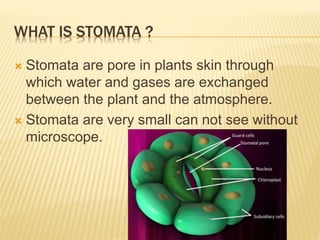
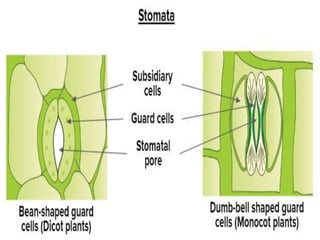
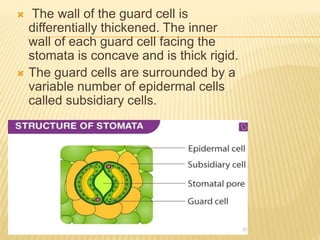
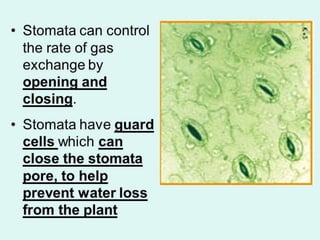
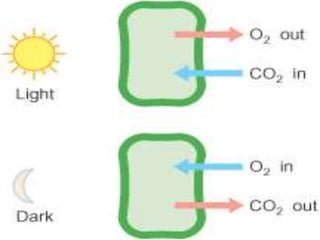
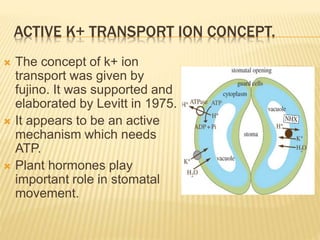
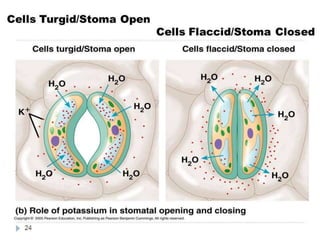
Stomata are small pores on plant leaves that allow for gas exchange. They open and close through changes in turgor pressure of guard cells surrounding each stoma. During the day, guard cells become turgid through ion transport, opening the stoma to intake CO2 and release O2. At night, guard cells become flaccid through ion efflux, closing the stoma. Various environmental factors like light, temperature, and CO2 levels influence this process of stomatal movement and gas exchange.