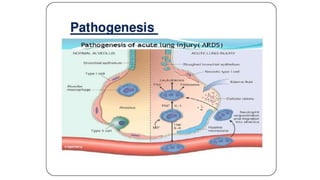
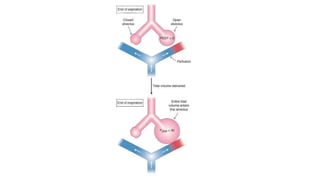
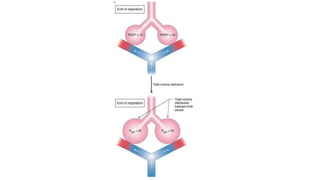
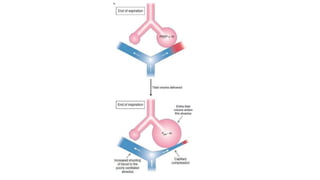
This document summarizes acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) by defining it, describing its severity, pathophysiology, etiology, risk factors, goals of therapy, and ventilator strategies. ARDS is defined by timing, radiographic changes, and origin of edema not due to heart failure. Severity is based on oxygenation. The pathophysiology involves diffuse alveolar damage and endothelial injury. Common causes are sepsis, aspiration, and trauma. Treatment aims to allow lung healing while avoiding further injury through strategies like low tidal volumes and positive end-expiratory pressure to reduce volutrauma, barotrauma, and atelectrauma.