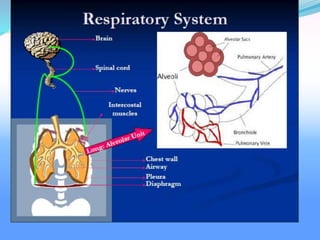
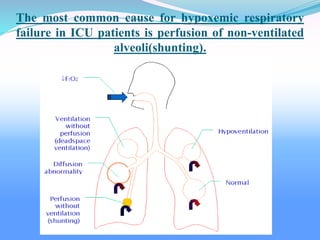
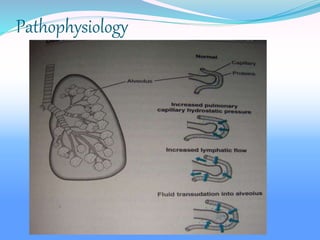
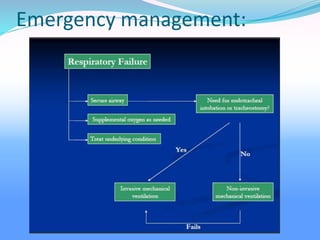
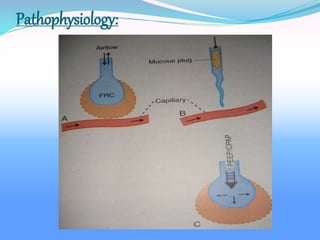
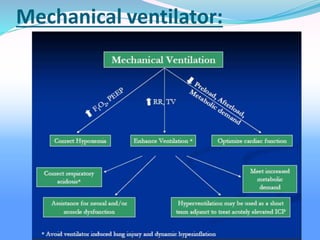
Acute respiratory failure occurs when the respiratory system fails to maintain adequate gas exchange. There are two main types: hypoxemic respiratory failure, characterized by low oxygen levels, and acute ventilatory failure, characterized by high carbon dioxide levels. Hypoxemic failure is most common and can result from conditions that impair gas exchange like pneumonia or pulmonary edema. Ventilatory failure involves impaired breathing and can be caused by conditions that increase breathing workload like COPD. Diagnosis involves blood gas analysis and imaging. Treatment focuses on supporting oxygenation and ventilation through oxygen supplementation, ventilation support, and treating underlying causes.