three major technologies for computer storage: magnetic, optical, and flash memory. Magnetic storage includes internal and external hard disks, which use magnetic platters and read/write heads. Optical storage uses CDs and DVDs in read-only, write-once, or read-write formats. Flash memory storage includes cards like CompactFlash, SD cards, and USB flash drives.