Embed presentation
Downloaded 634 times

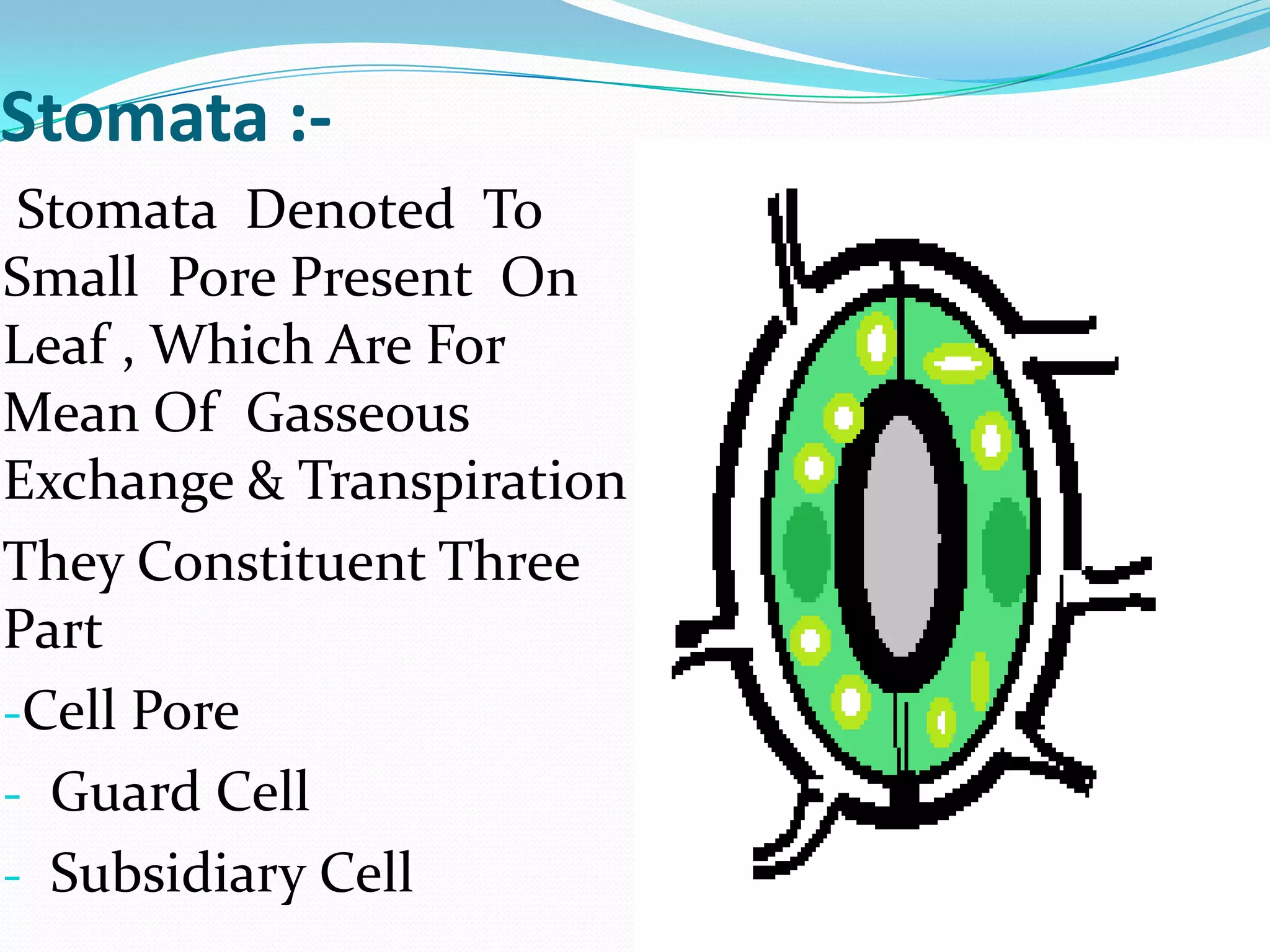

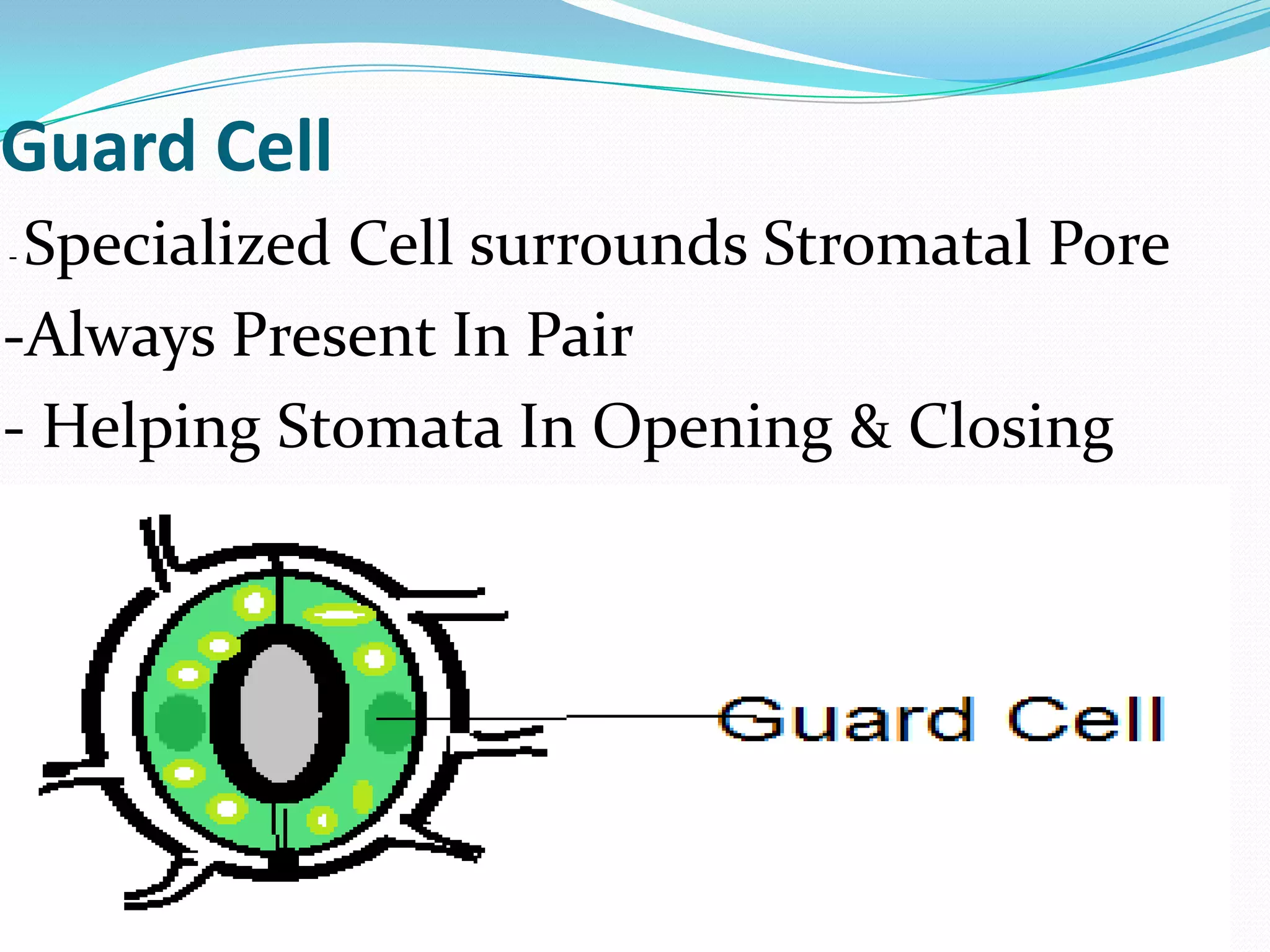
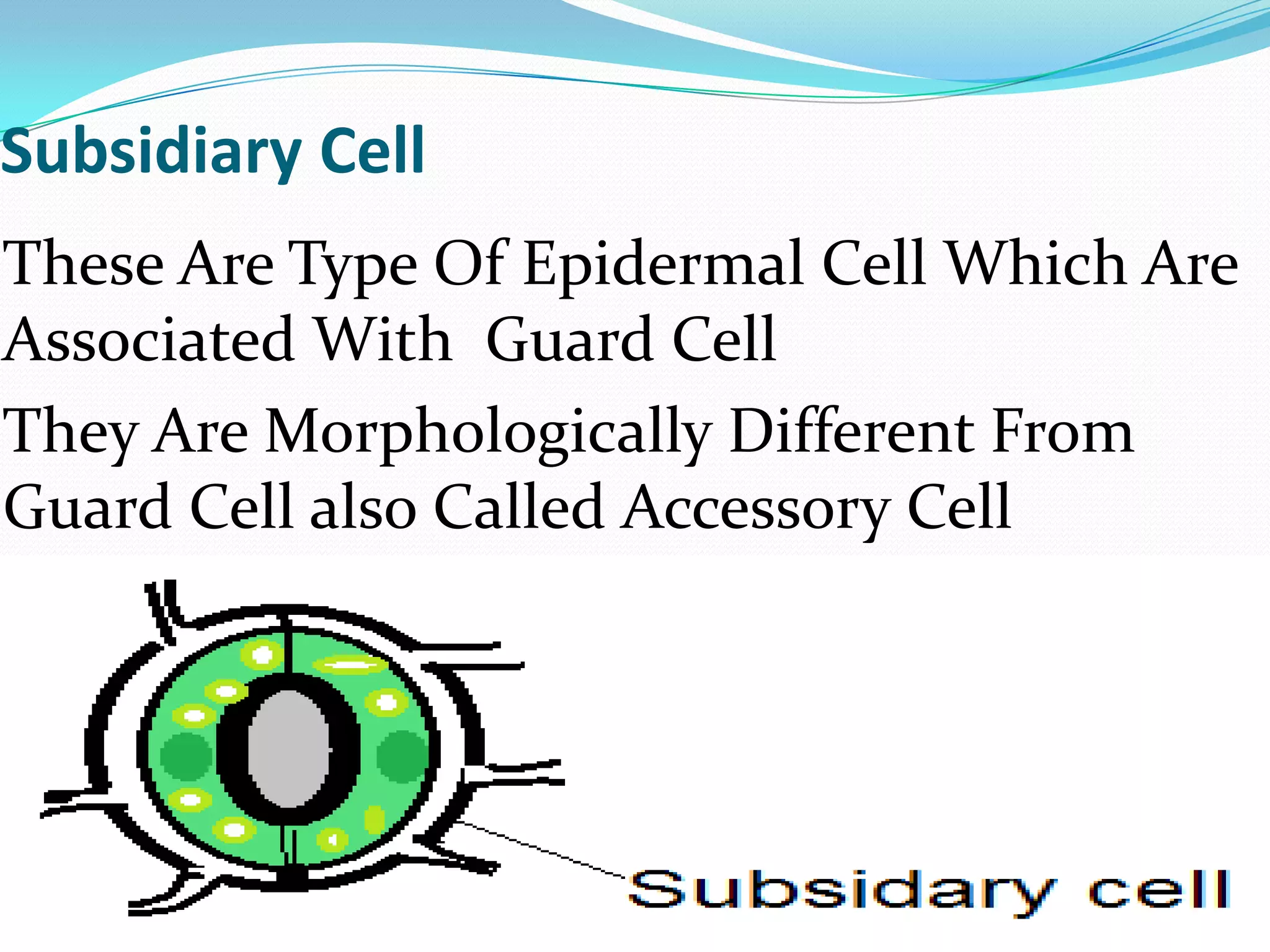
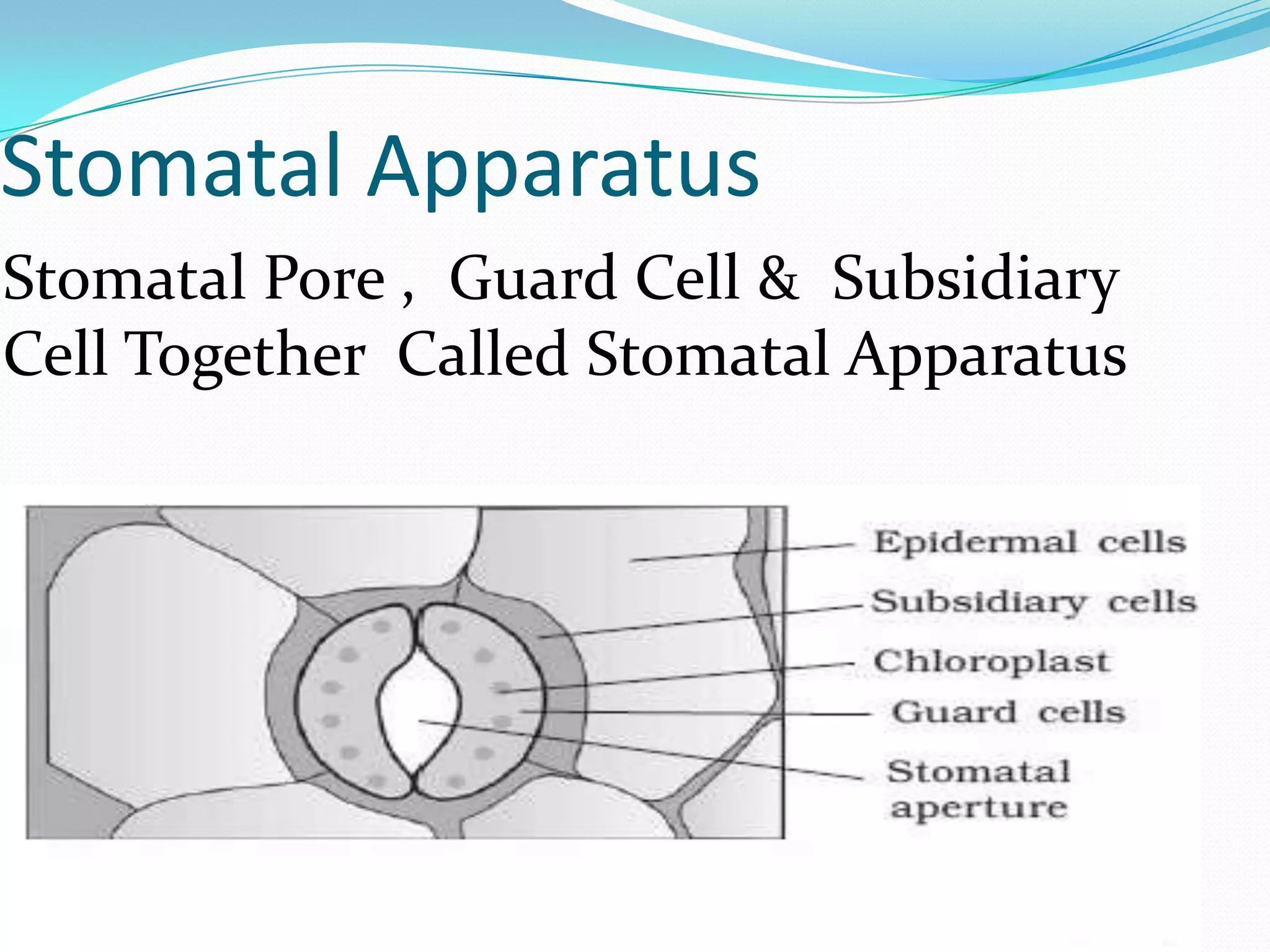
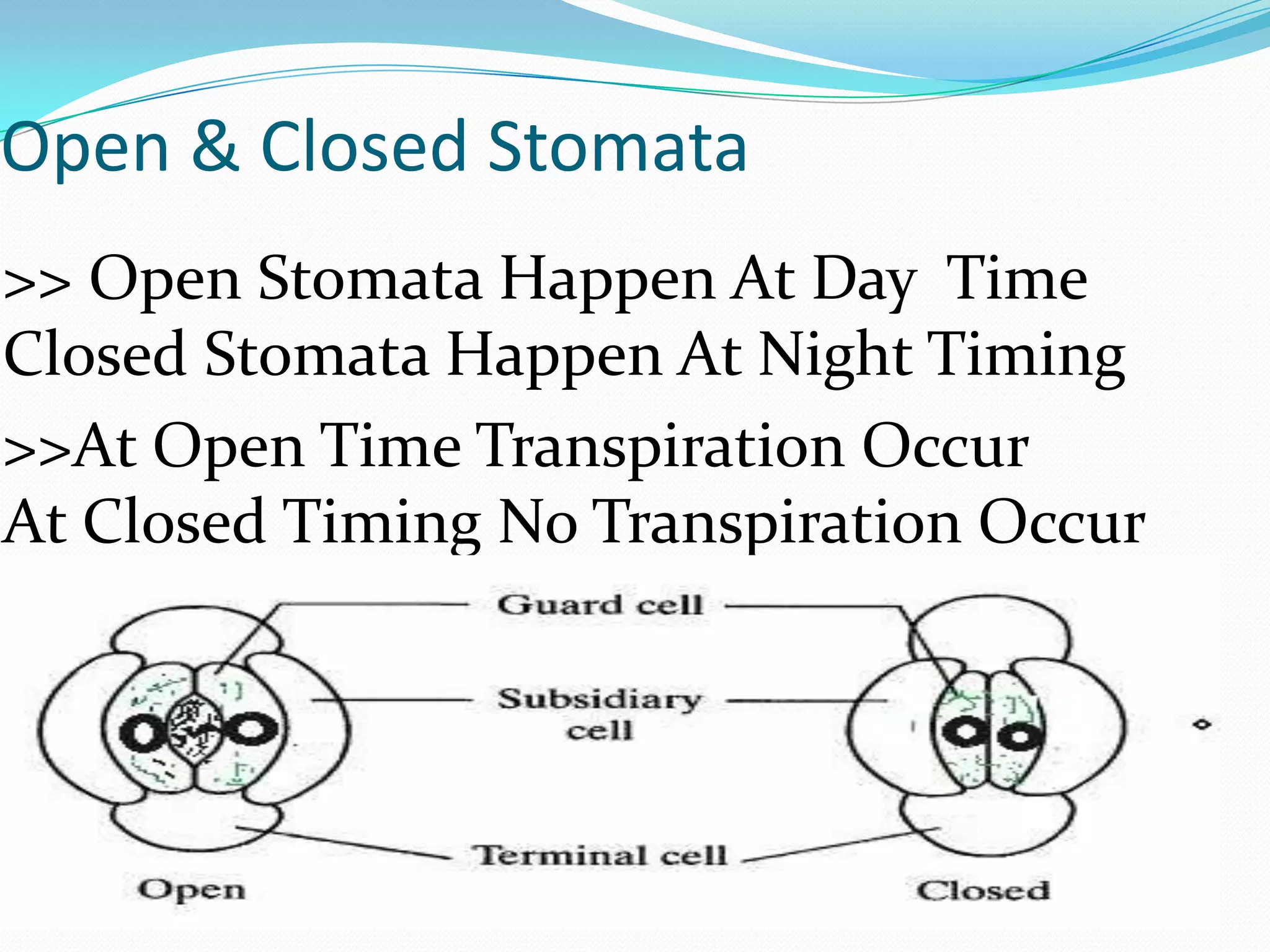
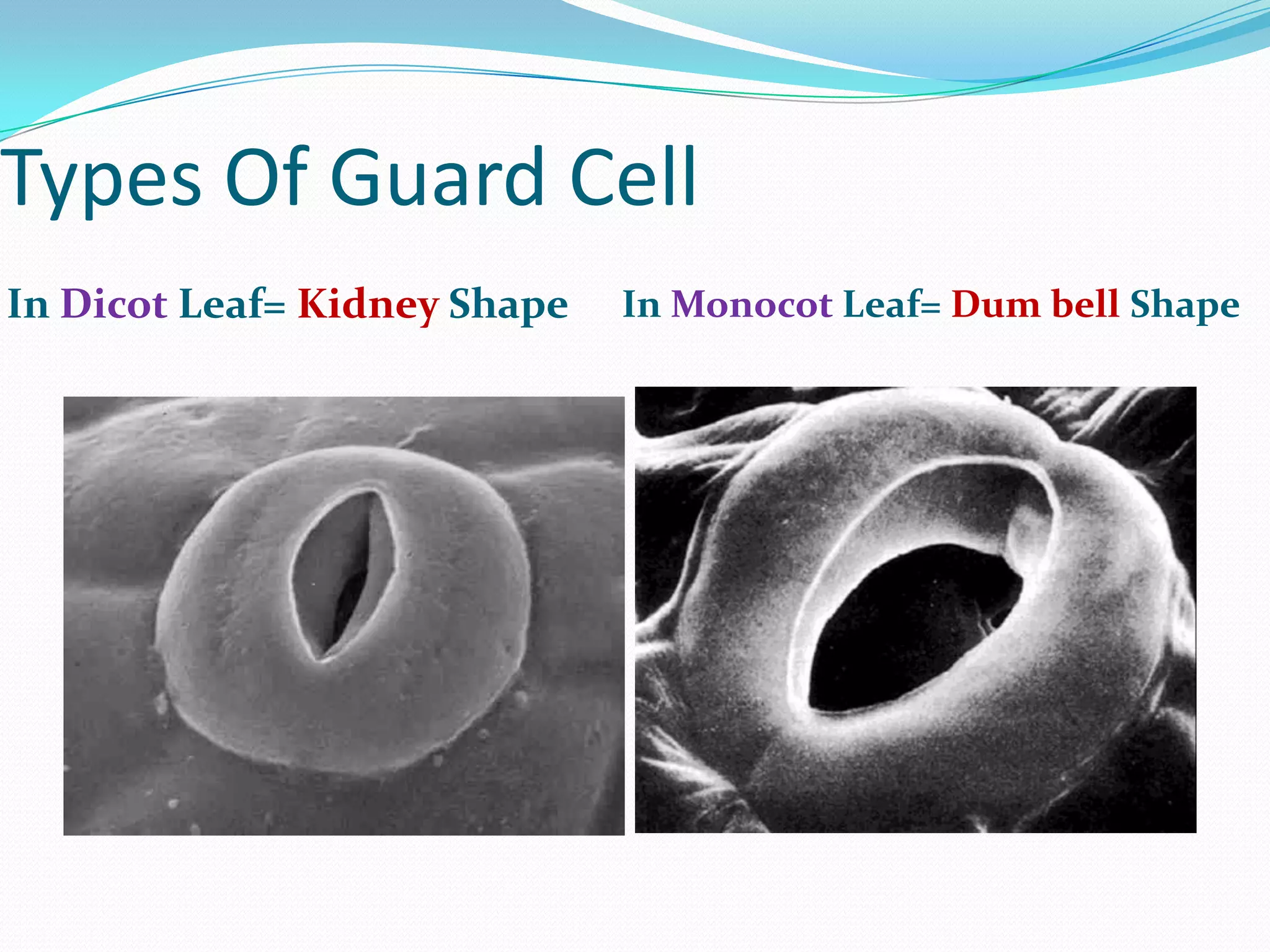
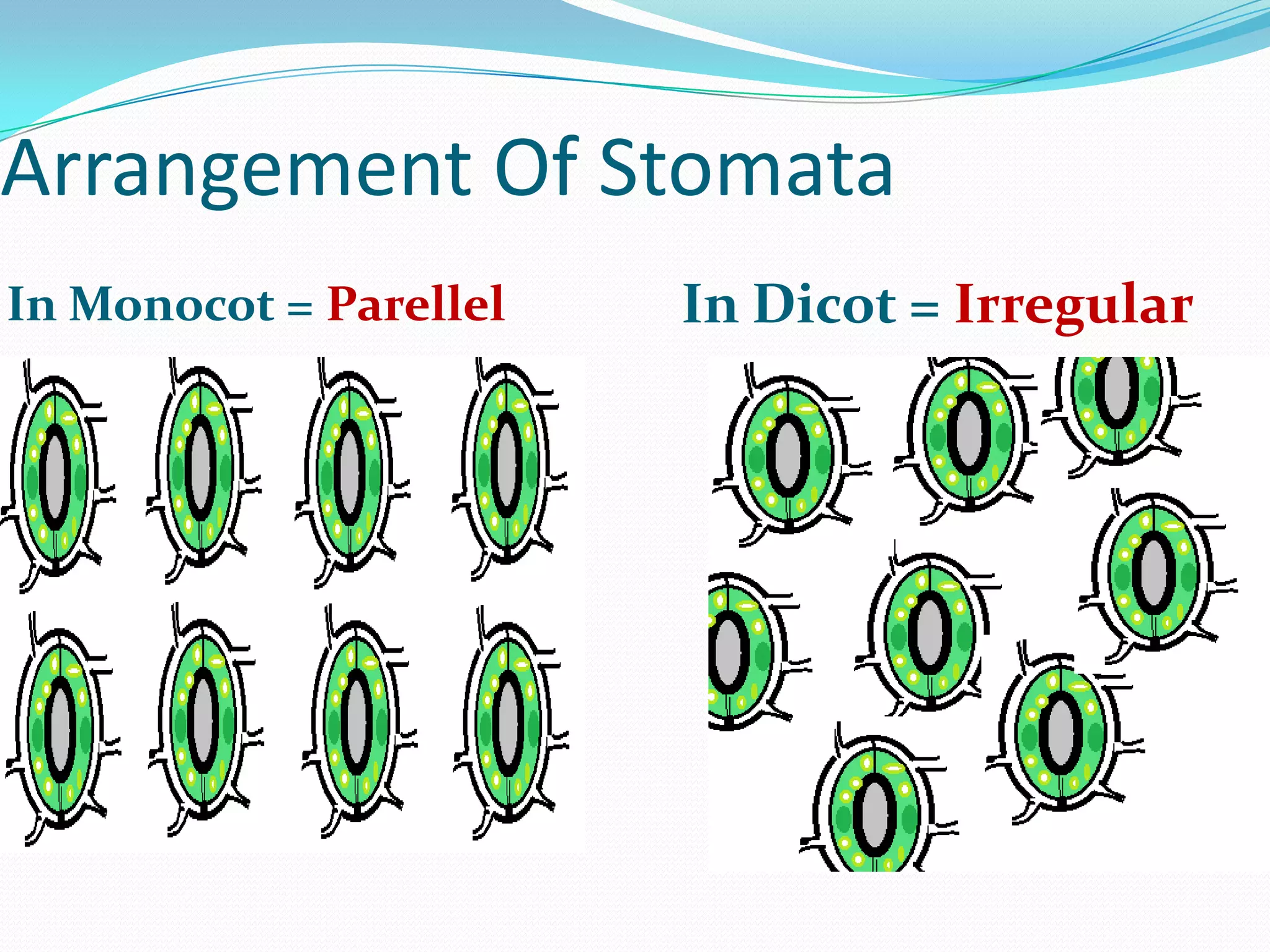
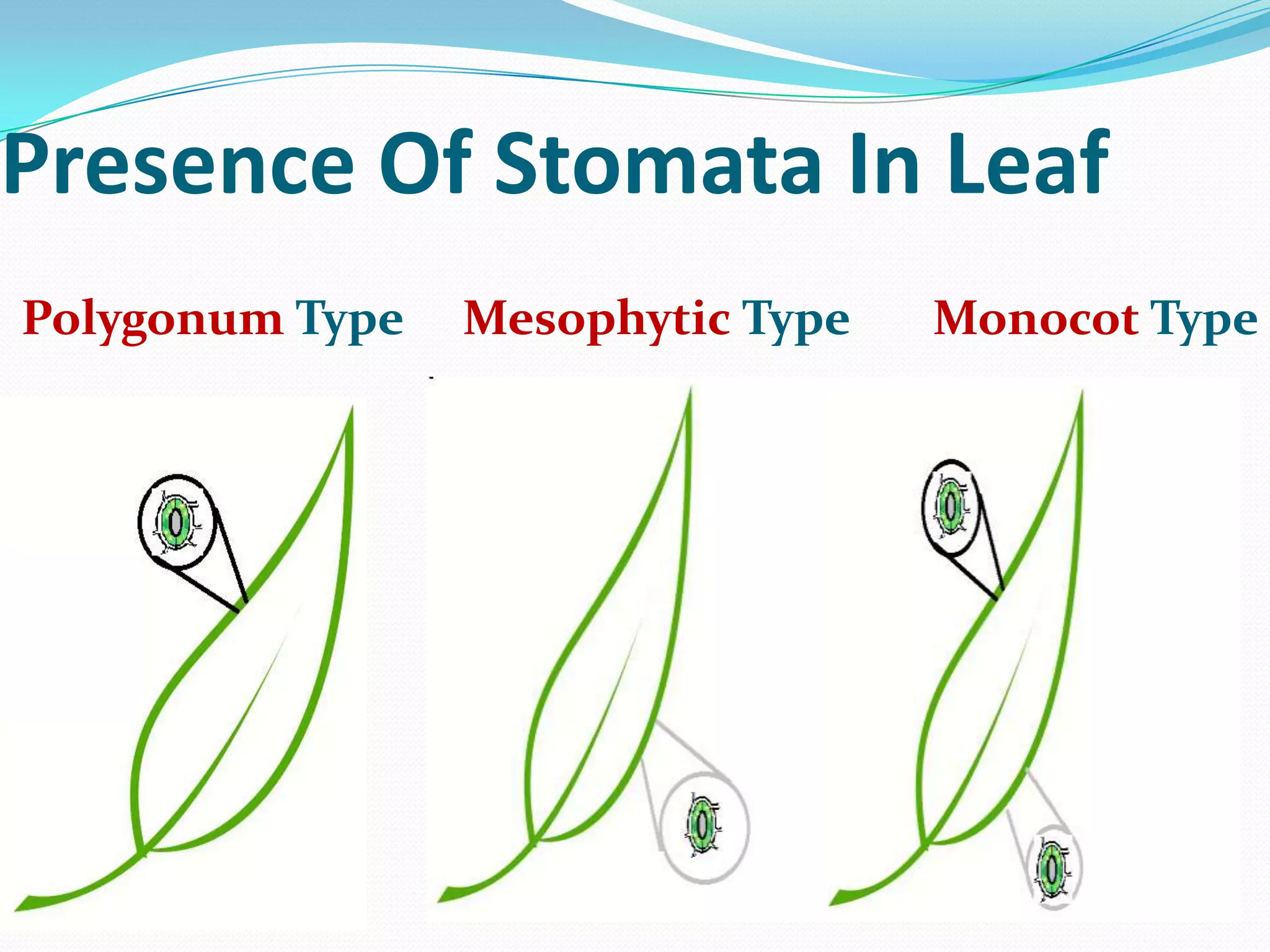
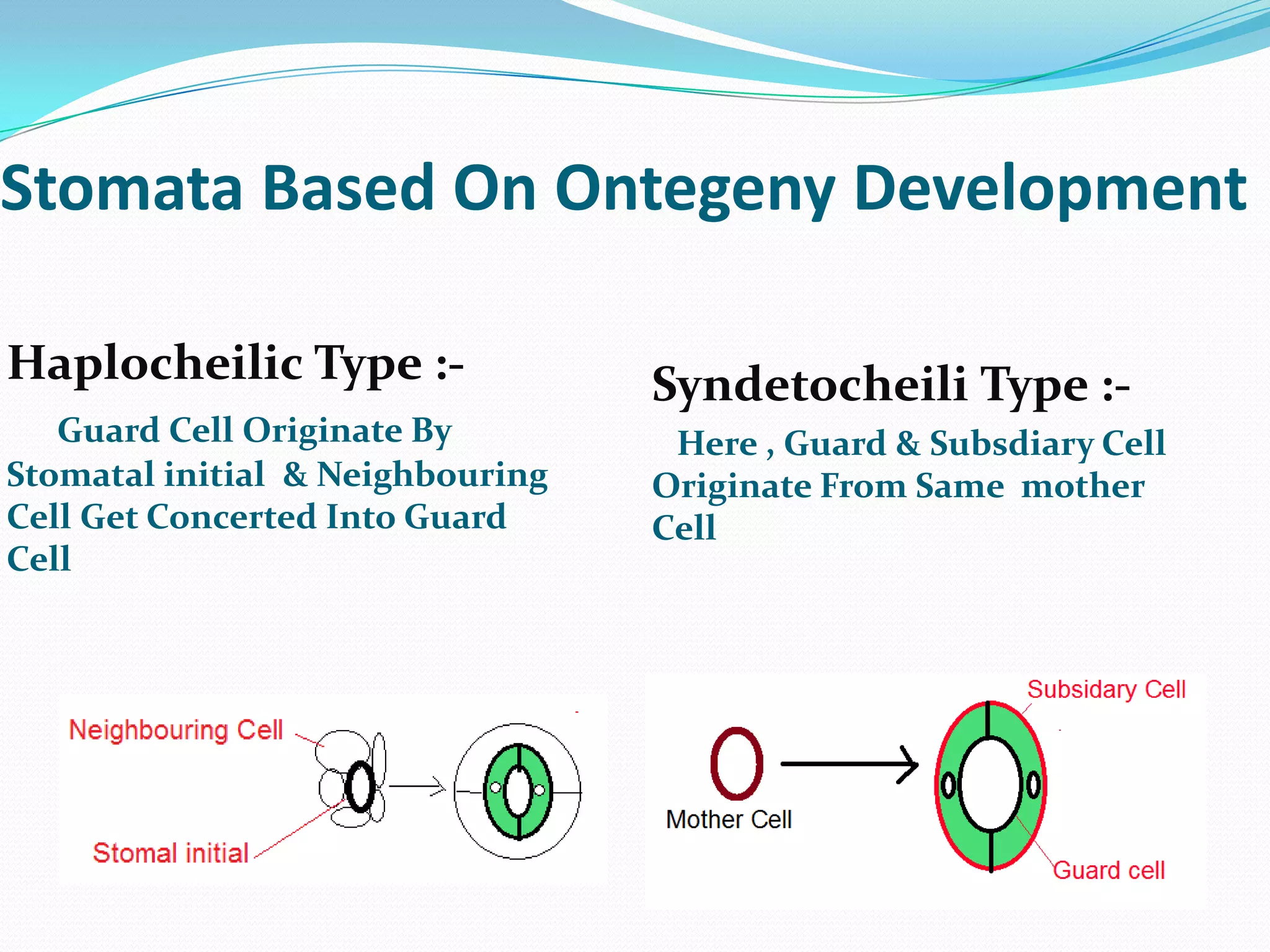
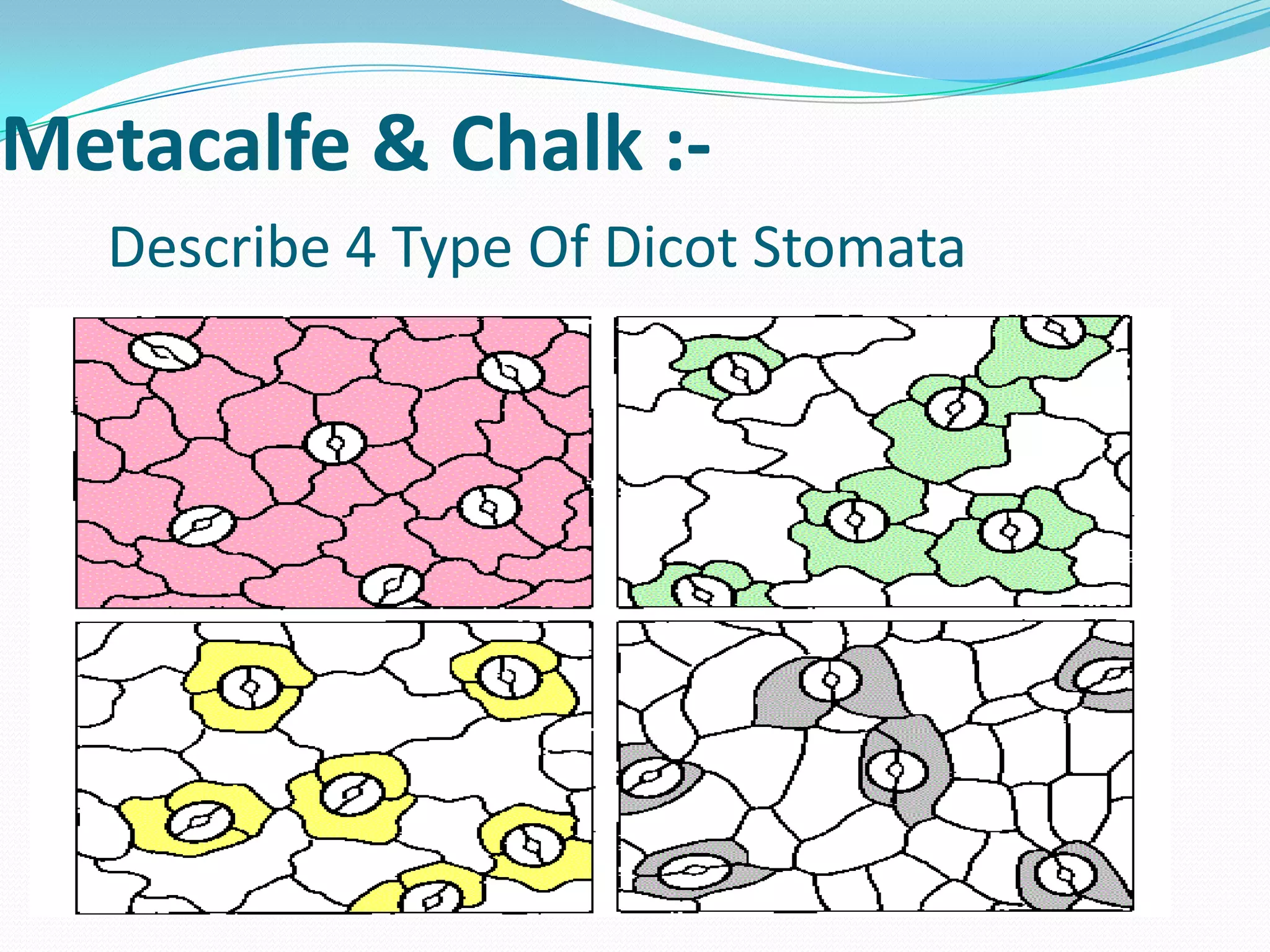
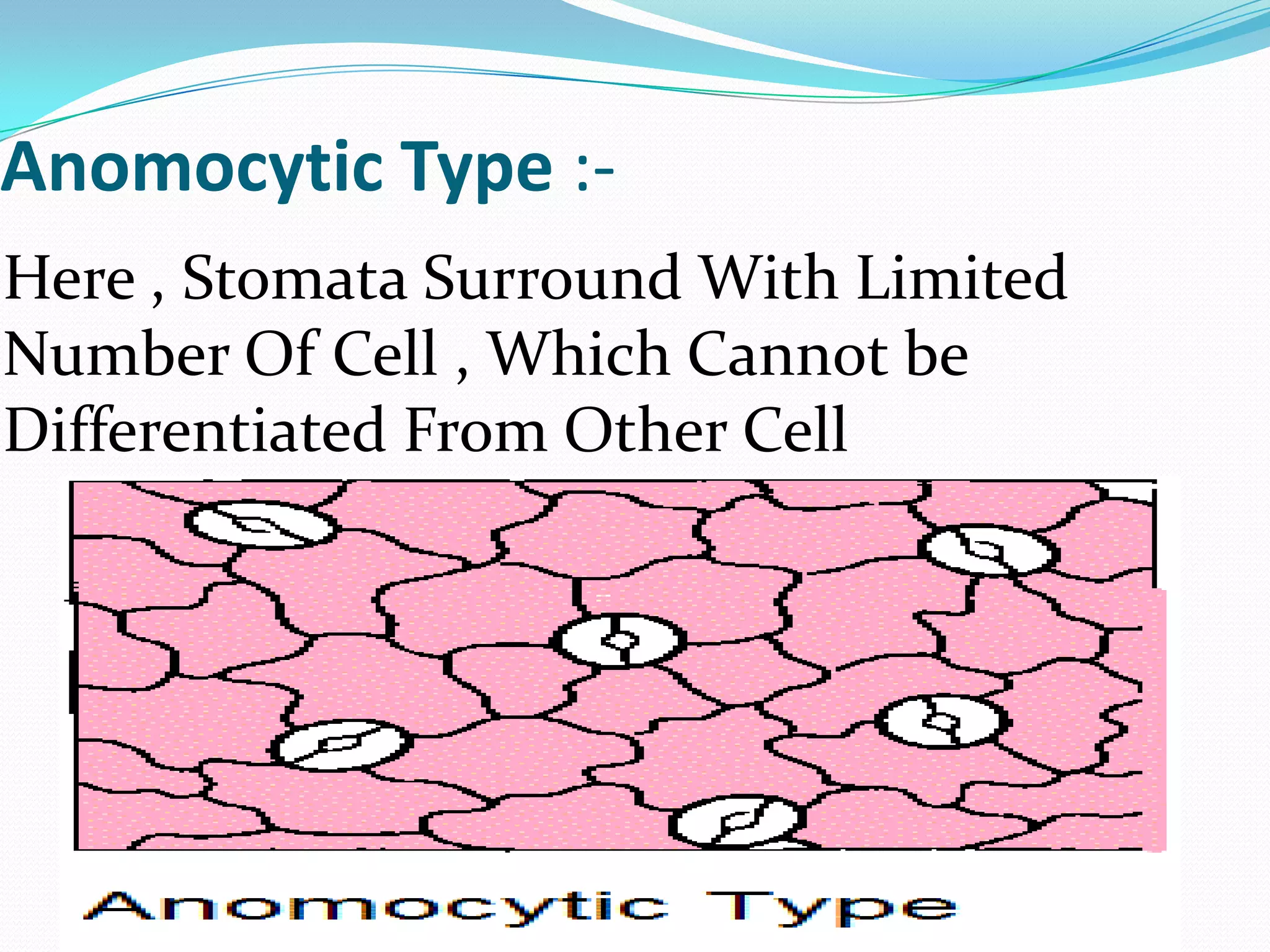

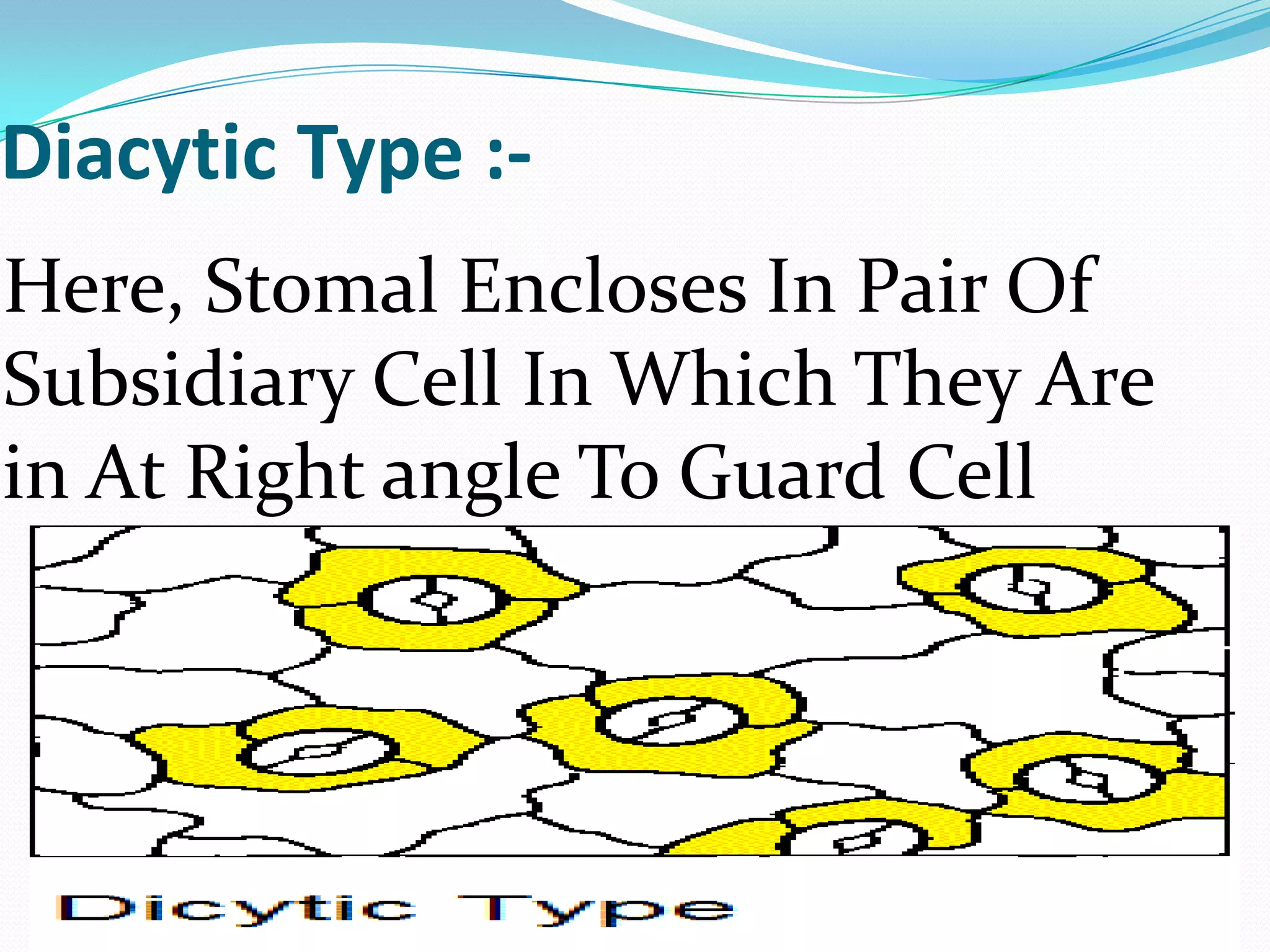
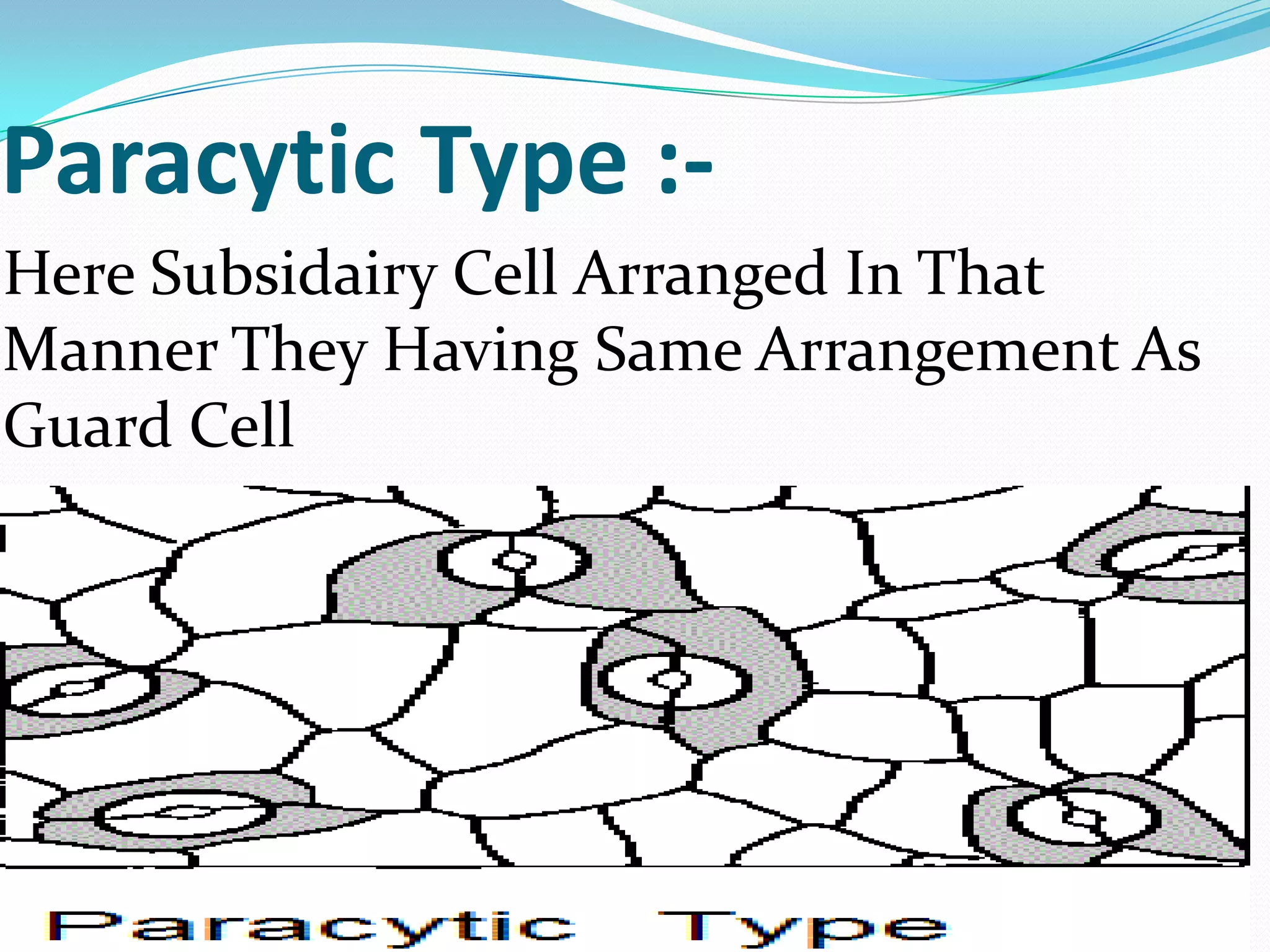

Stomata are small pores found on plant leaves that allow for gas exchange and transpiration. They consist of three main parts: the pore, guard cells, and subsidiary cells. The pore allows for gas exchange and transpiration. Guard cells are specialized cells that surround the pore and help open and close the stomata. Subsidiary cells are associated with the guard cells and help with their function. Together, the pore, guard cells, and subsidiary cells make up the stomatal apparatus. Stomata open during the day to allow for transpiration and photosynthesis, and close at night. There are different types of guard cell shapes and stomatal arrangements across monocot and dicot leaves.















