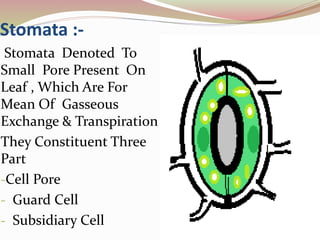
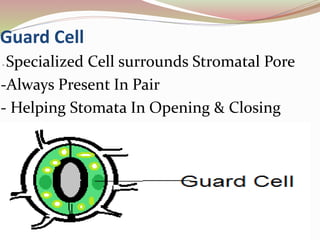
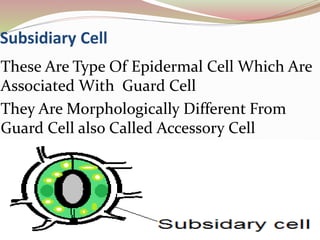
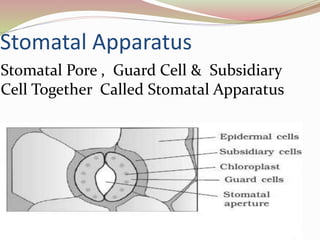
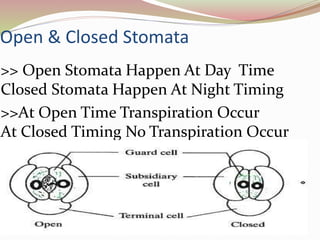
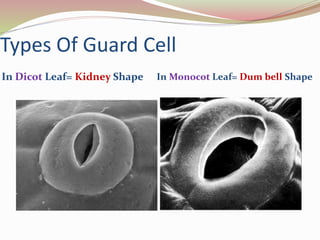
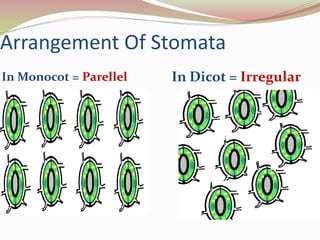
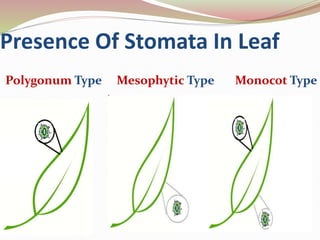
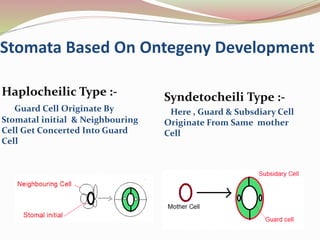
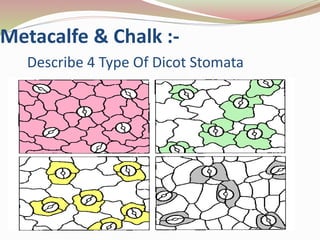
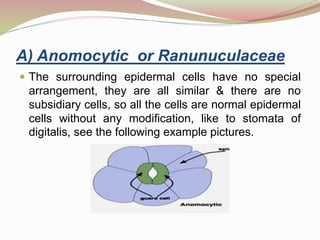
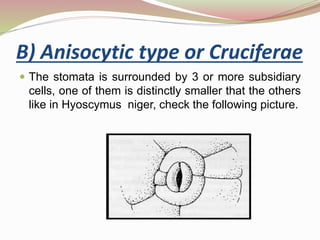
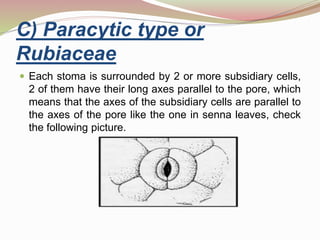
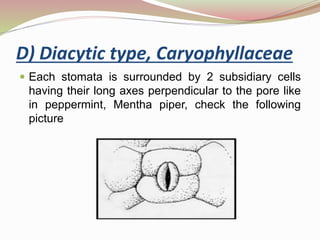
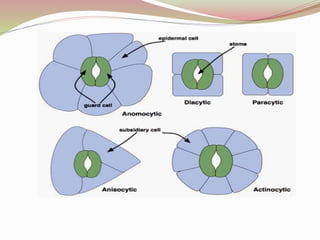
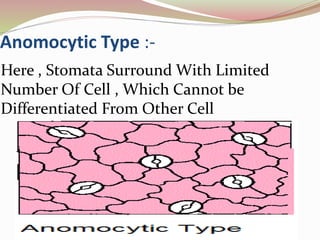
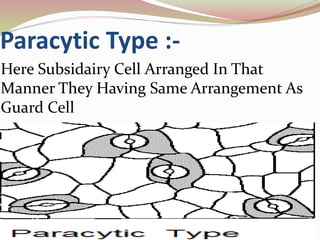
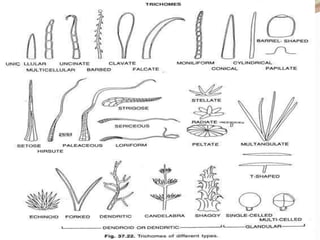
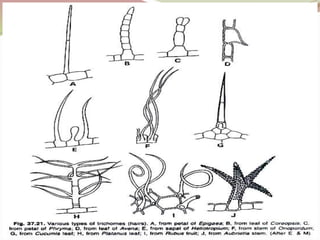
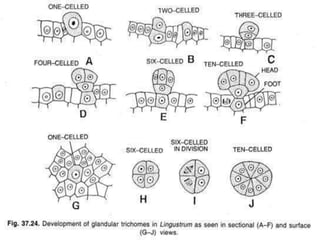
Stomata are small pores found on plant leaves that allow for gas exchange and transpiration. They consist of three parts: the pore, guard cells, and sometimes subsidiary cells. The pore allows for gas exchange and transpiration. Guard cells are specialized cells that surround the pore and control opening and closing. Subsidiary cells are associated with guard cells and help their function. There are four basic types of dicot stomata defined by Metcalfe and Chalk based on subsidiary cell arrangement: anomocytic (Ranunculaceae), anisocytic (Cruciferae), paracytic (Rubiaceae), and diacytic (Caryophyllaceae). Stomata types and arrangements vary