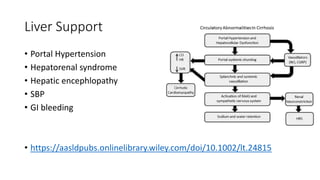
This document summarizes specific organ support considerations in the ICU, including the brain, heart, lungs, kidneys, liver, hematology/coagulation, skin/soft tissue, and endocrine system. Key points covered include oxygenation and ventilation strategies for respiratory support, indications for renal replacement therapy, transfusion thresholds for blood products, and general measures to prevent complications like bed sores.