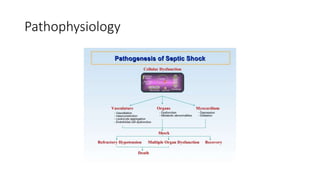
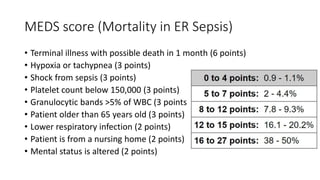
Sepsis is a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated response to infection. Septic shock, a subset of sepsis, involves circulatory and cellular abnormalities with high mortality. Sepsis signs include temperature changes, increased heart and breathing rates, and abnormal white blood cell counts. Diagnosis involves assessing these signs, blood pressure, lactate levels, and cultures of potential infection sources. Treatment focuses on rapidly restoring perfusion with IV fluids and antibiotics, controlling the infection source, and supporting organ functions.


![What is Septic shock
• Septic shock is a subset of sepsis with significantly increased mortality
due to severe abnormalities of circulation and/or cellular metabolism.
• persistent hypotension
• (defined as the need for vasopressors to maintain mean arterial pressure ≥ 65
mm Hg,
• serum lactate level > 18 mg/dL [2 mmol/L] despite adequate volume
resuscitation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sepsis-210320053025/85/Sepsis-3-320.jpg)