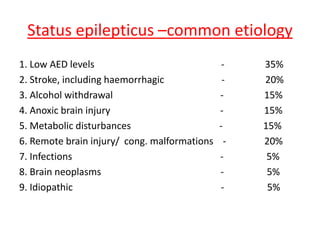
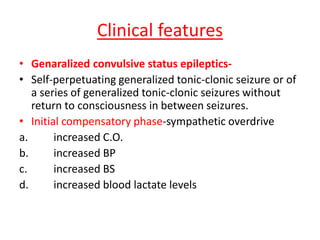
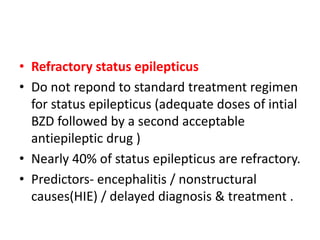
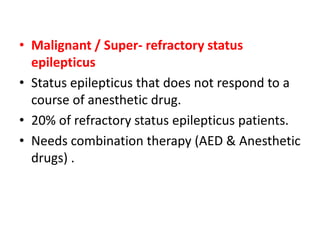
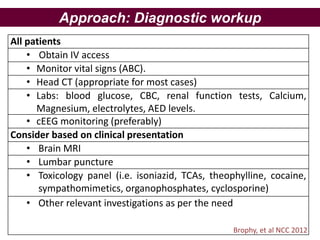
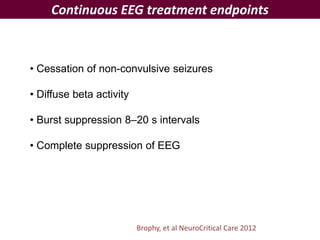
- Status epilepticus has a worldwide incidence of 3.8 to 38 per 100,000 people per year, with peaks in children and the elderly. Around 31-44% of cases are refractory to initial treatment.
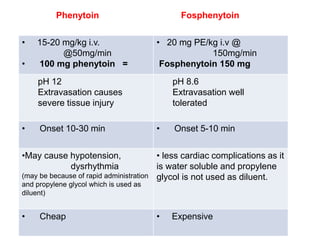
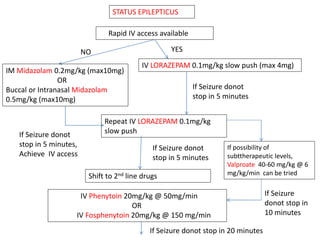
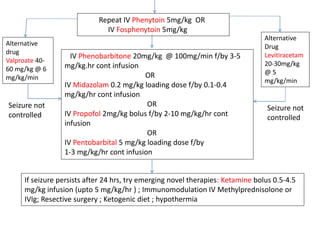
- Initial treatment involves benzodiazepines like lorazepam or diazepam. If seizures continue, second-line drugs like phenytoin, fosphenytoin, or valproate are used.
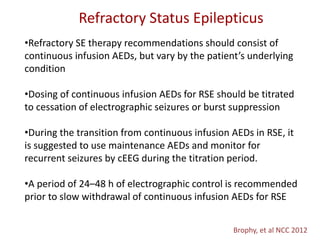
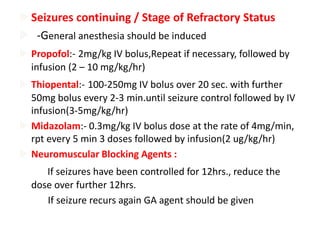
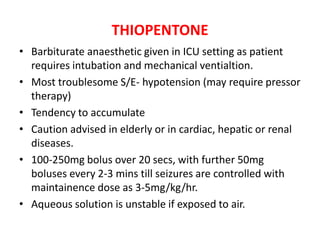
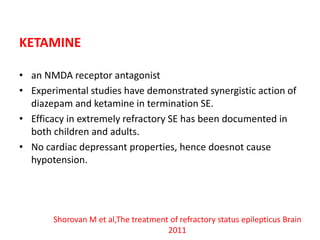
- Refractory status epilepticus is defined as failure to control seizures with benzodiazepines and other antiepileptics. It requires general anesthesia with drugs like propofol, thiopental, or midazolam along with