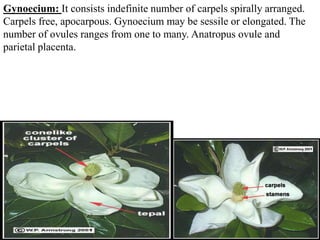
The document discusses the Magnoliaceae plant family. It belongs in the order Magnoliales and contains about 18 genera and 300 species of mostly trees and shrubs found in tropical and subtropical regions. Key features include alternate, simple leaves; bisexual, spiral flowers; numerous spirally arranged carpels and stamens; and fruits that are follicles, berries, or samaras. Economically important species include Michelia champaca for fragrant flowers used in perfumes and Liriodendron tulipifera for timber.

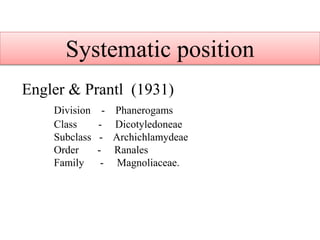
![Systematic position
Bentham and Hooker [1862]
Division - Phanerogams
Class - Dicotyledones
Subclass - Polypetalae
Series - Thalamiflorae
Order - Ranales
Family - Magnoliaceae.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-180830025717/85/1-magnoliaceae-2-320.jpg)
![Systematic position
Hutchinson[1959]
Division - Angiospermae
Class - Dicotyledones
Subclass - Lignosae
Order - Magnoliales
Family - Magnoliaceae.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-180830025717/85/1-magnoliaceae-4-320.jpg)