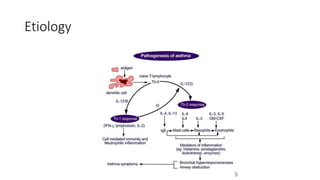
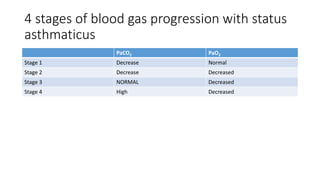
The document discusses status asthmaticus, focusing on its etiology, treatment goals, complications, and management strategies. It outlines the pathophysiology of acute exacerbation, the importance of early treatment, and various therapeutic approaches including bronchodilators and corticosteroids. Prognosis varies with risk factors, and specific assessments and hospitalization criteria are highlighted to guide treatment decisions.