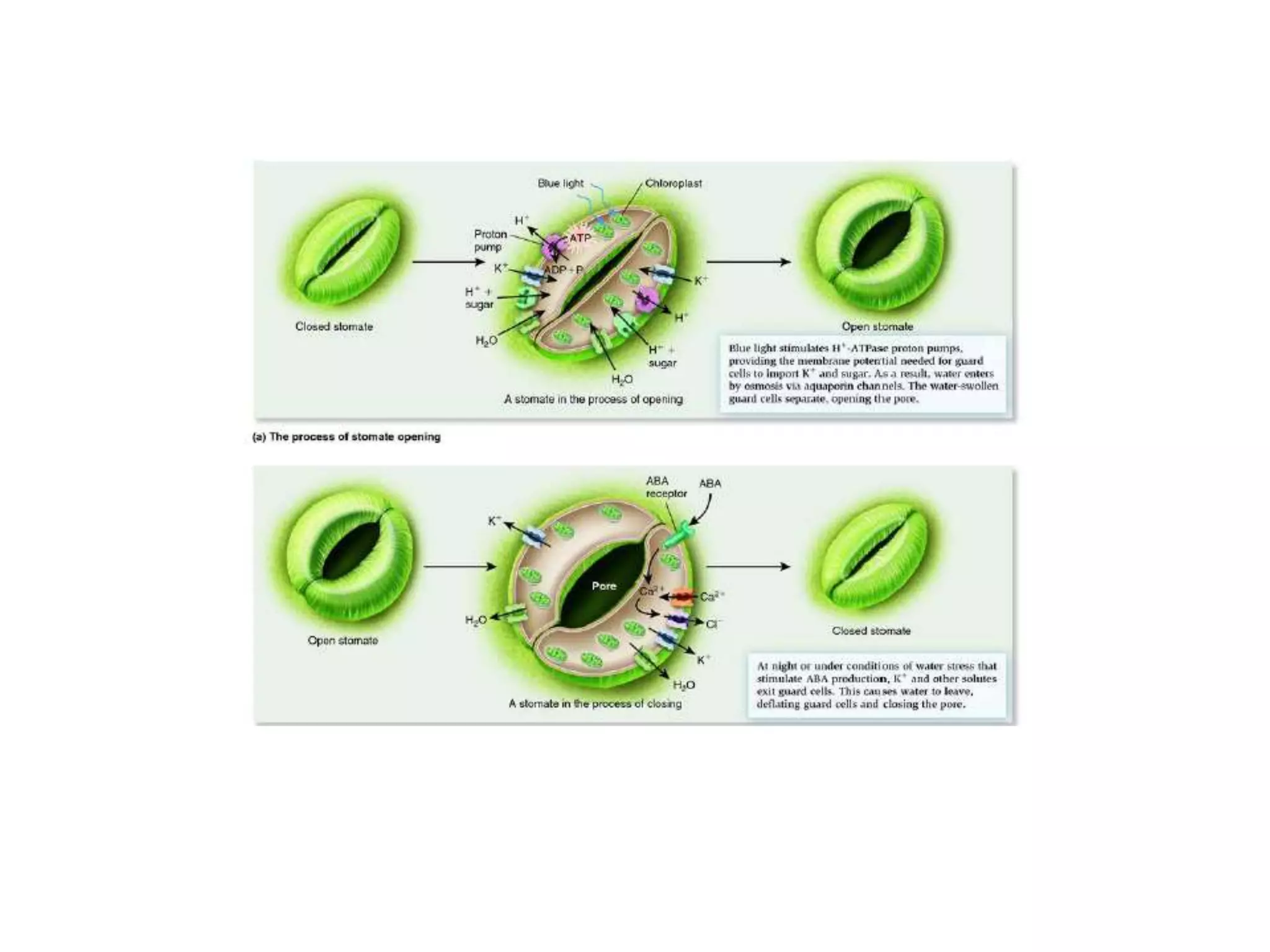
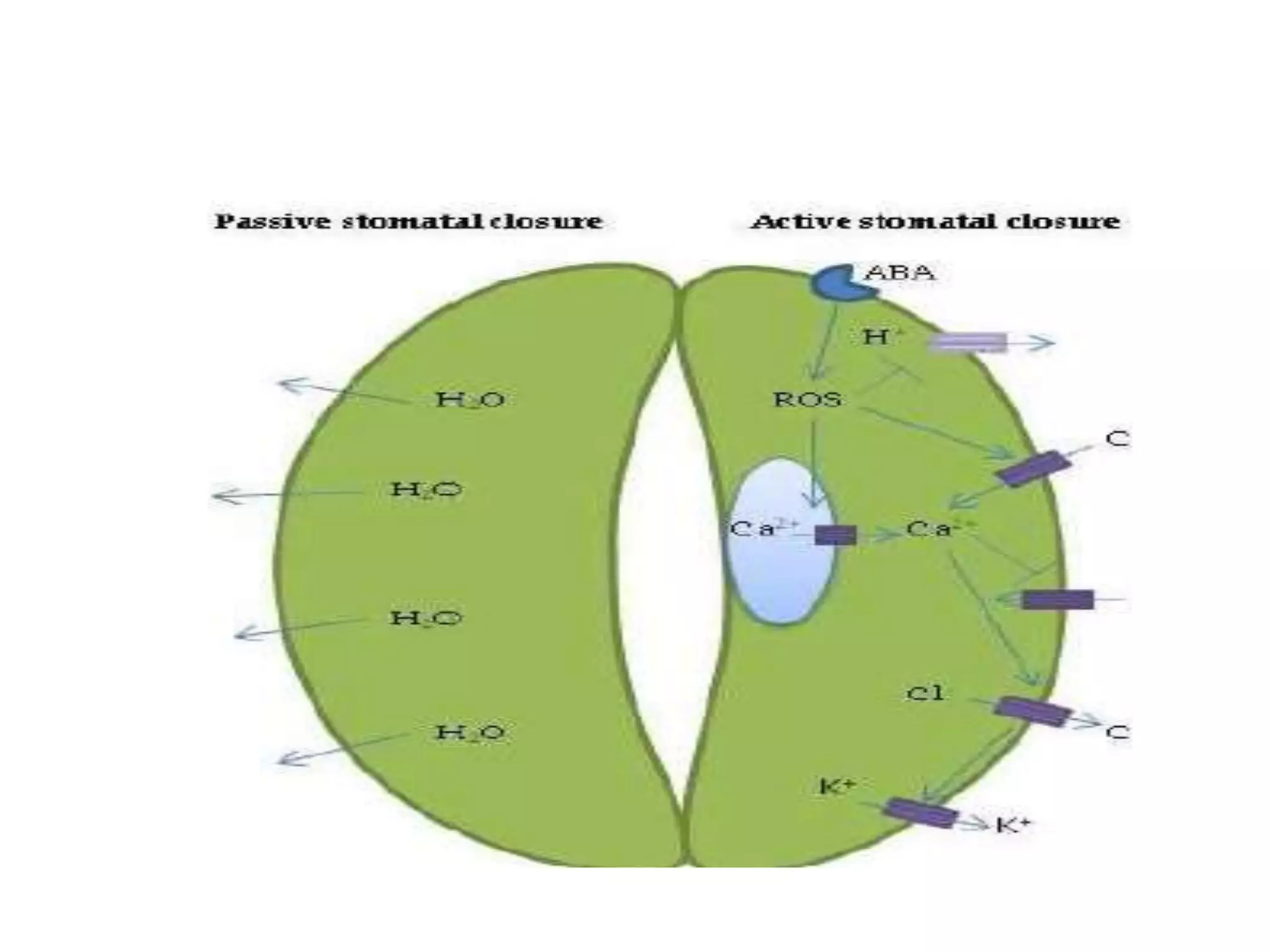
Stomatal movement is controlled by the guard cells surrounding each stoma. Guard cells take in water when the environment causes an increase in their osmotic potential, causing the cells to swell and open the stoma. When osmotic potential decreases, guard cells lose water and become flaccid, closing the stoma. Stomata open in response to light, potassium ion accumulation, and a higher pH/sugar concentration, and close in response to higher CO2 levels, low water availability, and the plant hormone abscisic acid. Multiple environmental factors and biochemical processes precisely regulate stomatal openings to control gas exchange and transpiration.